Anatomy And Function Of The Eye
The eye has many parts that must work together to produce clear vision. The optic nerve transmits these signals to the brain which forms an image so thereby providing sight.
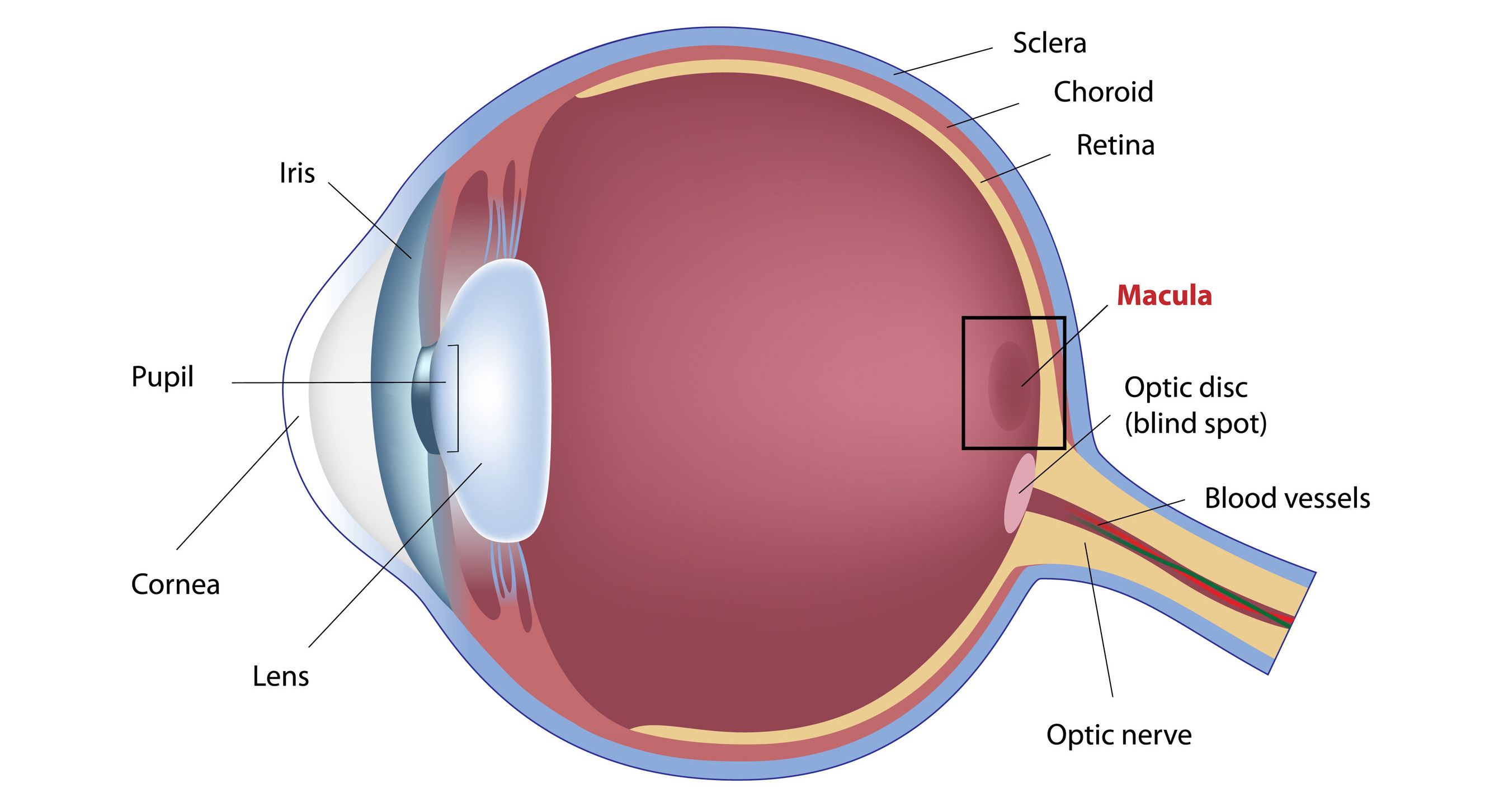
Anatomy of the eye.
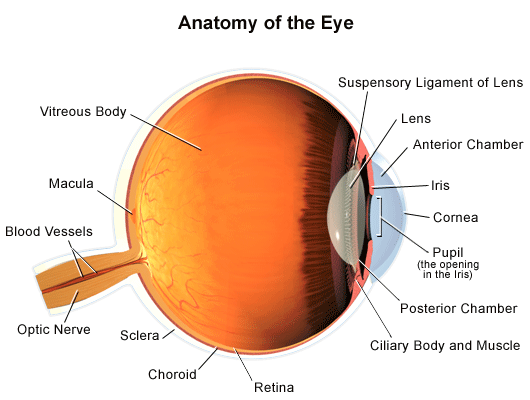
Anatomy and function of the eye. Extraocular muscles help move the eye in different directions. Multiple genes inherited from each parent determine a persons eye color. And when there is low light the iris opens up the pupil to let in more light.
Nerve signals that contain visual information are transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain. When there is bright light the iris closes the pupil to let in less light. Lens focuses light rays onto the retina.
Layer of the eye behind the retina contains blood vessels that nourish the retina. Iris the colored part of the eye which helps regulate the amount of light entering the eye. This is a short movie on the eye its anatomy and function.
The surface of the eye and of the inner eyelids is covered by a clear protective membrane called the conjunctiva. The outer layer of the eyeball is a tough white opaque membrane called the sclera the white of the eye. The photoreceptor nerve cells present in the macula and concentrated in the fovea the very center of the macula.
The eye is shaped like a round ball with a slight bulge at the front. The macula is a small extra sensitive area in the retina that gives you central vision. The eye has many parts which work together to accomplish vision and to keep the structures required for vision safe from infection and injury.
It collects light from the visible world around us and converts it into nerve impulses. Part of the eye above the lens that produces the aqueous humor. The eye has three main layers.
Anatomy of the eye. The eye is surrounded by the orbital bones and is cushioned by pads of fat within the orbital socket. The pupil or black dot at the centre of the eye is a hole through which light can enter the eye.
Light enters through the cornea past the iris through the pupil refracted by the lens and onto the retina of the eye. A note to all media companies or individuals who wish to use this animation. Behind the eye your optic nerve carries these impulses to the brain.
Eye color is created by the amount and type of pigment in your iris. The nerve at the back of the eye that transports electric signals to the brain. The sclera or white part of the eye protects the eyeball.
The iris or coloured part of the eye surrounds the pupil. The eye is a sensory organ. Image starts right side up from outside the eye and is flipped upside down on the retina.
These layers lie flat against each other and form the eyeball. Enable people to see fine detail and color. The anatomy of the eye.
Eye parts and functions. I do not own this vi.
 Neuroscience For Kids The Eye And Its Connections
Neuroscience For Kids The Eye And Its Connections
 Anatomy Of The Eye Children S Wisconsin
Anatomy Of The Eye Children S Wisconsin
Eye Health Anatomy Of The Eye Visionaware
 Human Eye Anatomy And Functions Diagram Eye Anatomy
Human Eye Anatomy And Functions Diagram Eye Anatomy
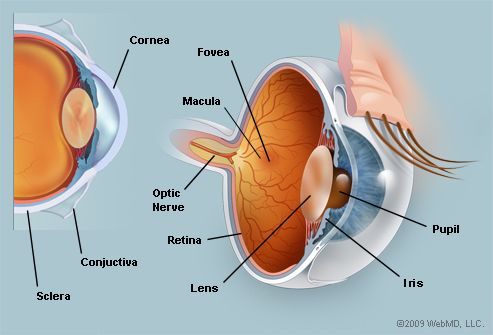 The Eyes Human Anatomy Diagram Optic Nerve Iris Cornea
The Eyes Human Anatomy Diagram Optic Nerve Iris Cornea
Photobiology Of The Uveal Tract
Gross Anatomy Of The Eye By Helga Kolb Webvision
Major Ocular Structures Laramy K Independent Optical Lab
 Eye Structure And Function In Dogs Dog Owners Merck
Eye Structure And Function In Dogs Dog Owners Merck
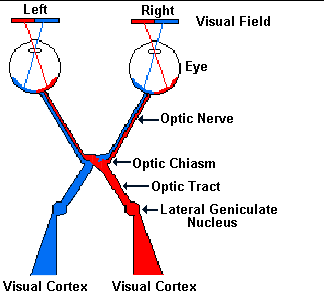 Neuroscience For Kids The Eye And Its Connections
Neuroscience For Kids The Eye And Its Connections
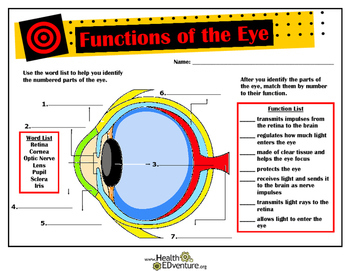 Functions And Anatomy Of The Eye
Functions And Anatomy Of The Eye
Human Eye Function Anatomy Light Rays Cornea Iris
 Eye Anatomy And Function Made Easy
Eye Anatomy And Function Made Easy
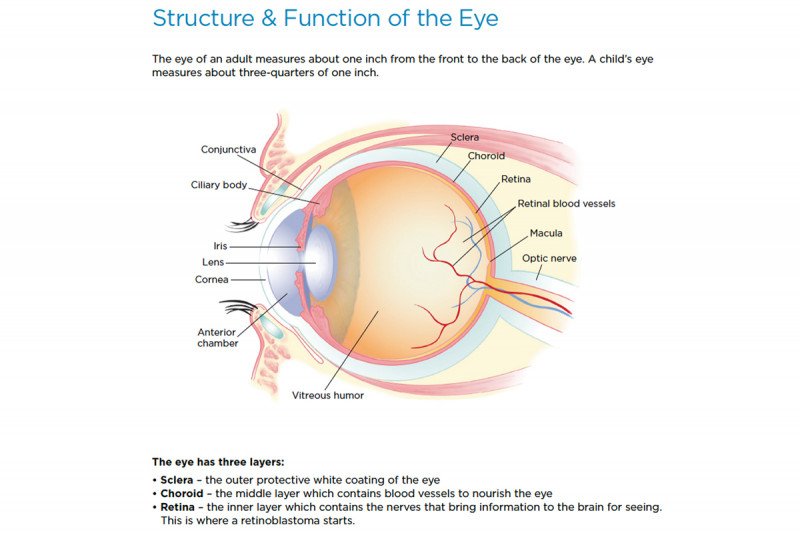 Retinoblastoma Anatomy Of The Eye Memorial Sloan
Retinoblastoma Anatomy Of The Eye Memorial Sloan
 Anatomy And Function Of The Eye
Anatomy And Function Of The Eye
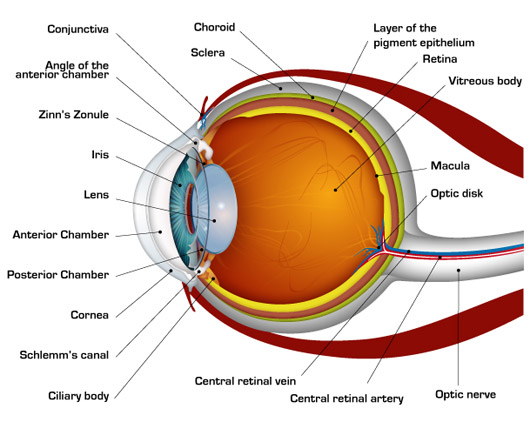 How The Human Eye Works Cornea Layers Role Light Rays
How The Human Eye Works Cornea Layers Role Light Rays
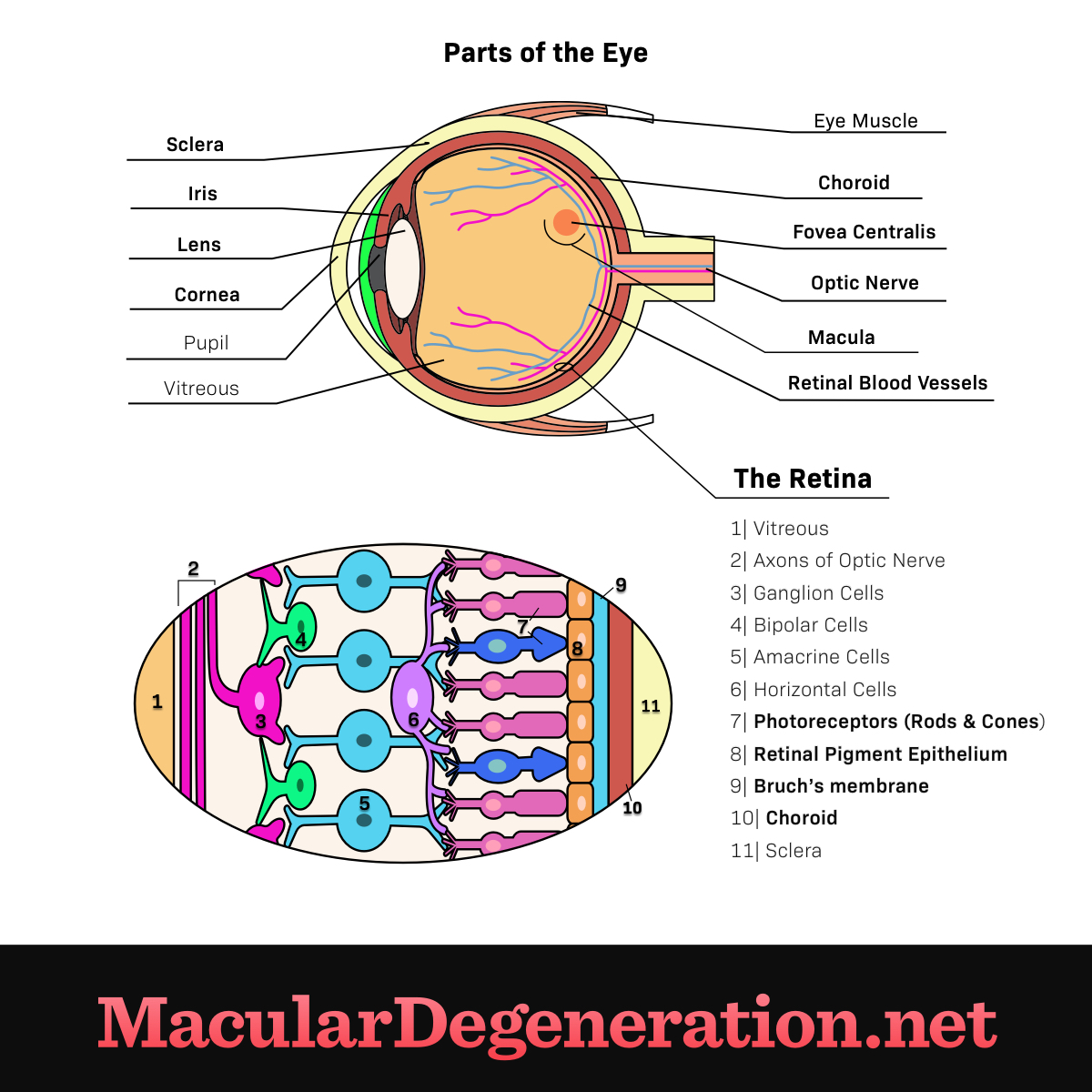 Eye Anatomy And Function Maculardegeneration Net
Eye Anatomy And Function Maculardegeneration Net
 Eye Structure And Function In Dogs Dog Owners Merck
Eye Structure And Function In Dogs Dog Owners Merck
 Anatomy And Structure Of The Eye Brightfocus Foundation
Anatomy And Structure Of The Eye Brightfocus Foundation
Dog Eye Problems Learn What To Look For And How To Examine
 Eye Anatomy Glaucoma Research Foundation
Eye Anatomy Glaucoma Research Foundation
Eye Health Online Course Module 1 Eye Anatomy



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy And Function Of The Eye"
Posting Komentar