Anatomy Of Omentum
It is formed by hepatogastric and hepatoduodenal ligaments. The greater omentum is larger than the lesser omentum which hangs down from the liver to the lesser curvature.
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/arteria-gastroomentalis-dextra/yBLyiRJmuej3FSyJeVg_A._gastroomentalis_dextra_01.png) Greater And Lesser Omentum Location Anatomy Function Kenhub
Greater And Lesser Omentum Location Anatomy Function Kenhub
The common anatomical term epiploic derives from epiploon from the greek epipleein.
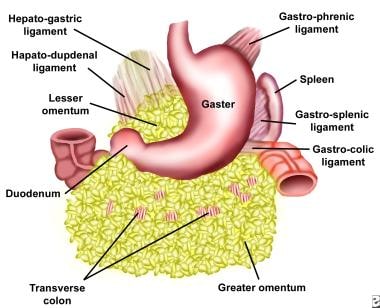
Anatomy of omentum. It descends from the greater stomach curvature and folds under itself and then connects to the transverse colon. The greater omentum hangs down from the transverse colon of the large intestine like an apron. The omentum is comprised of a double sheet of peritoneum made up of four layers.
It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach passing in front of the small intestines and doubles back to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. A medial hepatogastric ligament which passes between the stomach and liver and. The greater omentum is a double layer of peritoneum which mainly consists of fat connective tissue and lymphatic cells.
Omentum anatomy pathological conditions and surgical importance. Anatomy embryology of peritoneum. The omentum and mesentery contain blood vessels nerves lymph nodes fat elastic fibres for stretching and collagen fibres for strength.
Greater and lesser omentum peritoneum. It contains large quantities of fat that serve to keep the organs warm. A thin membrane continuous with the peritoneal coverings of the anterior and posterior surfaces of the stomach and the first part of the duodenum the lesser omentum is divided into.
Omentum is a fold of peritoneum extending from the stomach to adjacent abdominal organs. Omentum arises from. A lateral hepatoduodenal.
There are two omenta. It is the largest peritoneal fold and is well vascularized consisting of gastroepiploic arteries and draining veins. Omentum anatomy pathological conditions and surgical importance 1.
The omentum is thinner than the mesentery and is lacy in appearance. At its free edge which extends to the porta hepatis. The lesser omentum is much smaller and extends between read more.
The greater omentum is a large apron like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. As stated above the peritoneal cavity is the space between. Omenta are the fused peritoneal folds that connect the stomach and duodenum.
In animals the greater omentum is called caul. The abdominal wall and the abdominal organs are lined by a thin serous membrane called. It forms the anterior surface of the lesser sac.
The lesser omentum is the fold of peritoneum extending from the lesser curvature of the stomach and proximal 2cm of the duodenum to the porta hepatis of the liver. The omenta are folds of peritoneum enclosing nerves blood vessels lymph channels and fatty and connective tissue. The greater omentum is a part of the anatomy of the abdomen and consists of a prominent fold of peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach in front of the transverse colon to which it is attached.
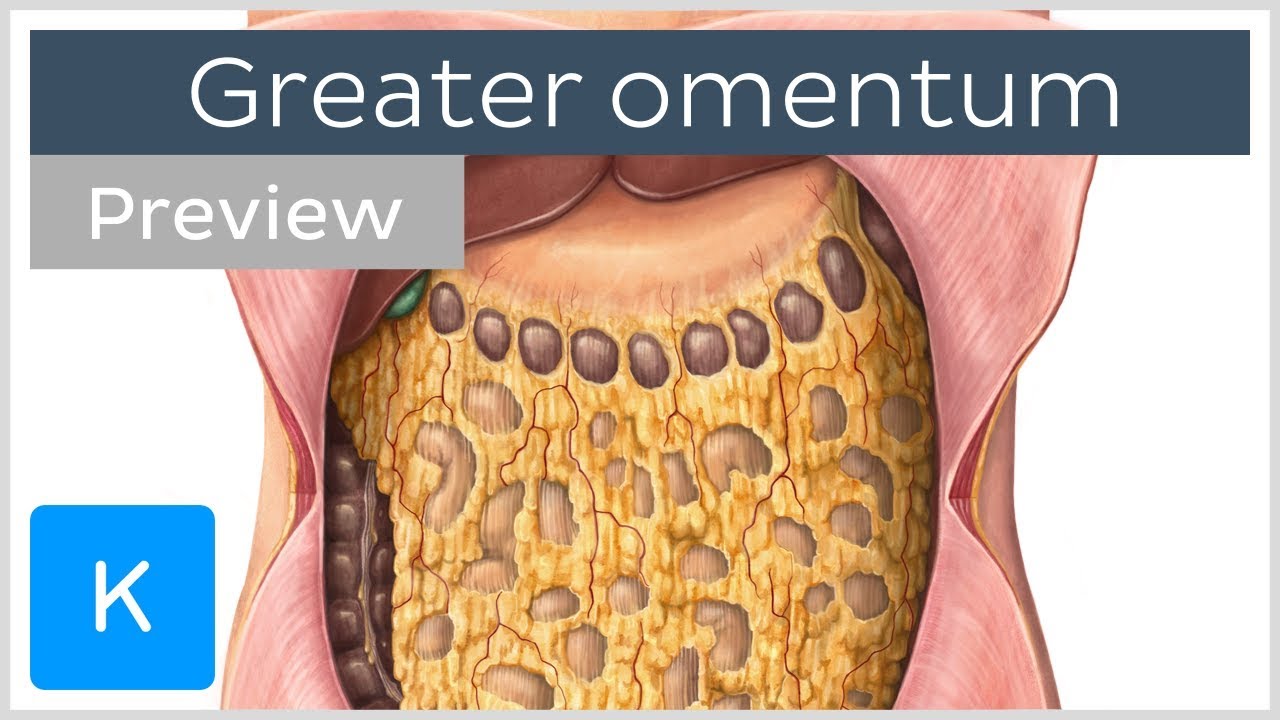 Overview Of The Greater Omentum Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
Overview Of The Greater Omentum Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
 Greater And Lesser Omentum Anatomy And Omentum Function
Greater And Lesser Omentum Anatomy And Omentum Function
 Solid Omental Tumors Practice Essentials Anatomy
Solid Omental Tumors Practice Essentials Anatomy
 Table Table 4 Definitions Of Figo Stage Iiia Pdq Cancer
Table Table 4 Definitions Of Figo Stage Iiia Pdq Cancer
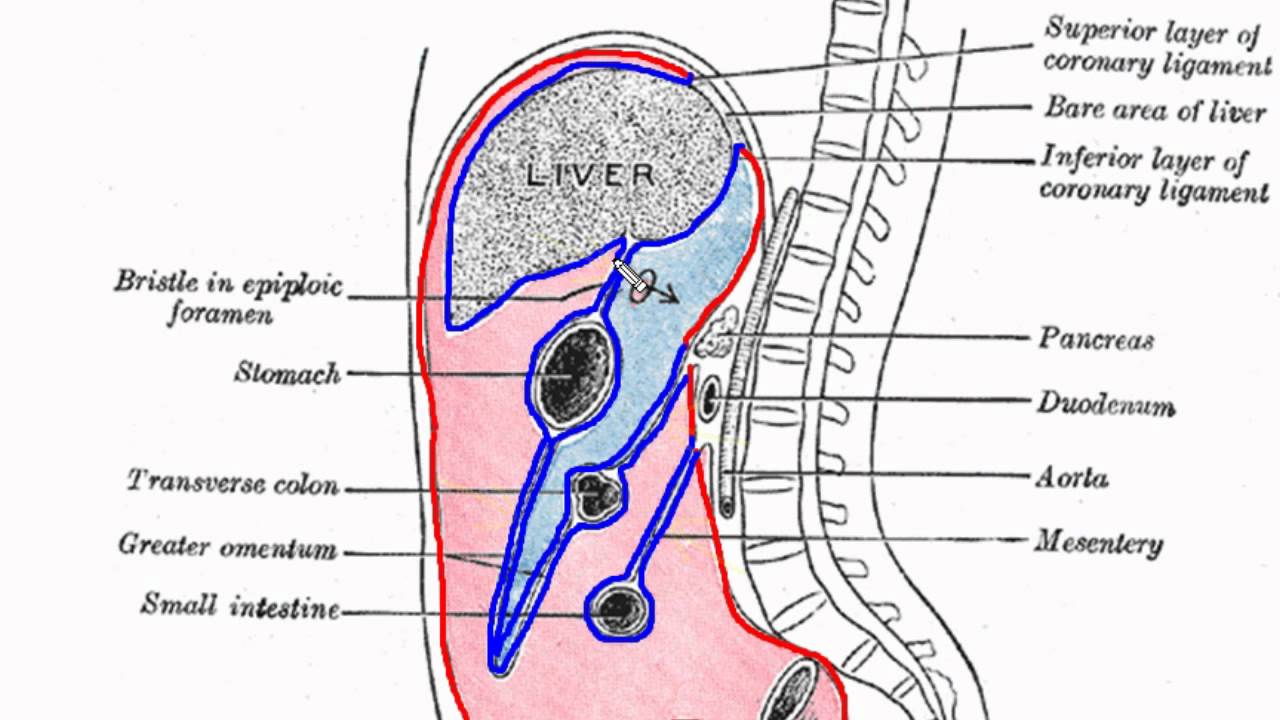 Peritoneal Cavity Part 1 Anatomy Tutorial
Peritoneal Cavity Part 1 Anatomy Tutorial
 Comparative Anatomy Veterinary Science Nsf With Alison At
Comparative Anatomy Veterinary Science Nsf With Alison At
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/612/MokDVBvJOwNquX1UXx8JbA_overview-of-the-mesentery_english.jpg) Greater And Lesser Omentum Location Anatomy Function Kenhub
Greater And Lesser Omentum Location Anatomy Function Kenhub
Peritoneum Mesentery And Omentum
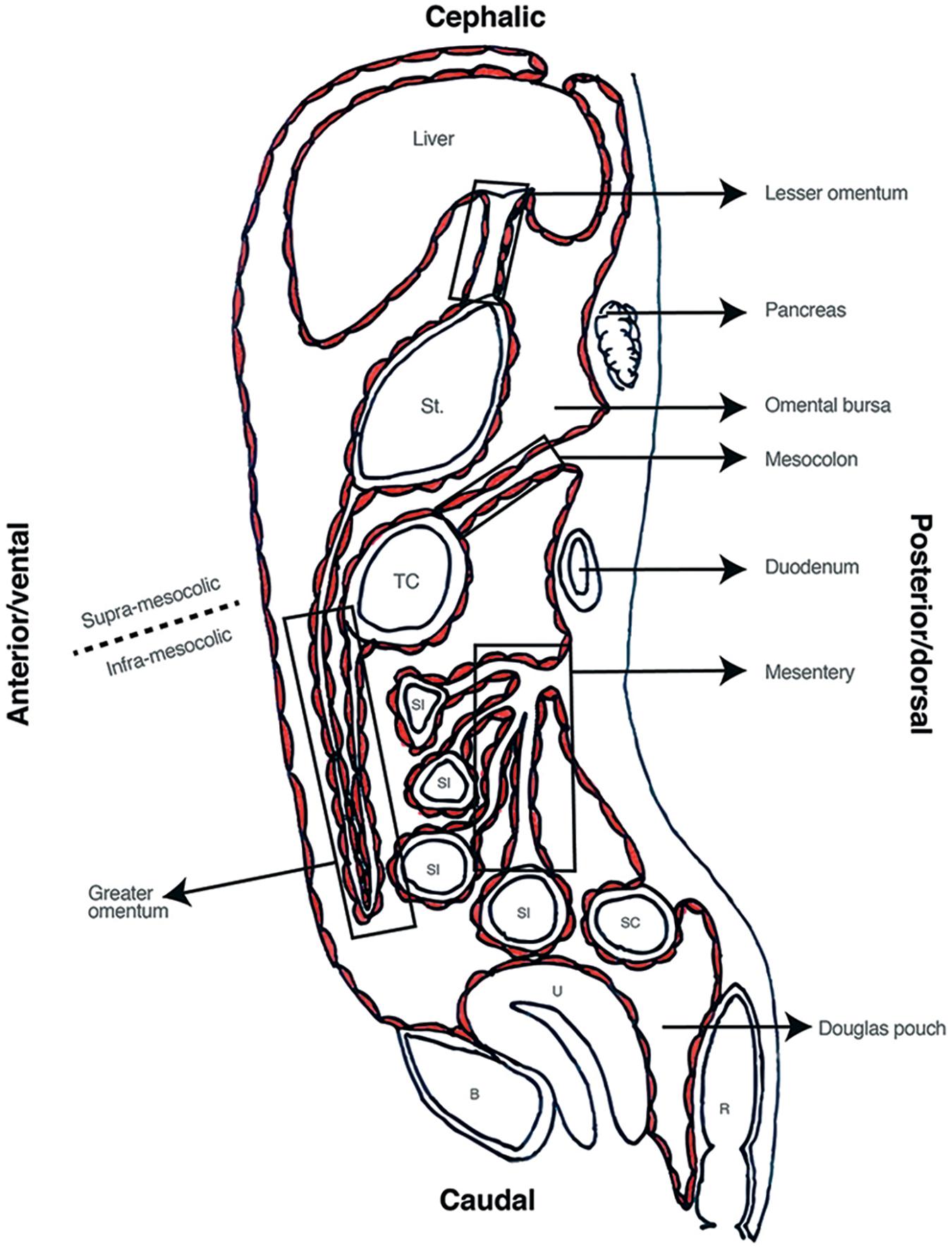 Frontiers The Peritoneum Beyond The Tissue A Review
Frontiers The Peritoneum Beyond The Tissue A Review
 Greater Omentum Clinical Anatomy Associates Inc
Greater Omentum Clinical Anatomy Associates Inc
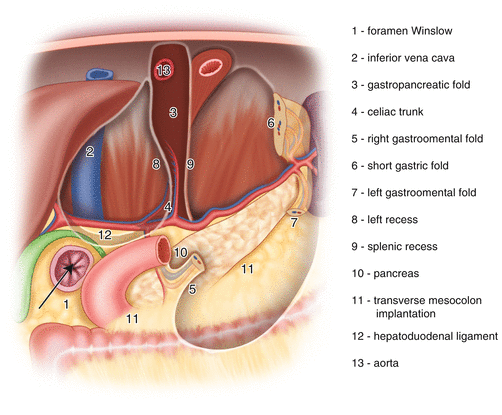 Surgical Anatomy Of The Omental Bursa Springerlink
Surgical Anatomy Of The Omental Bursa Springerlink
Gastrointestinal System Where Gists Form With Greater
 Abdominal Wall Omentum Mesentery And Retroperitoneum
Abdominal Wall Omentum Mesentery And Retroperitoneum
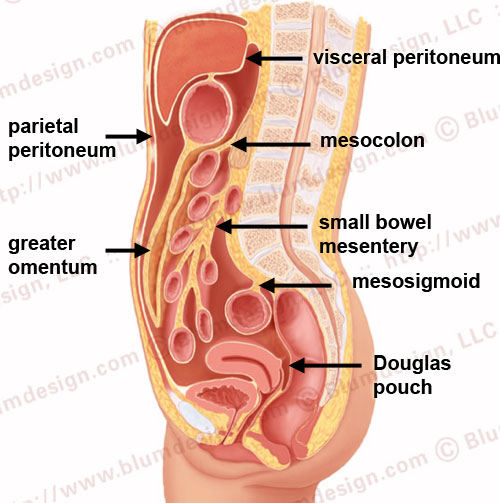 The Radiology Assistant Peritoneum And Mesentery Part I
The Radiology Assistant Peritoneum And Mesentery Part I
 Omental Flap Master Techniques In Surgery Thoracic
Omental Flap Master Techniques In Surgery Thoracic
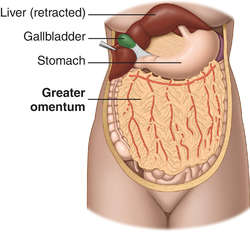 Omenta Definition Of Omenta By Medical Dictionary
Omenta Definition Of Omenta By Medical Dictionary
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/greater-omentum-7/f1Uoo50ZxkTPScKy1jiASA_Greater_Omentum.png) Greater And Lesser Omentum Location Anatomy Function Kenhub
Greater And Lesser Omentum Location Anatomy Function Kenhub
 Omentum Development Animation Acland S Video Atlas Of
Omentum Development Animation Acland S Video Atlas Of
 Omentum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Omentum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12400/the-greater-omentum_english.jpg) Greater And Lesser Omentum Location Anatomy Function Kenhub
Greater And Lesser Omentum Location Anatomy Function Kenhub



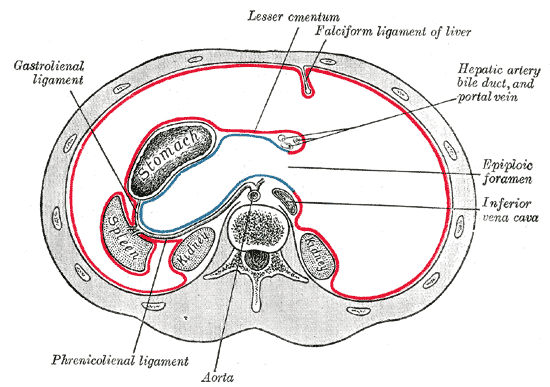

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Omentum"
Posting Komentar