Airway Anatomy Intubation
This predisposes to airway obstruction in asleep children. The first anatomical difference between the pediatric and adult patient becomes important when positioning the child prior to or immediately after the induction of anesthesia.
 Chapter 19 Airway Management Morgan Mikhail S Clinical
Chapter 19 Airway Management Morgan Mikhail S Clinical
Paediatric airway anatomy appropriately positioning children undergoing intubation.
Airway anatomy intubation. Interpreting structures seen on direct laryngoscopy. Nasal cavity and nasopharynx. Anatomical abnormalities may affect only intubation only airway management or both.
Nasotracheal intubation is an alternative approach to orotracheal intubation. Indications for endotracheal intubation include. Formed by union of facial bones nasal floor towards ear not eye lined with mucous membranes cilia tissues are delicate vascular adenoids.
It includes the mouth the nose the palate the uvula the pharynx and the larynx. The most widely used route is orotracheal in which an en. A good understanding of airway and intubation is fundamental to managing a sick patient.
Lymph tissue filters bacteria commonly infected. Warm filter and humidify air. This section also describes the functional physiology of this airway.
This demonstration by anthony lewis from isimulate and todd slesinger provides a brief overview of the basics of the upper airway and laryngoscopy. The nasal fossae are divided by the midline cartilaginous septum and medial portions of the lateral cartilages fig. The airway jedi is a website dedicated to teaching techniques for intubation airway management anesthesia safe patient care medical team communication.
Physical airway obstructions due to choking or a foreign object lodged in the airway. The two nasal fossae extend from the nostrils to the nasopharynx. Tracheal intubation usually simply referred to as intubation is the placement of a flexible plastic tube into the trachea to maintain an open airway or to serve as a conduit through which to administer certain drugs.
Home airway and intubation. Managing the airway of a patient with craniofacial disorders poses many challenges to the anesthesiologist. The need for mechanical ventilation.
It is frequently performed in critically injured ill or anesthetized patients to facilitate ventilation of the lungs including mechanical ventilation and to prevent the possibility of asphyxiation or airway obstruction. Selecting the correct equipment for intubation. The head of a pediatric patient is larger relative to body size with a prominent occiput.
 Airway Anatomy Its Assessment And Anaesthetic Implication
Airway Anatomy Its Assessment And Anaesthetic Implication
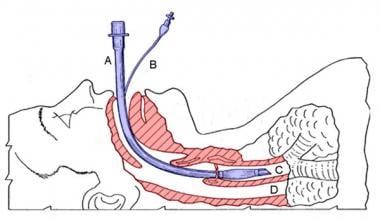 Medications Used In Tracheal Intubation Medications For
Medications Used In Tracheal Intubation Medications For
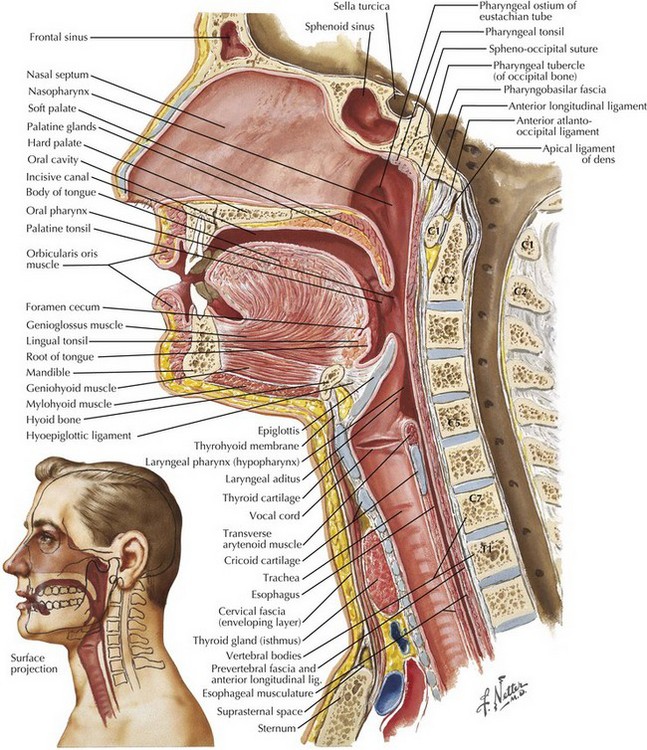 Tracheal Intubation And Endoscopic Anatomy Basicmedical Key
Tracheal Intubation And Endoscopic Anatomy Basicmedical Key
 1 Endotracheal Intubation Extubati On 2 Upper Airway
1 Endotracheal Intubation Extubati On 2 Upper Airway
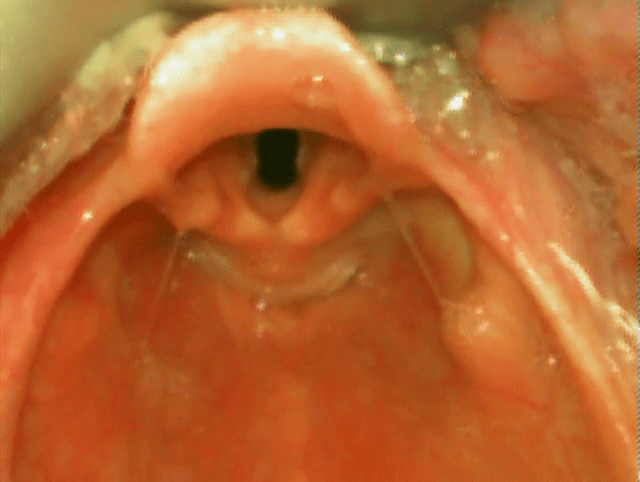
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
 Airway Anatomy Its Assessment And Anaesthetic Implication
Airway Anatomy Its Assessment And Anaesthetic Implication
 Intubation Step By Step Intubation Technique Explained
Intubation Step By Step Intubation Technique Explained
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
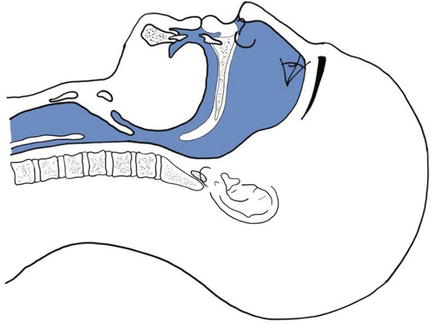
 Paediatric Airway Anatomy Paediatric Emergencies
Paediatric Airway Anatomy Paediatric Emergencies
 10 Rules For Approaching Difficult Intubation
10 Rules For Approaching Difficult Intubation
Airway Anatomy And Physiology Clinical Essentials
Essential Procedures For Emergency Urgent And Primary Care
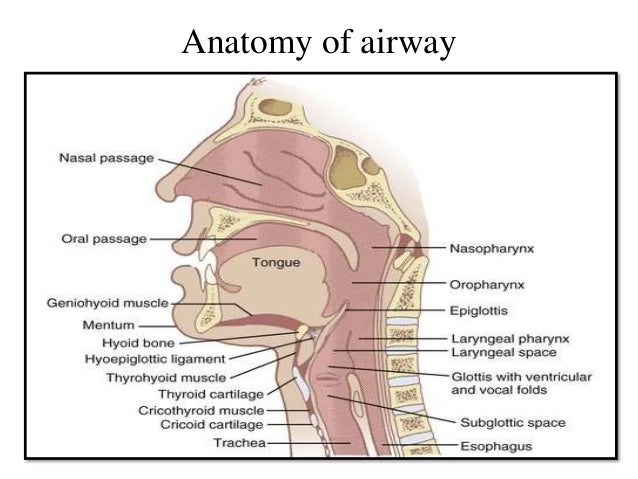 Endotracheal Intubation In Oral Maxillofacial Surgery
Endotracheal Intubation In Oral Maxillofacial Surgery
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
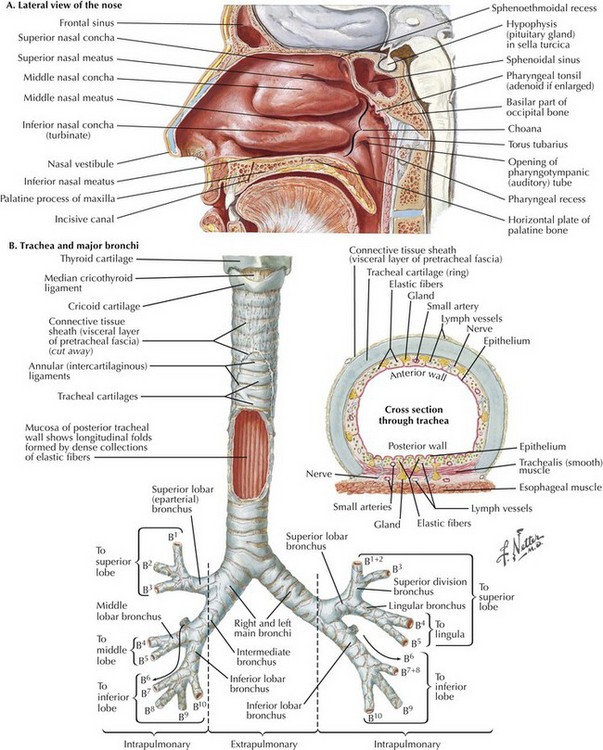 Tracheal Intubation And Endoscopic Anatomy Clinical Gate
Tracheal Intubation And Endoscopic Anatomy Clinical Gate
 Vevor Intubation Manikin Pvc Material Tracheal Intubation Training Simulator Model Laboratory Airway Training Intubation Manikin Study Teaching Model
Vevor Intubation Manikin Pvc Material Tracheal Intubation Training Simulator Model Laboratory Airway Training Intubation Manikin Study Teaching Model
 Chapter 38 Airway Management Principles And Practice Of
Chapter 38 Airway Management Principles And Practice Of
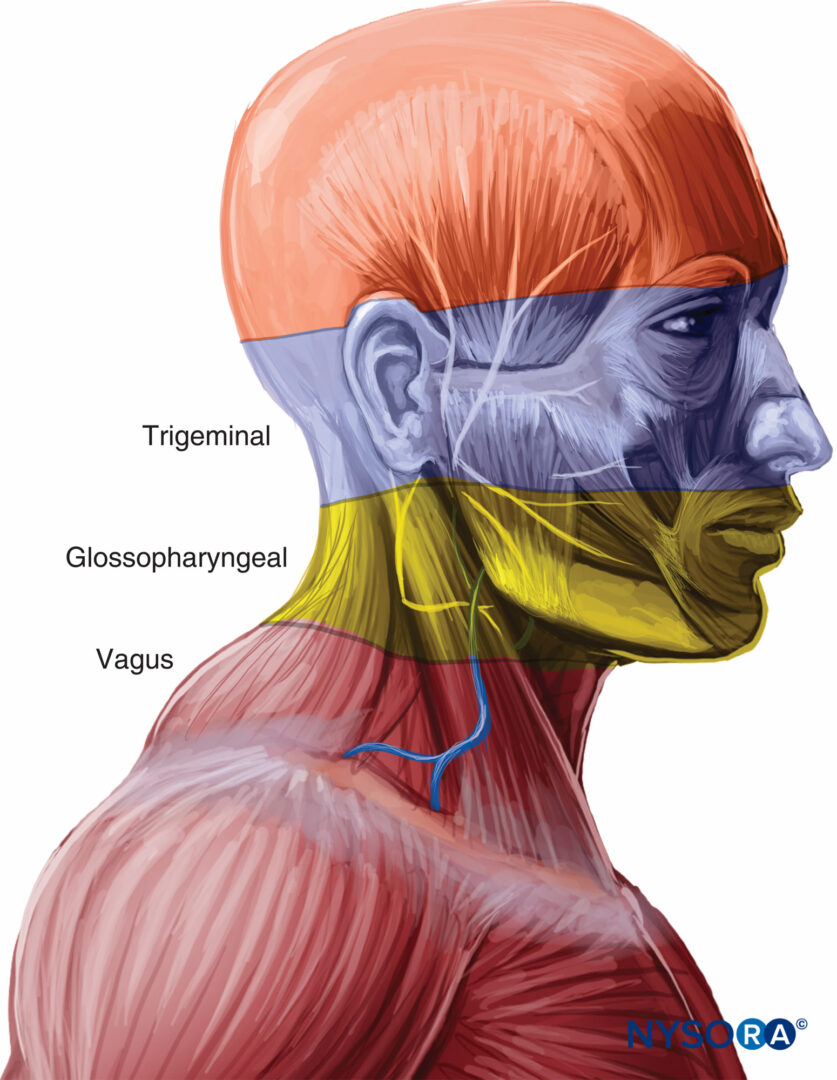 Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
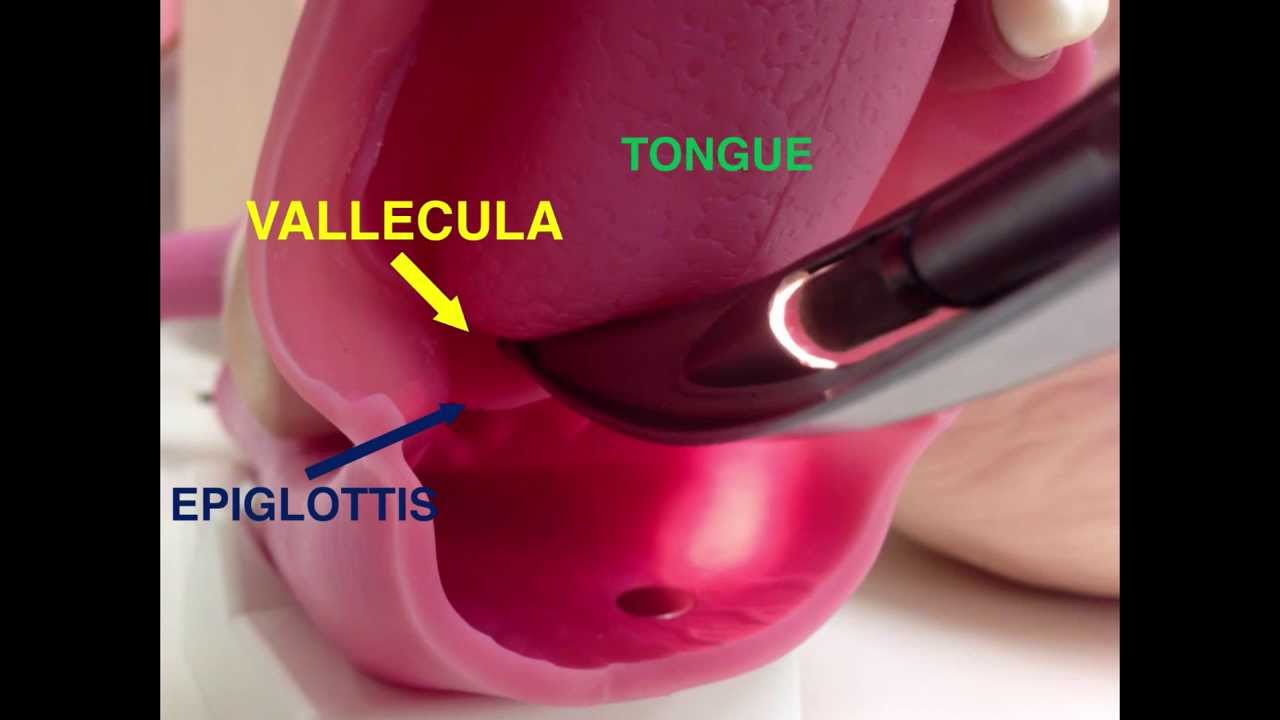 Airway Devices 01 Direct Laryngoscopy
Airway Devices 01 Direct Laryngoscopy
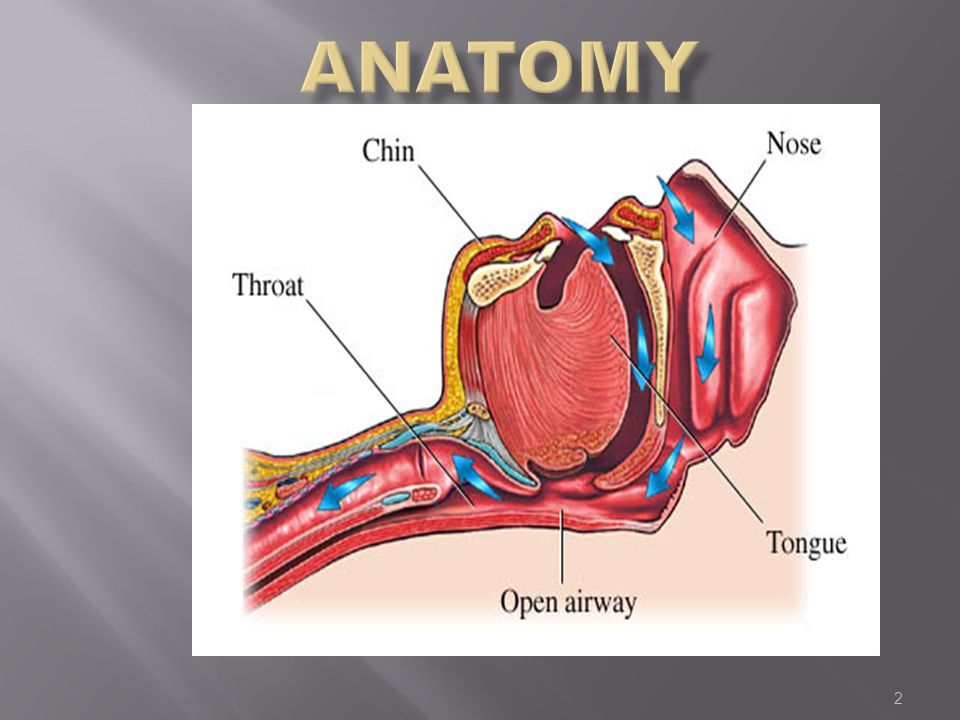 Intubation And Anatomy Of The Airway Ppt Video Online Download
Intubation And Anatomy Of The Airway Ppt Video Online Download
 Emergency Airway Management Part 3 Intubation The
Emergency Airway Management Part 3 Intubation The
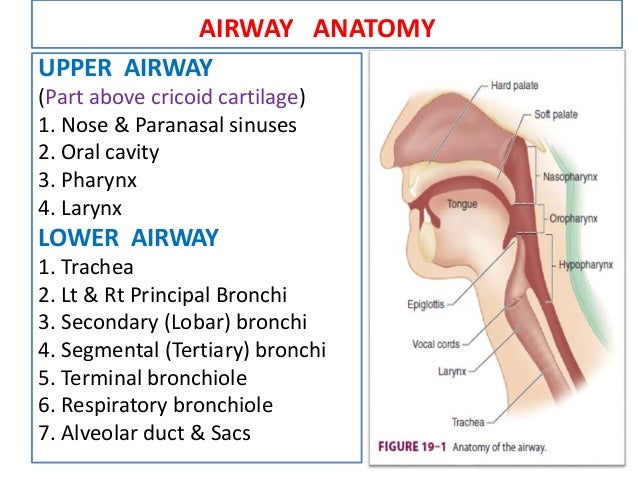

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Airway Anatomy Intubation"
Posting Komentar