Shin Splints Anatomy
With true shin splints the muscles surrounding the tibia are strained sometimes to the point of tearing leading in extreme cases to the tibia also sustaining tiny fractures due to the overuse of its surrounding connective tissue specifically the tibialis posterior muscle the tibialis anterior muscle and the periosteum. Your doctor may refer to the condition as medial tibial stress syndrome mtss.
 Shin Splints Self Help Tips Treatment And Prevention From
Shin Splints Self Help Tips Treatment And Prevention From
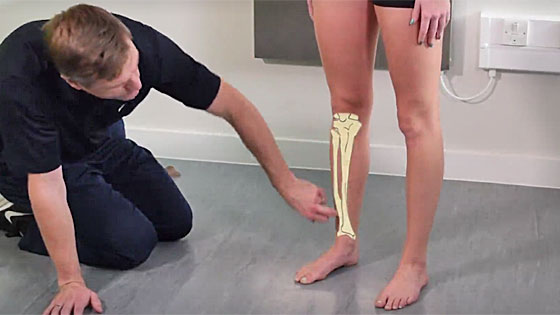
The term shin splints describes pain felt along the front of your lower leg at the shin bone.

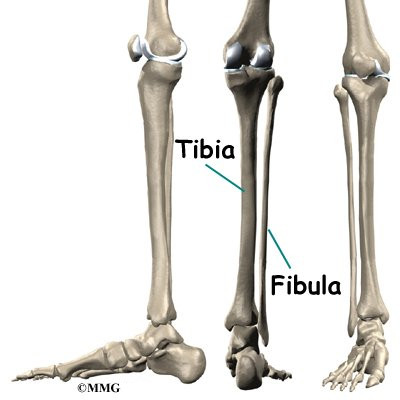
Shin splints anatomy. These are the two bones in the lower leg. The most common symptom of shin splints is pain. The main components of the lower leg that are affected by the pain associated with shin splints are.
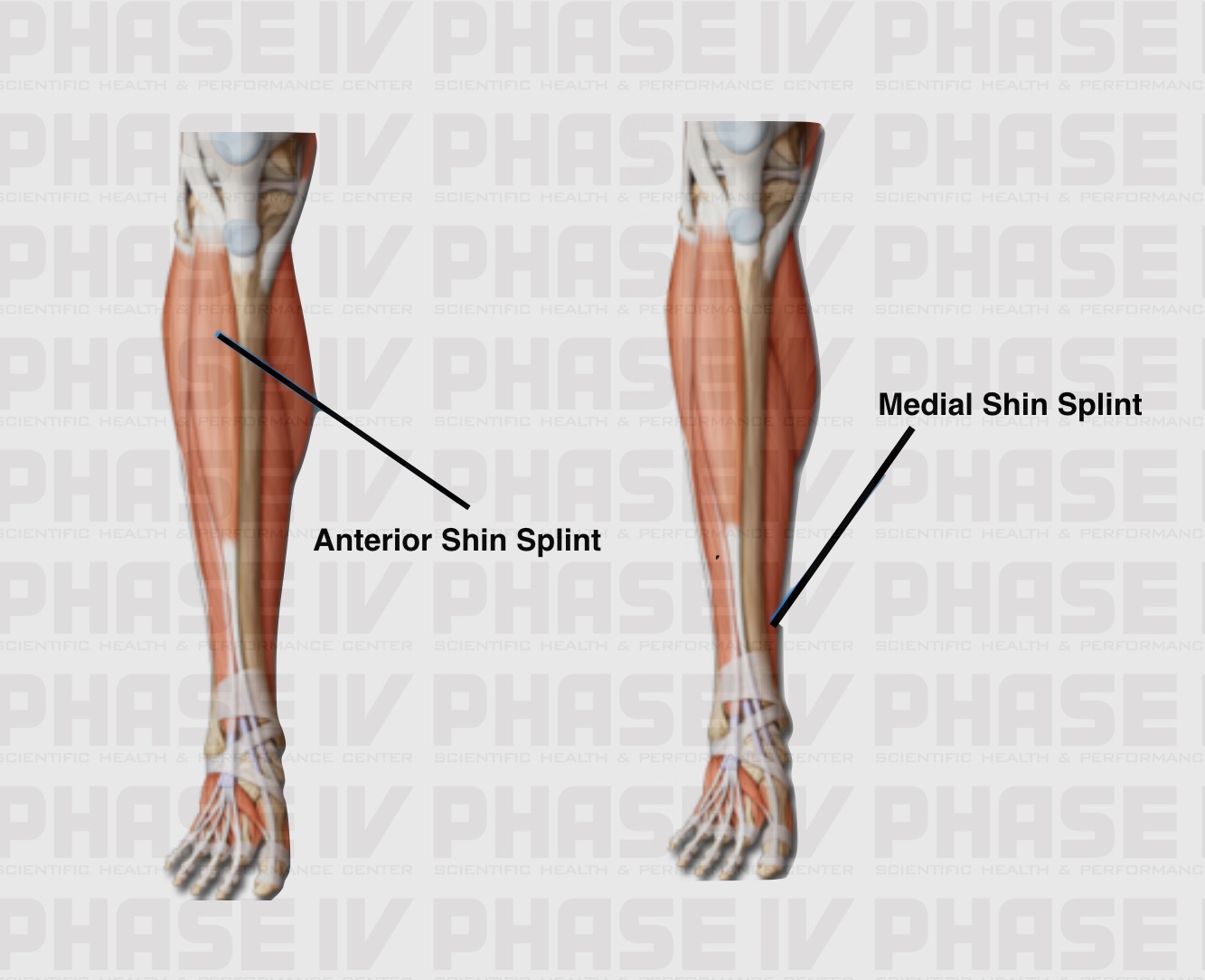
Shin splints the anatomy causes symptoms and treatments shin splints also known as medial tibial stress syndrome mtss are a common running injury in all athletes and actually account for about 15 of all running injuries. Shin splints injuries are specifically located in the middle to lower thirds of the anterior or lateral part of the tibia which is the larger of two bones comprising the lower leg. Shin splint pain most often occurs on the inside edge of your tibia shinbone.
A number of specific injuries may cause shin splints type pain but medial tibial stress syndrome probably the most common. Shin splints frequently affect people who engage in moderate to heavy physical activity. They are characterized by general pain in the lower region of the leg between the knee and the ankle.
Anatomy of shin splints. Shin splints medial tibial stress syndrome is an inflammation of the muscles. In general shin splints develop when the muscle and bone tissue periosteum.
Shin splint anatomy and treatment not just athletes. The tibia and fibula. This pain concentrates in the lower leg between the knee and ankle.
Shin splints not a specific injury but a term used to describe pain on the lower inside of the shin. Pain typically occurs along the inner border of the tibia where muscles attach to the bone. The literature varies greatly on specific causes of shin splints.
Usually they are symptoms of another underlying problem such as over pronation of your feet when you run. The pathophysiology of shin splints is more easily understood after examining the relevant cross sectional anatomy. The major muscles in the lower leg that are associated with shin splints are the.
Biomechanical malfunction of structures in the lower leg. Location of pain defines the condition as anterior or posterior shin splints. Shin splints medial tibial stress syndrome is an inflammation of the muscles tendons and bone tissue around your tibia.
Treatment and prevention description. Medial tibial stress syndrome occurs when the lower leg muscles repeatedly pull on the tibia shin bone. Anatomy of a shin splint.
There are 4 muscle compartments in the leg. This compartiment contains the tibialis anterior muscle the extensor hallucis longus the extensor digitorum longus and the peroneus tertius.
 Complete Guide To Shin Splints 2019
Complete Guide To Shin Splints 2019
 Shin Splint Treatment In Nyc Nydnrehab Com
Shin Splint Treatment In Nyc Nydnrehab Com
 Tibial Stress Syndrome Shin Splints Knee Sports
Tibial Stress Syndrome Shin Splints Knee Sports
 Natural Home Remedies How To Cure Shin Splints Naturally
Natural Home Remedies How To Cure Shin Splints Naturally
 Shin Splint To Stress Fracture Cause Prevention
Shin Splint To Stress Fracture Cause Prevention
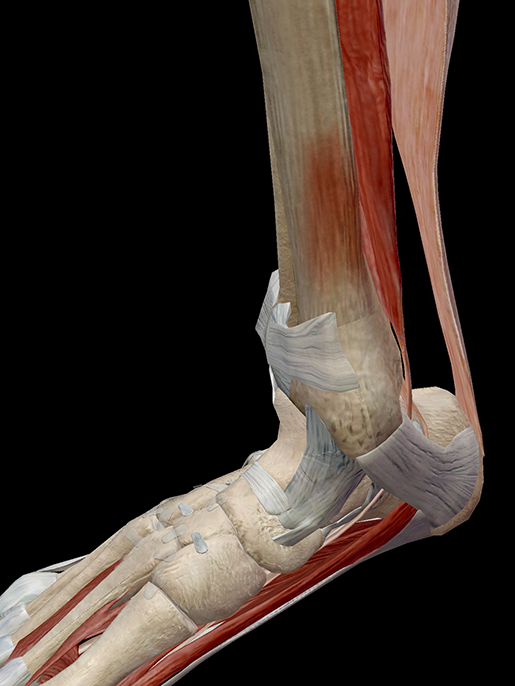 Hold On To Your Tibias The Anatomy And Causes Of Shin Splints
Hold On To Your Tibias The Anatomy And Causes Of Shin Splints
Shin Splints Diversified Integrated Sports
 Anatomy Of Shin Splints Treatment And Prevention
Anatomy Of Shin Splints Treatment And Prevention
 Tibial Stress Syndrome Shin Splints Accelerate Physiotherapy
Tibial Stress Syndrome Shin Splints Accelerate Physiotherapy
 What Is Shin Splints And Are You Suffering From It Know
What Is Shin Splints And Are You Suffering From It Know
 Physiotherapy For Shin Splints Physiologic Plus
Physiotherapy For Shin Splints Physiologic Plus
 Shin Splints Thermoskin Supports And Braces For Injury
Shin Splints Thermoskin Supports And Braces For Injury
 Shin Splints Shin Pain Treatment Prevention Exercises
Shin Splints Shin Pain Treatment Prevention Exercises
I Suffer From Shin Splints What Should I Do
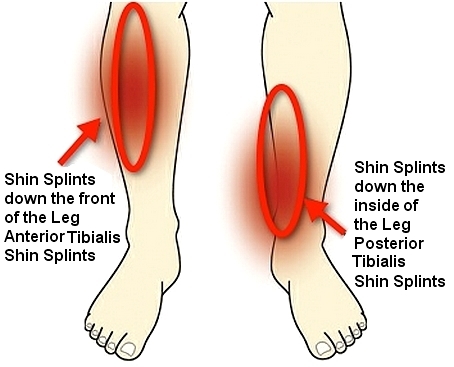 Stretches For Shin Splints And How To Prevent Shinsplints
Stretches For Shin Splints And How To Prevent Shinsplints
 Shin Splints Explained Helpful Guide To Help You Run
Shin Splints Explained Helpful Guide To Help You Run
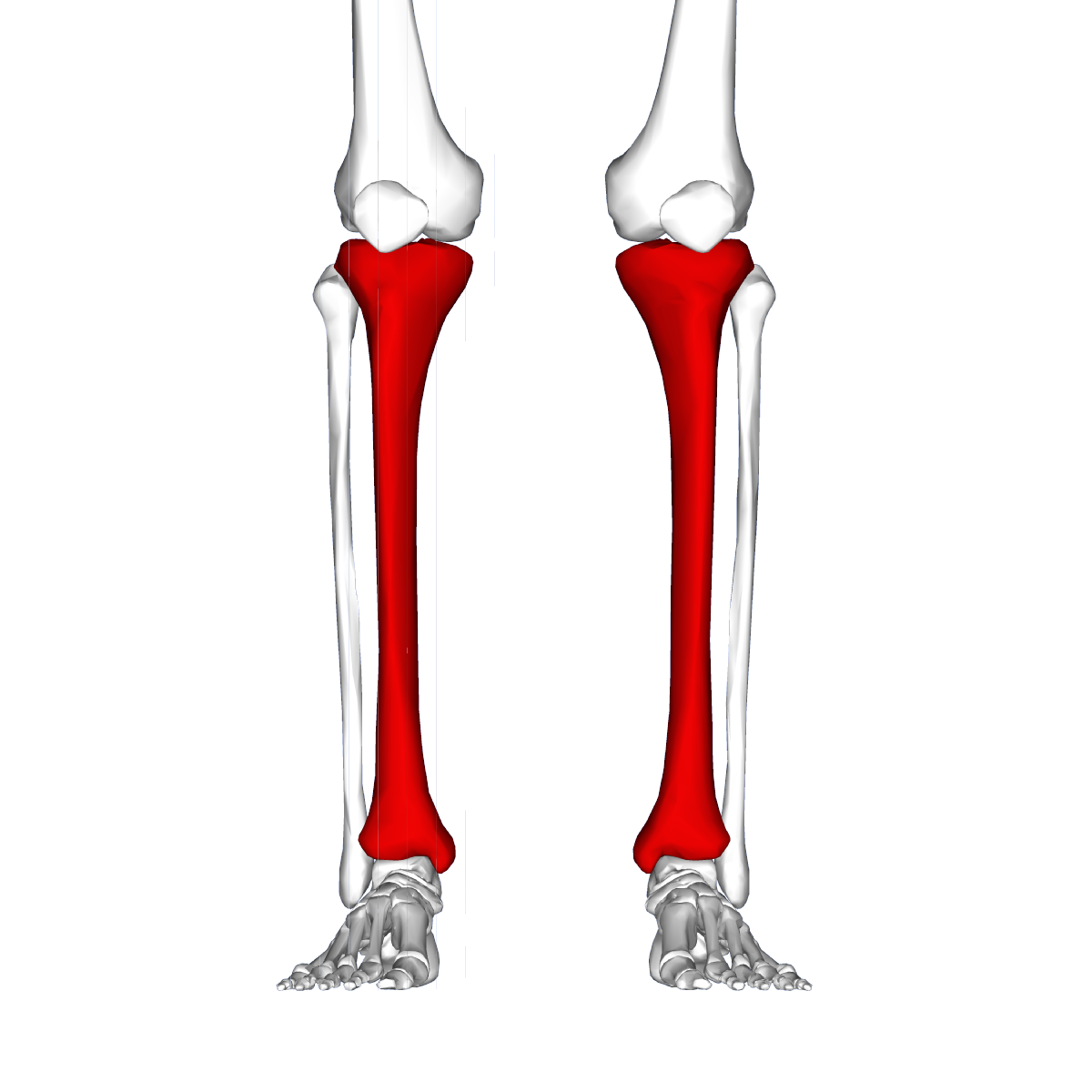





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Shin Splints Anatomy"
Posting Komentar