Anatomy Of Airway For Intubation
Look at the anatomy thick short neck high palate narrow face trauma large tongue teeth or dentures. Cartilages of the larynx 3.
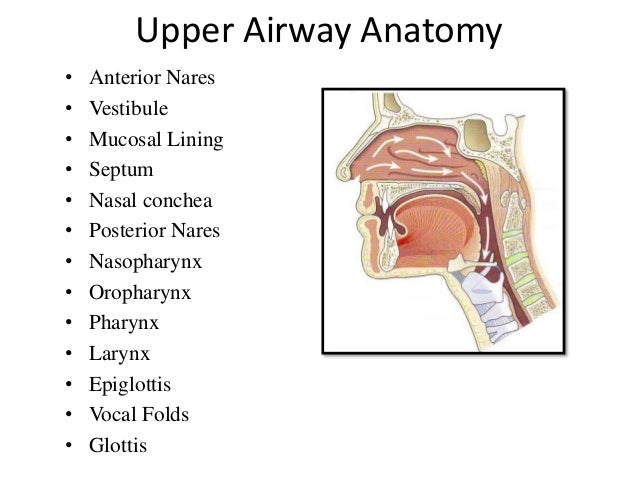
 Anatomy Of Airway And Intubation Nour Ghnaimat Ppt Download
Anatomy Of Airway And Intubation Nour Ghnaimat Ppt Download
A good understanding of airway and intubation is fundamental to managing a sick patient.

Anatomy of airway for intubation. This demonstration by anthony lewis from isimulate and todd slesinger provides a brief overview of the basics of the upper airway and laryngoscopy. Endotracheal intubation can be done either nasally or orally but oral intubation is easier in most contexts. Be careful as most men with small jaws grow beards to hide them.
Warm filter and humidify air. Formed by union of facial bones nasal floor towards ear not eye lined with mucous membranes cilia tissues are delicate vascular adenoids. This chapter provides an overview of airway anatomy for tracheal intubation with conventional laryngoscopy videolaryngoscopy glidescope and flexible fiberoptic bronchoscopy.
Understanding airway anatomy is vital to proper intubation. Gold sivam ramanathan i. Try using search on phones and tablets.
Managing the airway of a patient with craniofacial disorders poses many challenges to the anesthesiologist. Think of the mnemonic lemon to determine difficulty of intubation. The head of a pediatric patient is larger relative to body size with a prominent occiput.
Chapter 1 functional anatomy of the airway lee coleman mark zakowski julian a. Nasal cavity and nasopharynx. A keen understanding of airway anatomy can make the process of intubating a patient much easier.
Lymph tissue filters bacteria commonly infected. Defense against pathogens 2. Upper airway obstruction c.
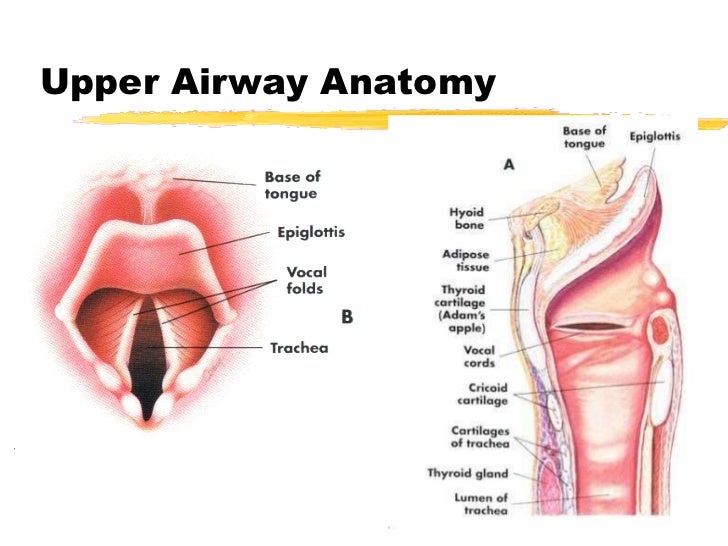
It includes the mouth the nose the palate the uvula the pharynx and the larynx. Evaluate the 3 3 2 rule. Muscles innervation and blood supply of the larynx iii.
This section also describes the functional physiology of this airway. Bones of the larynx 2. Anatomical abnormalities may affect only intubation only airway management or both.
This predisposes to airway obstruction in asleep children. Airway assessment and recognition of a difficult airway are also reviewed. The first anatomical difference between the pediatric and adult patient becomes important when positioning the child prior to or immediately after the induction of anesthesia.
Although the numerous airway management devices include video laryngoscopes. Navigation best viewed on larger screens.
 Airway Anatomy Its Assessment And Anaesthetic Implication
Airway Anatomy Its Assessment And Anaesthetic Implication
 Applied Functional Anatomy Of The Airway Manual Of
Applied Functional Anatomy Of The Airway Manual Of
 10 Rules For Approaching Difficult Intubation
10 Rules For Approaching Difficult Intubation
 Intubation Medicine Flashcards Quizlet
Intubation Medicine Flashcards Quizlet
/intubation-021-5a299722e258f8003693b043.png) What Is Intubation And Why Is It Done
What Is Intubation And Why Is It Done
 Intubation Step By Step Intubation Technique Explained
Intubation Step By Step Intubation Technique Explained
 Chapter 3 Preparation For Awake Intubation Management Of
Chapter 3 Preparation For Awake Intubation Management Of
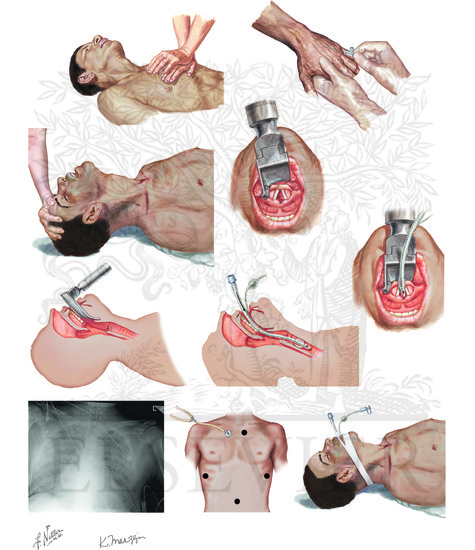
 Classic Intubation And Tracheostomy Procedures Medical
Classic Intubation And Tracheostomy Procedures Medical
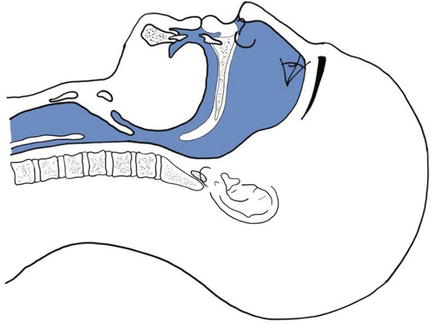
 Endotracheal Intubation In Oral Maxillofacial Surgery
Endotracheal Intubation In Oral Maxillofacial Surgery
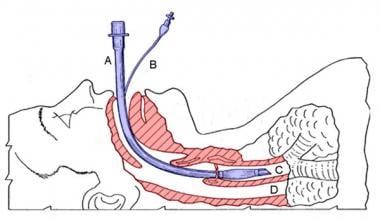
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
 Emcrit Podcast 226 Airway Update Bougie And Positioning
Emcrit Podcast 226 Airway Update Bougie And Positioning
Acute Post Operative Airway Complications Following Anterior
 Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
Regional And Topical Anesthesia For Awake Endotracheal
 Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
Chapter 6 Essential Anatomy Of The Airway Emergency
 Medications Used In Tracheal Intubation Medications For
Medications Used In Tracheal Intubation Medications For
 Chapter 19 Airway Management Morgan Mikhail S Clinical
Chapter 19 Airway Management Morgan Mikhail S Clinical
 Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Functional Anatomy And Physiology Of Airway Intechopen
Essential Procedures For Emergency Urgent And Primary Care
 Chapter 19 Airway Management Morgan Mikhail S Clinical
Chapter 19 Airway Management Morgan Mikhail S Clinical
 Assessing And Finessing An Airway Update Emottawa
Assessing And Finessing An Airway Update Emottawa
 Pelvic Ring Ao Surgery Reference
Pelvic Ring Ao Surgery Reference
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationtrach Travails
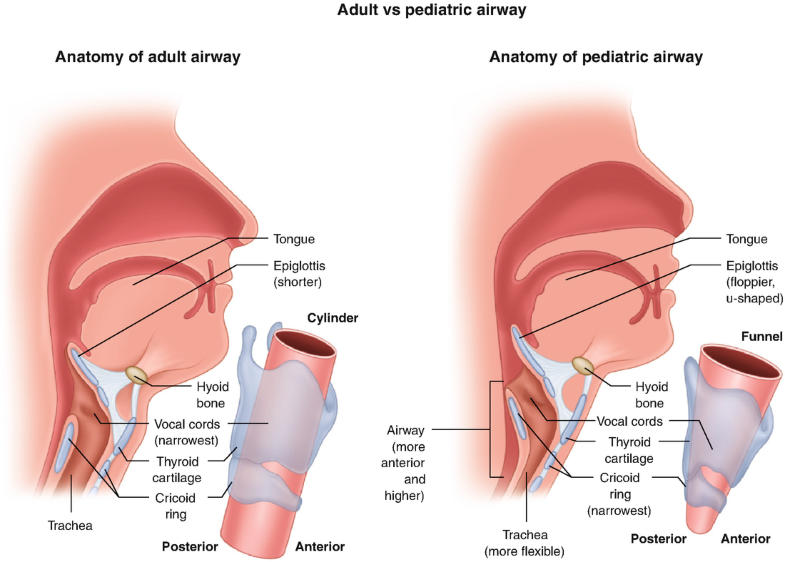 Airway Pediatric Anatomy Infants And Children Springerlink
Airway Pediatric Anatomy Infants And Children Springerlink
 Airway Airway Anatomy Pediatric Airways
Airway Airway Anatomy Pediatric Airways



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Airway For Intubation"
Posting Komentar