Pediatric Airway Anatomy
The airway of the pediatric patient differs in many ways which impact the anesthesiologists management of the airway. Infants up to one year old have a large occiput which flexes the neck when the infant lies supine on a flat surface.
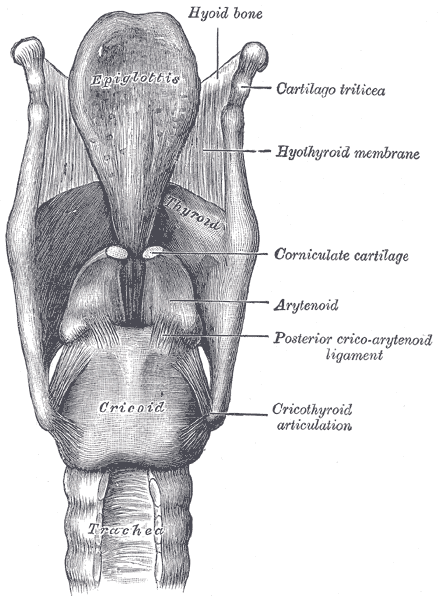 Paediatric Airway Anatomy Paediatric Emergencies
Paediatric Airway Anatomy Paediatric Emergencies
The main site of airway resistance in the adult is the upper airway.

Pediatric airway anatomy. Pediatric airways are often challenging due to the size of the patient. Knowledge of the functional anatomy of the airway in children forms the basis of understanding the pathological conditions that may occur. However it has been shown that peripheral airway resistance in children younger than 5 years of age is four times higher than adults the major site of resistance is the medium sized bronchi.
Predictably these differences are most pronounced at birth and the most unfamiliar non adult like airway is encountered in neonates and infants under 1 year of age. In order to open the paediatric airway and gain the best view of the laryngeal inlet the oral pharyngeal and tracheal axes must be brought into alignment. This in turn allows a comprehensive assessment of the pediatric airway to take place including a detailed.
Specific issues in the management of the pediatric airway. This in turn allows a comprehensive assessment of the pediatric airway to take place including a detailed medical history clinical examination and specific investigative procedures. To achieve a neutral position.
The airway changes in size shape and position throughout its development from the neonate to the adult 1. With a smaller body size comes an increase in the precision needed to successfully maintain airway patency if any injury or insult to the airway occurs. This requires suitable patient positioning during preparation for intubation and differs based on the age of the child.
Knowledge of the functional anatomy of the airway in children forms the basis of understanding the pathological conditions that may occur. The paediatric airway differs from that of adults in terms of anatomy and there are important management implications.
 Pediatric Vs Adult Airway Pediatric Nursing Pediatrics
Pediatric Vs Adult Airway Pediatric Nursing Pediatrics
 Anatomy Of Pediatric Airway With Severe Laryngomalacia
Anatomy Of Pediatric Airway With Severe Laryngomalacia
Airway Management Module 2 1 Ceu Continuing Education From
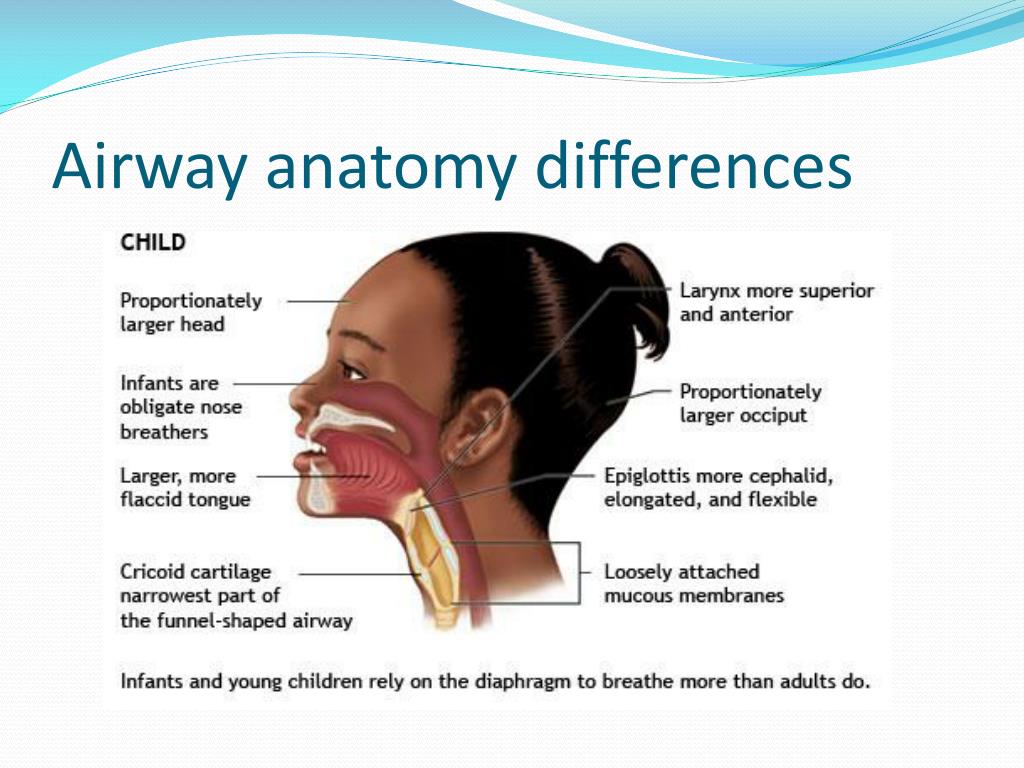 Ppt Pediatric Airway Management Powerpoint Presentation
Ppt Pediatric Airway Management Powerpoint Presentation
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
 18 Basics Of Pediatric Airway Anatomy Physiology And Management
18 Basics Of Pediatric Airway Anatomy Physiology And Management
 Paediatric Airway Anatomy Paediatric Emergencies
Paediatric Airway Anatomy Paediatric Emergencies
 10 Common Pediatric Airway Problems And Their Solutions
10 Common Pediatric Airway Problems And Their Solutions
Pediatric Airway Management Harless J Ramaiah R Bhananker
 Anatomy And Assessment Of The Pediatric Airway Adewale
Anatomy And Assessment Of The Pediatric Airway Adewale
 Anatomy And Assessment Of The Pediatric Airway Adewale
Anatomy And Assessment Of The Pediatric Airway Adewale
 10 Common Pediatric Airway Problems And Their Solutions
10 Common Pediatric Airway Problems And Their Solutions
 Normal Pediatric Airway Medical Illustration Human
Normal Pediatric Airway Medical Illustration Human
 Pediatric Airway Anatomy May Not Be What We Thought
Pediatric Airway Anatomy May Not Be What We Thought
 Glidescope Pediatric Airway Rounds Small Anatomies
Glidescope Pediatric Airway Rounds Small Anatomies
Pediatric Airway Respiratory Emergencies Lessons Tes Teach

 10 Common Pediatric Airway Problems And Their Solutions
10 Common Pediatric Airway Problems And Their Solutions
Search Anatomy Of Pediatric Airway With Severe Laryngomalacia
 Pediatric Airway Management A Step By Step Guide Textbook
Pediatric Airway Management A Step By Step Guide Textbook
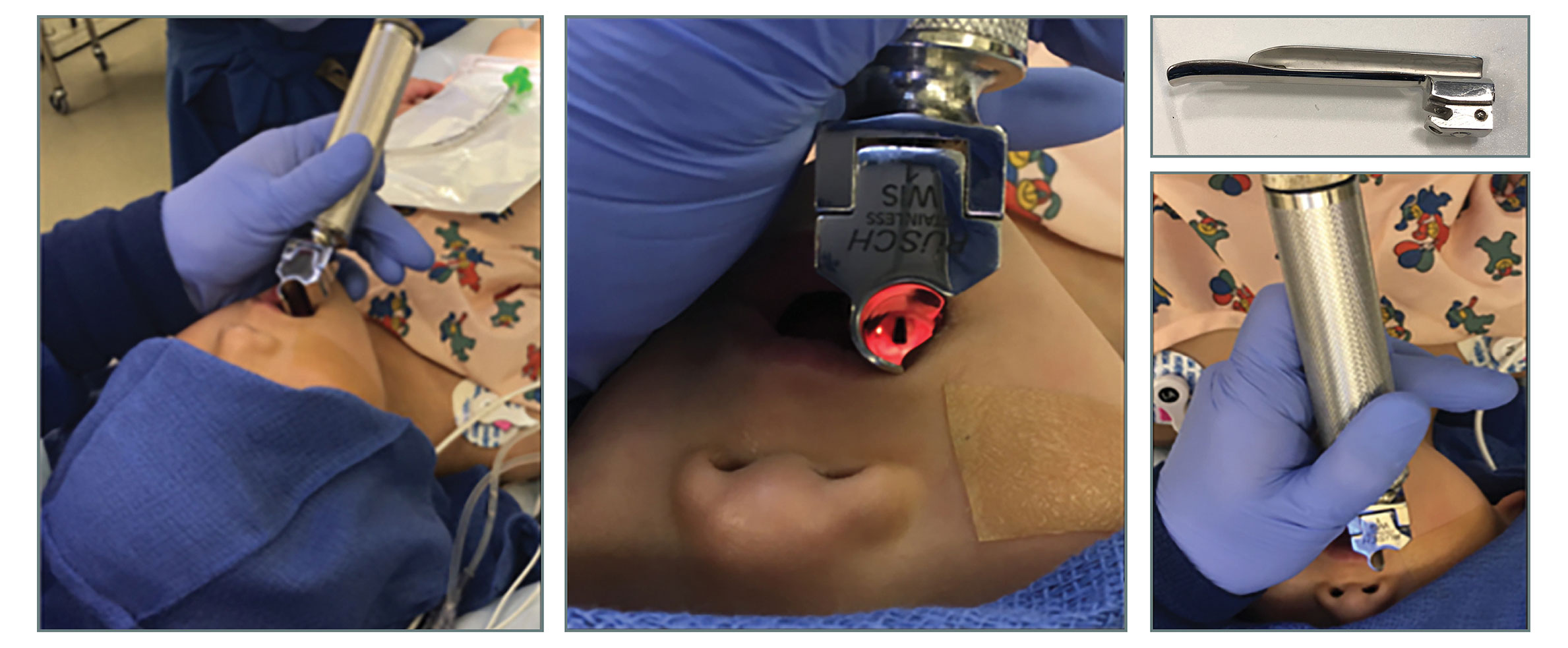 Planning Prevents Poor Performance An Approach To Pediatric
Planning Prevents Poor Performance An Approach To Pediatric
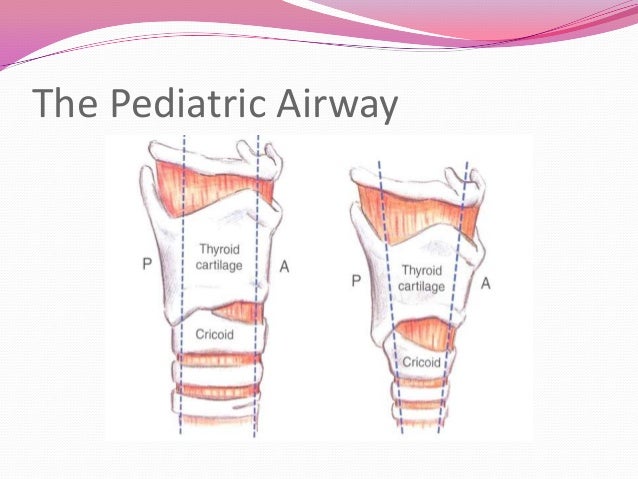 Respiratory Emergencies In Pediatrics
Respiratory Emergencies In Pediatrics
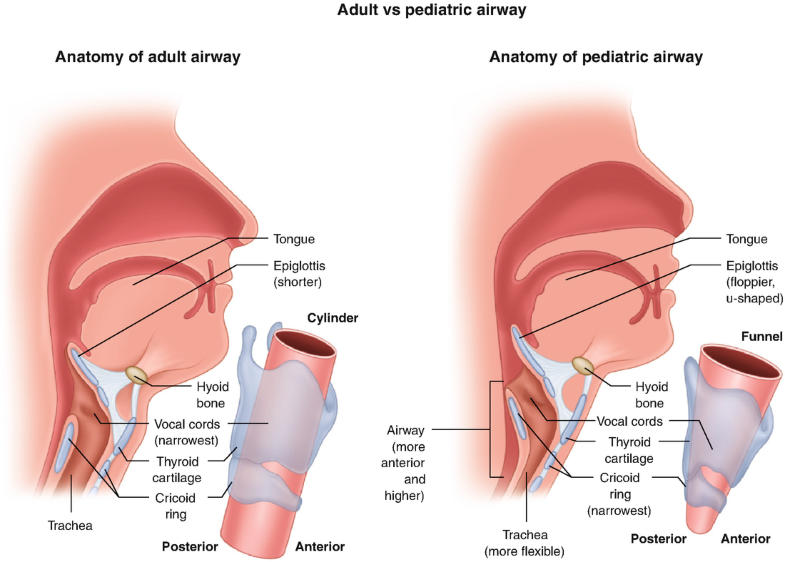 Airway Pediatric Anatomy Infants And Children Springerlink
Airway Pediatric Anatomy Infants And Children Springerlink
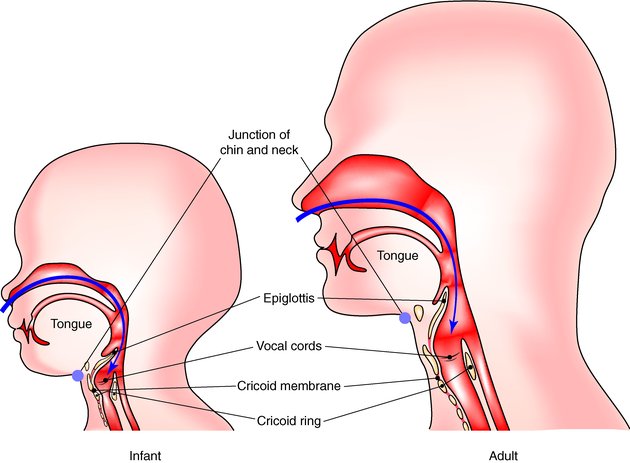 Airway Management Chapter 2 An Introduction To Clinical
Airway Management Chapter 2 An Introduction To Clinical
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Pediatric Airway Anatomy"
Posting Komentar