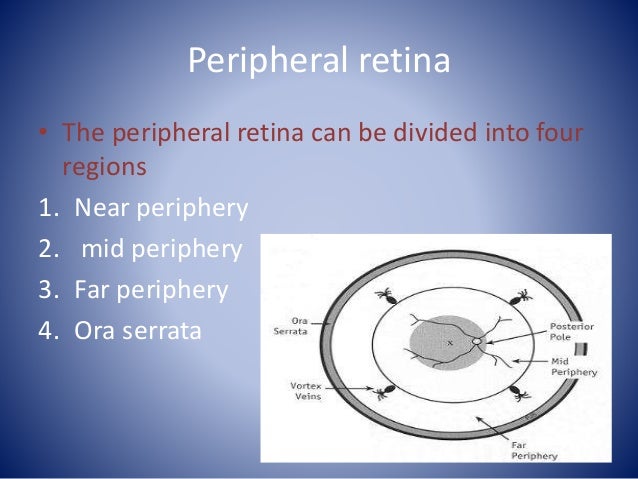
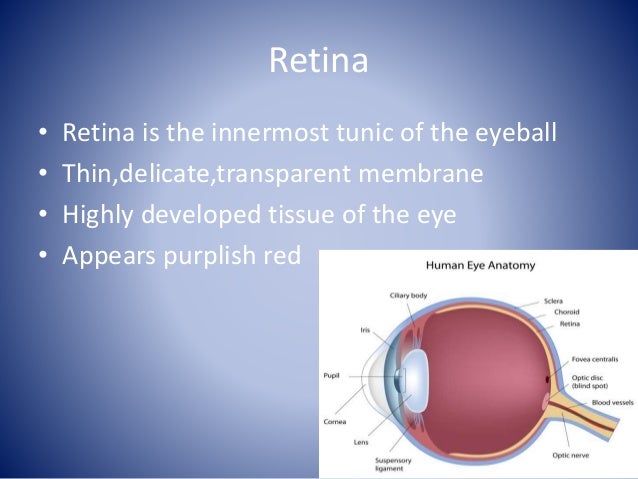
Retinal Anatomy
Refer to this page for comparison with the retinal disease pages. This layer senses light and sends signals to the brain so you can see.
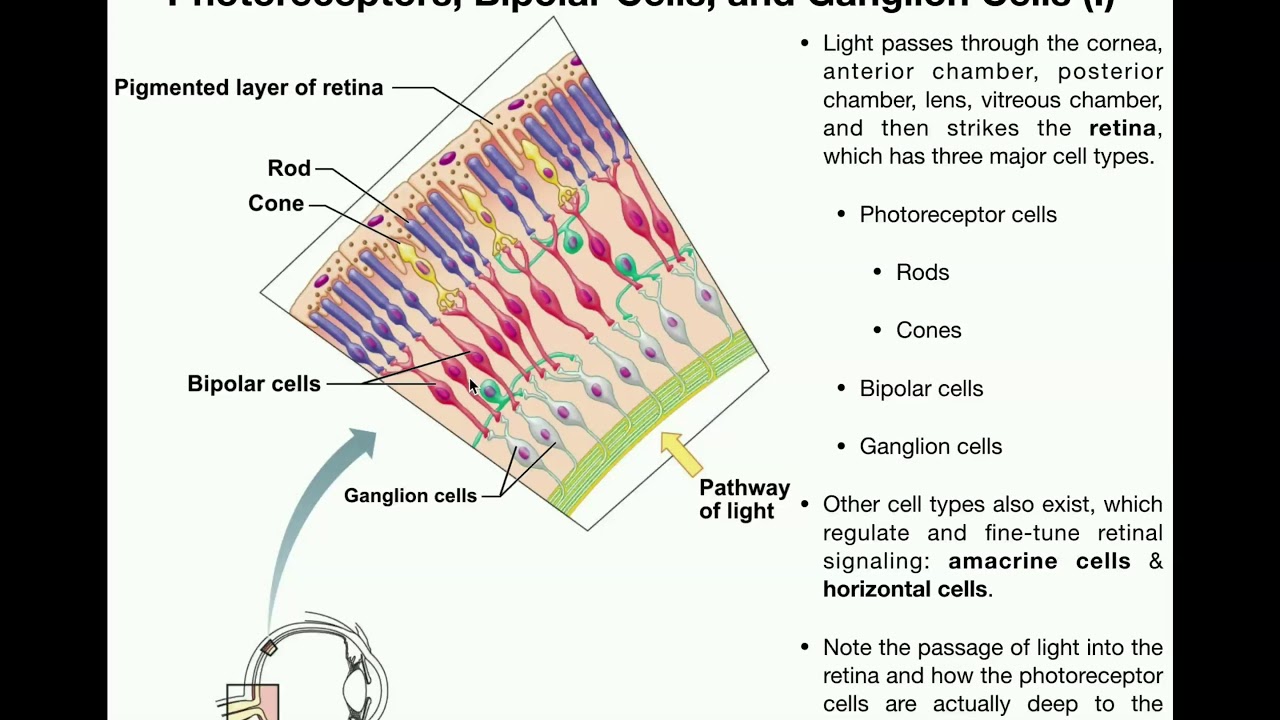 Anatomy Vision Part 1 Retina Photoreceptors Bipolar Cells Ganglion Cells
Anatomy Vision Part 1 Retina Photoreceptors Bipolar Cells Ganglion Cells
The retina is approximately 05 mm thick and lines the back of the eye.
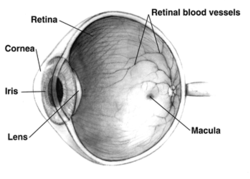
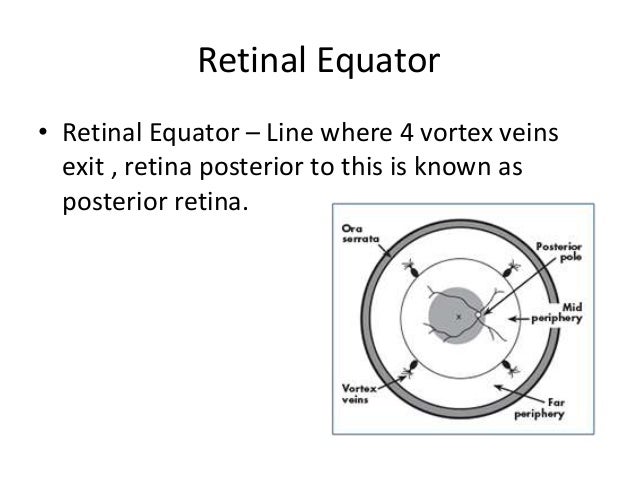
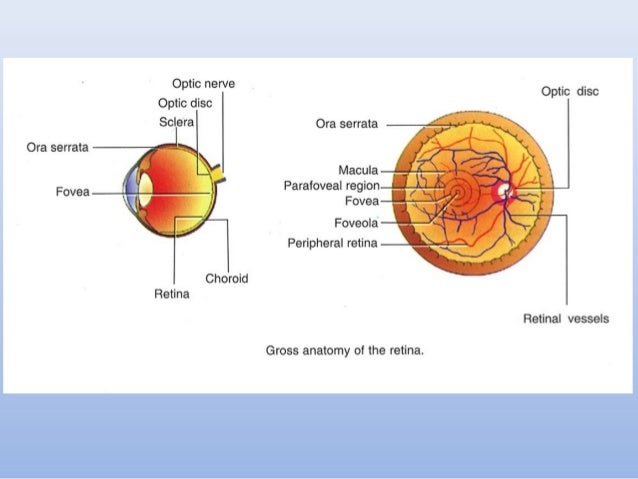
Retinal anatomy. The red curving structures are blood vessels which enter the retina through the nerve. This page describes normal retinal anatomy. Several parts of the eye are associated with the retina.
The whitish circle is the nerve that connects the retina to the brain. Photoreceptors rods and cones comprise the inner sensory layer of the retina. Retina lines the globe inner surface and contains light sensitive neuron s that transmit signals to the optic nerve.
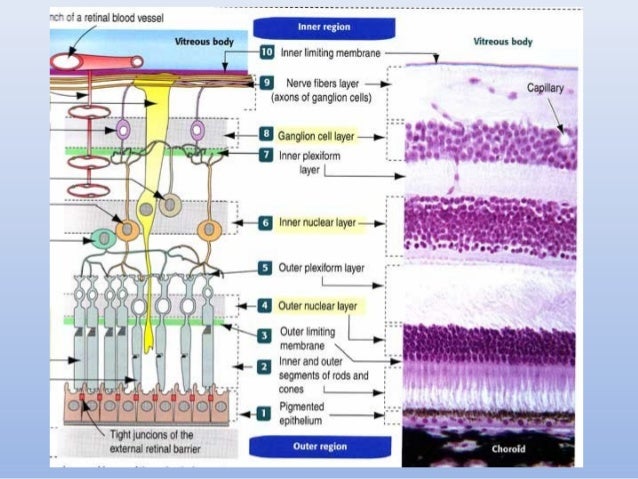
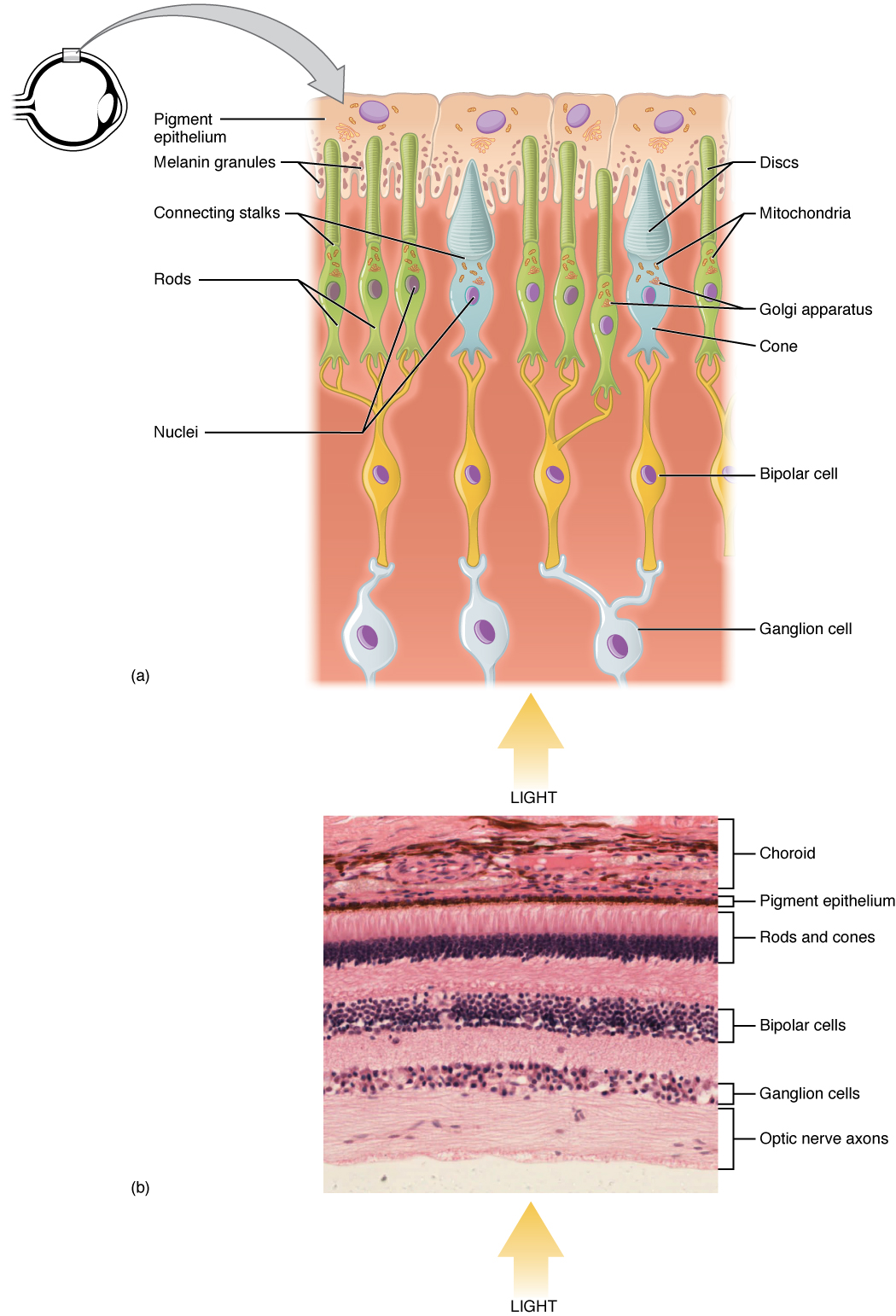
The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported b. These are essentially light sensitive cells responsible for detecting qualities such as color and light intensity. Read an overview of general eye anatomy to learn how the parts of the eye work together.
Cellular anatomy of the retina. The retina is the innermost light sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The retina processes light through a layer of photoreceptor cells.
The retina consists of millions of cells packed together in a tightly knit network spread over the surface of the back of the eye. The retina is the layer of nerve cells lining the back wall inside the eye. These cells can be divided into a three basic cell types photoreceptor cells neuronal cells and glial cells.
Simple anatomy of the retina by helga kolb. The optics of the eye create a focused two dimensional image of the visual world on the retina which translates that image into electrical neural impulses to the brain to create visual perception the retina serving a function analogous to that of the film or image sensor in a camera. The optic nerve contains the ganglion cell axons running to the brain and additionally incoming blood vessels that open into the retina to vascularize the retinal layers and neurons fig.
The retina processes the information gathered by the photoreceptor cells and sends this information to the brain via the optic nerve. This fundus photograph shows the normal appearance of the retina.
 Pdf Retinal Anatomy And Pathology
Pdf Retinal Anatomy And Pathology

 Figure Retina Anatomy Image Courtesy Orawan Statpearls
Figure Retina Anatomy Image Courtesy Orawan Statpearls
Normal Retinal Anatomy The Retina Reference
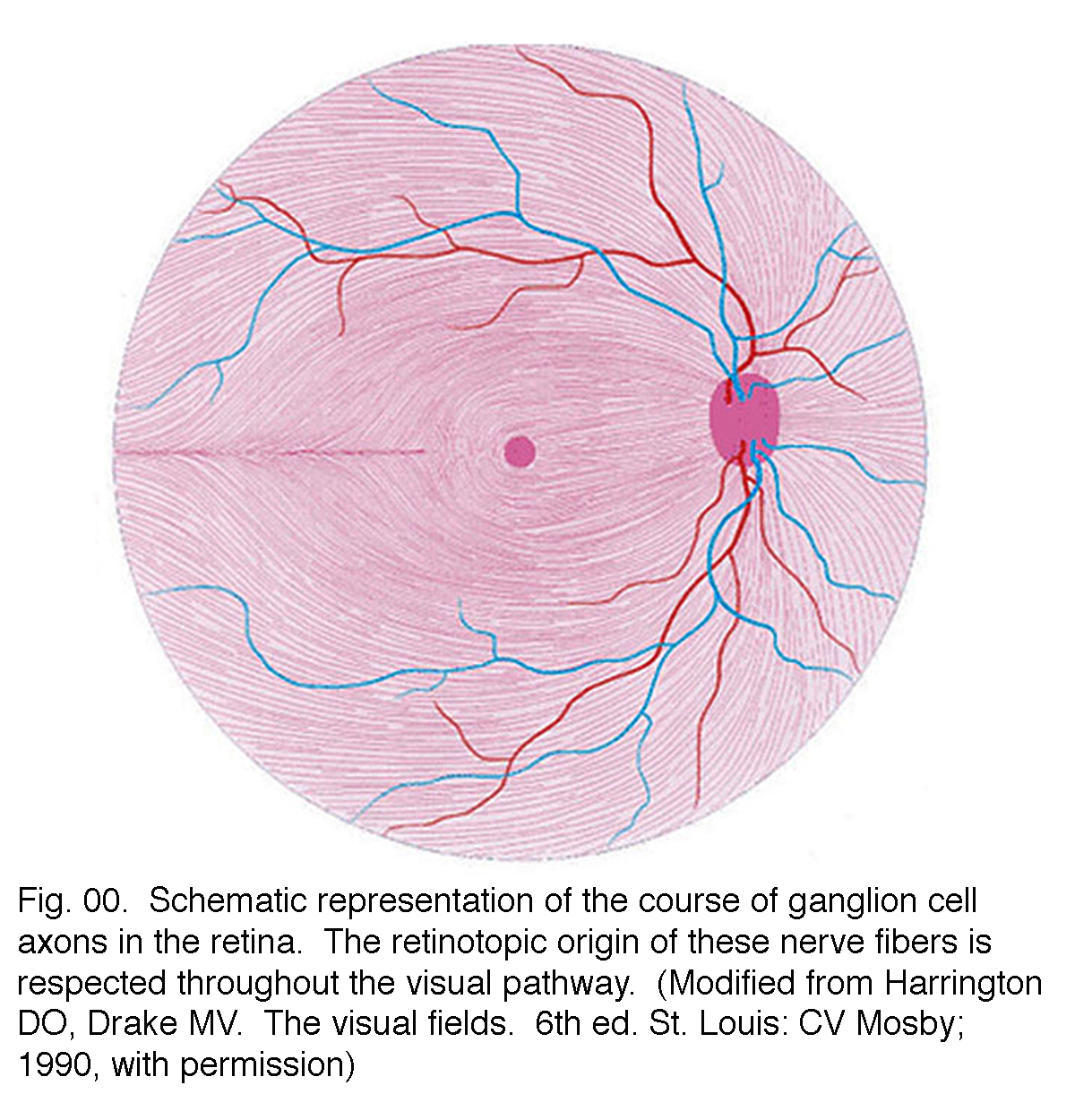 Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
 Anatomy Of The Adult Human Eye And Retinal Layers 10 A
Anatomy Of The Adult Human Eye And Retinal Layers 10 A
Normal Retinal Anatomy The Retina Reference
 Anatomy Of The Adult Human Eye And Retinal Layers 10 A
Anatomy Of The Adult Human Eye And Retinal Layers 10 A
1 2 Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
Normal Retinal Anatomy The Retina Reference
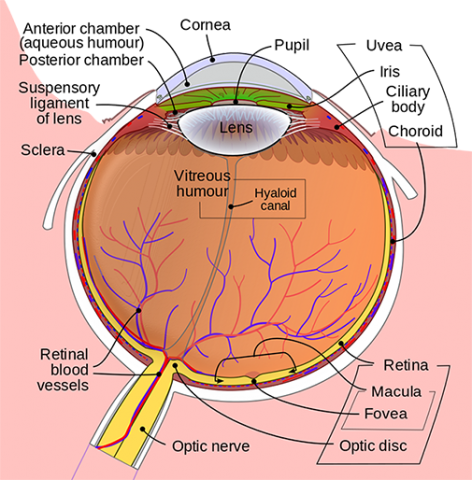 Anatomy Of The Eye Kellogg Eye Center Michigan Medicine
Anatomy Of The Eye Kellogg Eye Center Michigan Medicine
Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
Retina Specialists Seattle Retina Doctor Seattle
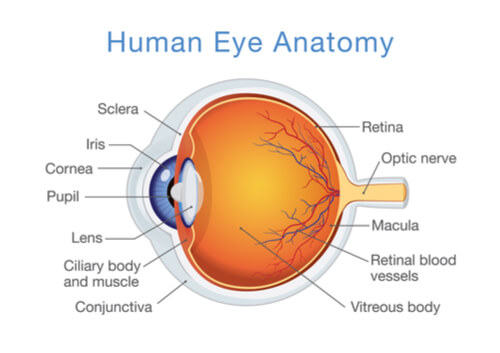 Anatomy Lesson What Is The Retina Eye Care Specialists
Anatomy Lesson What Is The Retina Eye Care Specialists
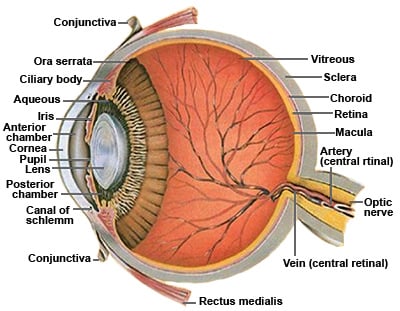 Eye Anatomy Ocular Anatomy Vision Conditions Problems
Eye Anatomy Ocular Anatomy Vision Conditions Problems
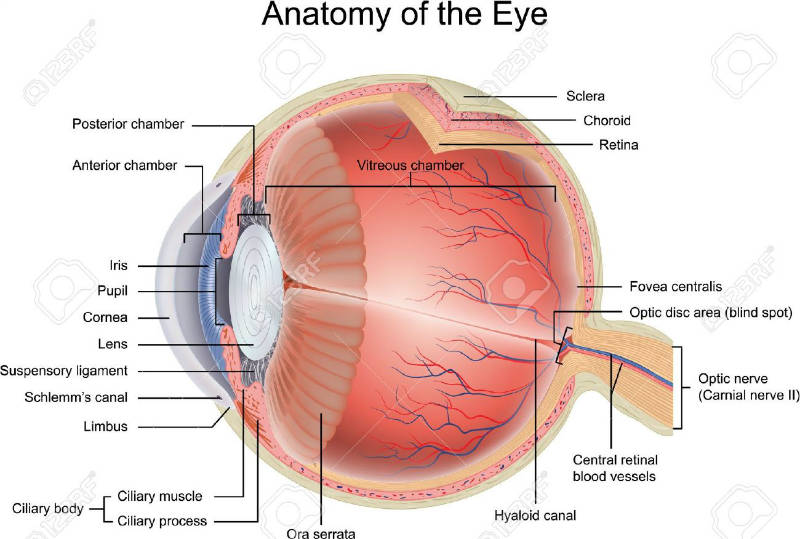 Anatomy Of The Eye Retina Ophthalmologist Gettysburg Pa
Anatomy Of The Eye Retina Ophthalmologist Gettysburg Pa
Simple Anatomy Of The Retina By Helga Kolb Webvision
 Illustration Of Eye Anatomy And Retinal Layers 2 3 A
Illustration Of Eye Anatomy And Retinal Layers 2 3 A
Normal Retinal Anatomy The Retina Reference


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Retinal Anatomy"
Posting Komentar