Uterine Anatomy
Causes can include hormones thyroid problems fibroids polyps cancer infection or pregnancy. The uterus is held in position within the pelvis by ligaments which are called endopelvic fascia.
 Anatomy Location Of Bladder Vaginal Canal Cervix And
Anatomy Location Of Bladder Vaginal Canal Cervix And
It is neatly tucked into the pelvic area of most mammals and of course in humans.

Uterine anatomy. The uterus can be divided anatomically into four regions. The middle layer or myometrium makes up most of the uterine volume and is the muscular layer. R elations of the body of uterus.
The inner layer called the endometrium is the most active layer and responds to cyclic ovarian. The anatomy of the uterus consists of the following 3 tissue layers see the following image. The first sign of a problem with the uterus may be bleeding between periods or after sex.
The uterus is a secondary sex organ. In sagittal plane it is merely a slit. It is important to dissect the anatomy of the human uterus.
The uterus itself is a hollow organ that is shaped in the form of a pear and interestingly enough measures about that size. The cavity communicates with the cervical canal via internal os. The cervix protrudes into the vagina.
The fundus the uppermost rounded portion of the uterus the corpus body the cervix and the cervical canal. The uterus or womb is the place where a baby grows when a woman is pregnant. In the female body the upper end of the uterus called the fundus will join the fallopian tubes at either side while the lower end will open into the vagina.
Treatment depends on the cause. Secondary sex organs are components of the reproductive tract that mature during puberty under the influence of sex hormones produced from primary sex organs the ovaries in females and the testes in males. It functions to nourish and house the fertilized egg until the unborn child or offspring is ready to be delivered.
What are the relations of uterus. Uterus also called womb an inverted pear shaped muscular organ of the female reproductive system located between the bladder and rectum. The uterus or womb is shaped like an inverted pear.
The cervical canal opens into vagina via external os. Is triangular in shape in coronal section.
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/438/D6gDneJuqlI2XKK2u6ckw_overview-uterus-and-vagina_english.jpg) Uterus Anatomy Blood Supply Histology Functions Kenhub
Uterus Anatomy Blood Supply Histology Functions Kenhub
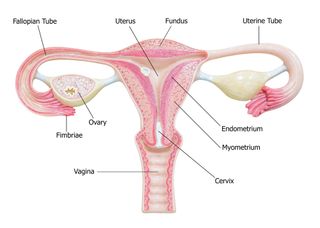 Ovaries Facts Function Disease Live Science
Ovaries Facts Function Disease Live Science
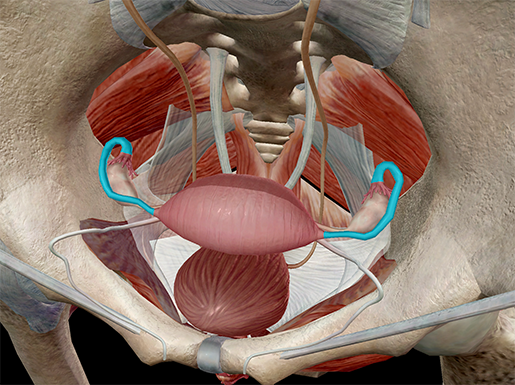 Anatomy And Physiology Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy
Anatomy And Physiology Internal Female Reproductive Anatomy
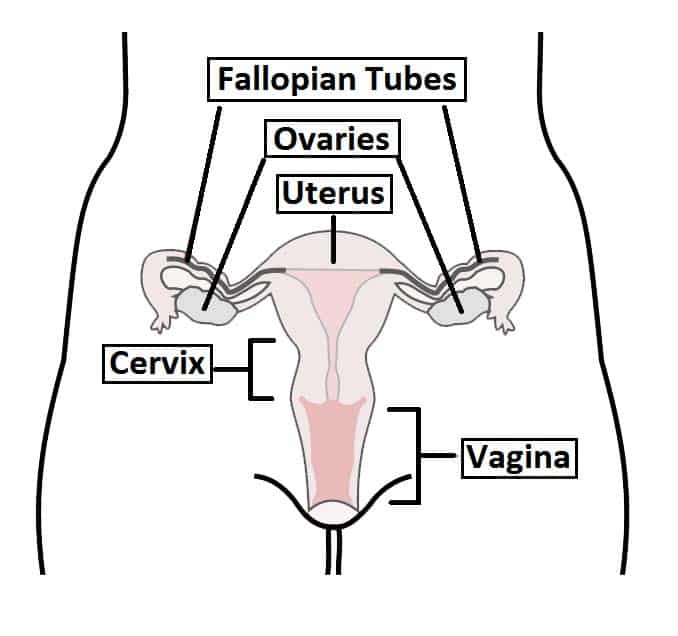 The Uterus Structure Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Uterus Structure Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
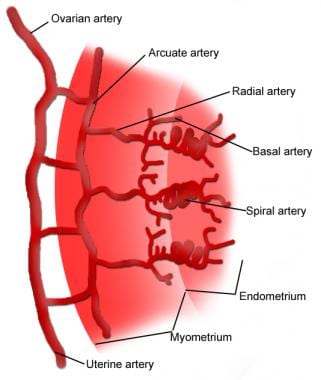 Uterus Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants
Uterus Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/female-genitalia--illustration-502865563-599d7bf5845b340010fcee15.jpg) The Function And Anatomy Of The Uterus
The Function And Anatomy Of The Uterus
 Pelvis Clinical Anatomy A Case Study Approach
Pelvis Clinical Anatomy A Case Study Approach
 Surgical Anatomy Of The Female Pelvis By Laparoscopy
Surgical Anatomy Of The Female Pelvis By Laparoscopy
 Figure 1 Uterine Anatomy Stembook Ncbi Bookshelf
Figure 1 Uterine Anatomy Stembook Ncbi Bookshelf
 Ovarian Uterine Anatomy At University Of Cincinnati Studyblue
Ovarian Uterine Anatomy At University Of Cincinnati Studyblue
 Ovarian Uterine Anatomy At University Of Cincinnati Studyblue
Ovarian Uterine Anatomy At University Of Cincinnati Studyblue
 Uterine Fibroids The Center For Innovative Gyn Care
Uterine Fibroids The Center For Innovative Gyn Care
 Uterine Blood Supply Elearning
Uterine Blood Supply Elearning
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/480/Wx4xsnGNJz0G5IjNKhXiA_uterus-and-ovaries_english.jpg) Uterus Anatomy Blood Supply Histology Functions Kenhub
Uterus Anatomy Blood Supply Histology Functions Kenhub
 Uterus Anatomy Definition Function Location Biology
Uterus Anatomy Definition Function Location Biology
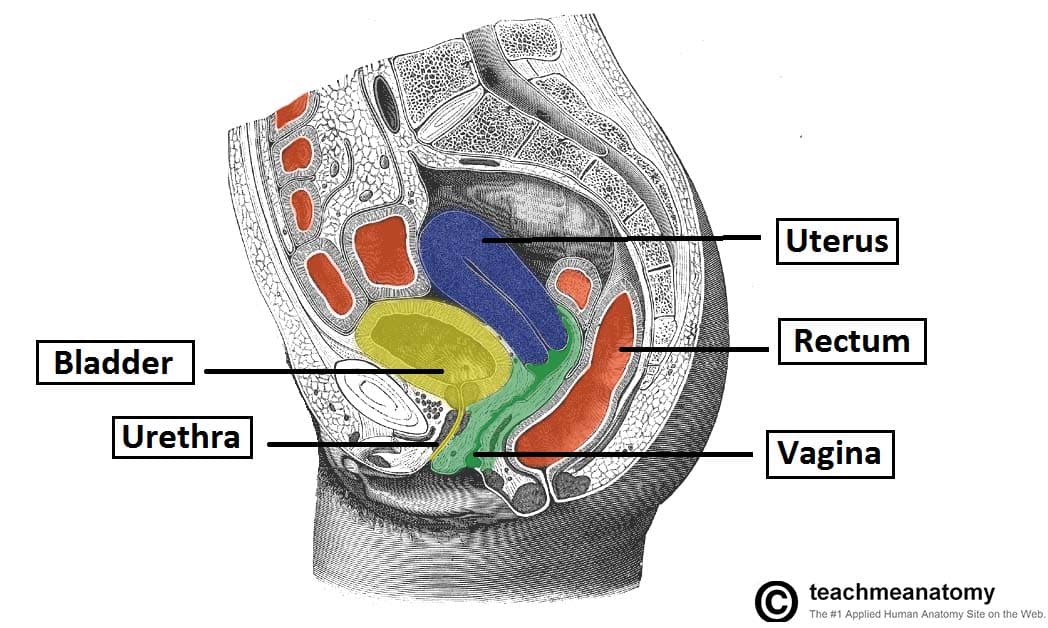 The Uterus Structure Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Uterus Structure Location Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
 Female Reproductive Anatomy Reproductive Medbullets Step 1
Female Reproductive Anatomy Reproductive Medbullets Step 1
 Foetal Fetal Development Illustrations Heart Vascular
Foetal Fetal Development Illustrations Heart Vascular
 The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
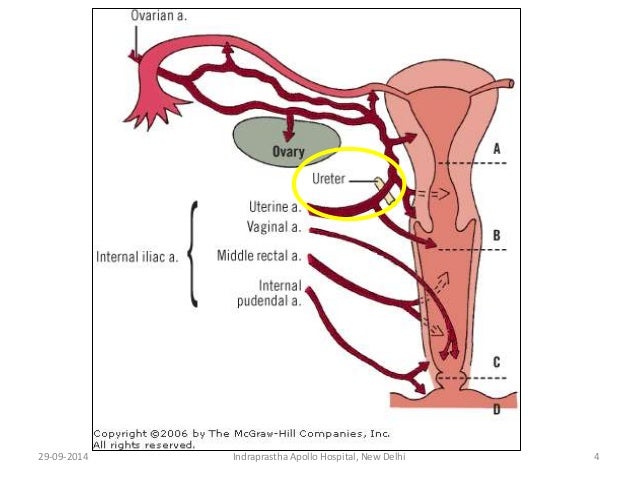 Anatomy For Anaesthesia Nerve Supply Of Uterus Cervix
Anatomy For Anaesthesia Nerve Supply Of Uterus Cervix




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Uterine Anatomy"
Posting Komentar