Anatomy Of The Patella
The front and back surfaces are joined by a thin margin and towards centre by a thicker margin. The height of the patella influences pf joint pressure as well.
 Patella Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Patella Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
The patella is a thick flat triangular bone with its apex pointing downwards.
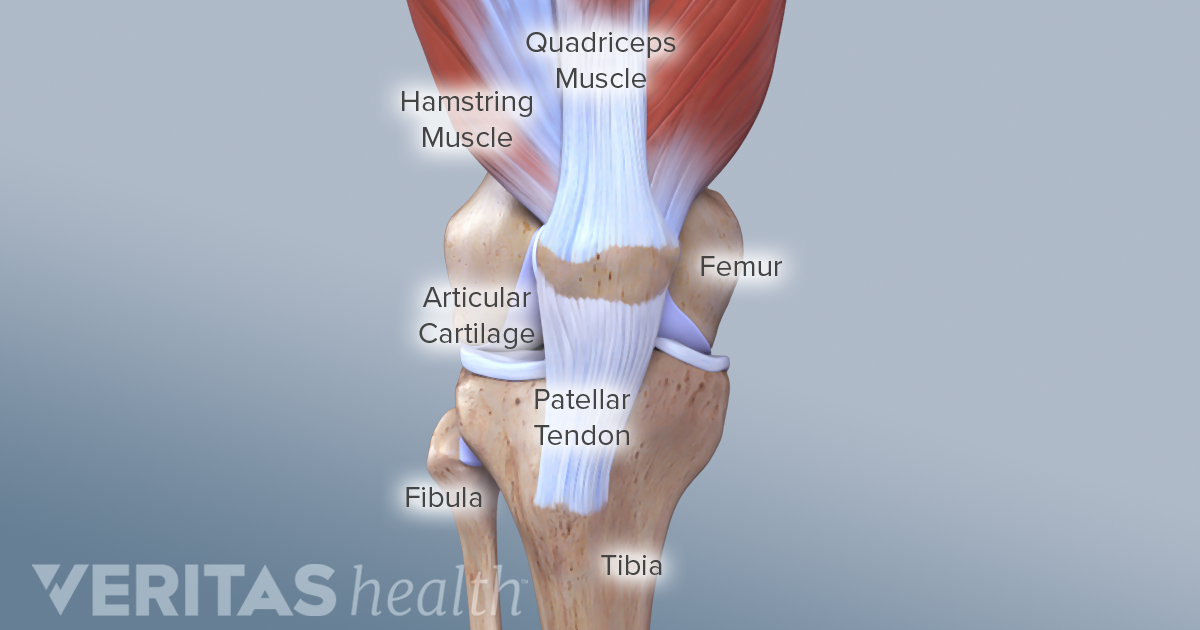
Anatomy of the patella. The patella is commonly referred to as the kneecap. It is a small freestanding bone that rests between the femur thighbone and tibia shinbone. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body and it lies within the quadriceps tendon in front of the knee joint.
The anterior surface is rough and nonarticular. The patella protects the knee joint. The patella is a sesamoid bone roughly triangular in shape with the apex of the patella facing downwards.
The patella is the technical name for the kneecap the triangular shaped bone at the front of the knee joint. The apex is the most inferior lowest part of the patella. Determination of side of patella a triangular with the apex of the triangle directed downwards.
It is pointed in shape and gives attachment to the patellar ligament. It attaches superiorly to the quadriceps tendon and inferiorly to the patellar ligament. The bone originates from multiple ossification centres that develop from the ages of three to six which rapidly coalesce.
The patella bone is part of the appendicular skeleton and it gets its name from a latin word that means shallow pan or dish. The femur has a dedicated groove along which the kneecap slides. The patella knee cap is located at the front of the knee joint within the patellofemoral groove of the femur.
As a form of protection both bones also contain cartilage strong flexible tissue in the areas near the patella. Patella anatomy in this anatomy lesson im going to cover the patella bone also known as the kneecap. The patella is held in place by muscles the lower end of which surrounds the patella and is then attached to the upper part of the tibia shin by patellar tendons.
This pressure is in fact increased at high degrees of flexion and reduced near full extension in cases of patella alta while the opposite behavior occurs in the presence of normal patellar height 4. The upper three fourths of the posterior surface is smooth and articular.
 Patella Tendon Rupture Core Em
Patella Tendon Rupture Core Em
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/patellar-ligament/GuoCCEMCN4CMLXhBgIyuAQ_Ligamentum_patellae_02.png) Patella Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Patella Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Anatomy And Biomechanics Of The Patella
 Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Conditions Treatments
Knee Human Anatomy Function Parts Conditions Treatments
 Knee Patella Instability Relevant Anatomy And Function
Knee Patella Instability Relevant Anatomy And Function
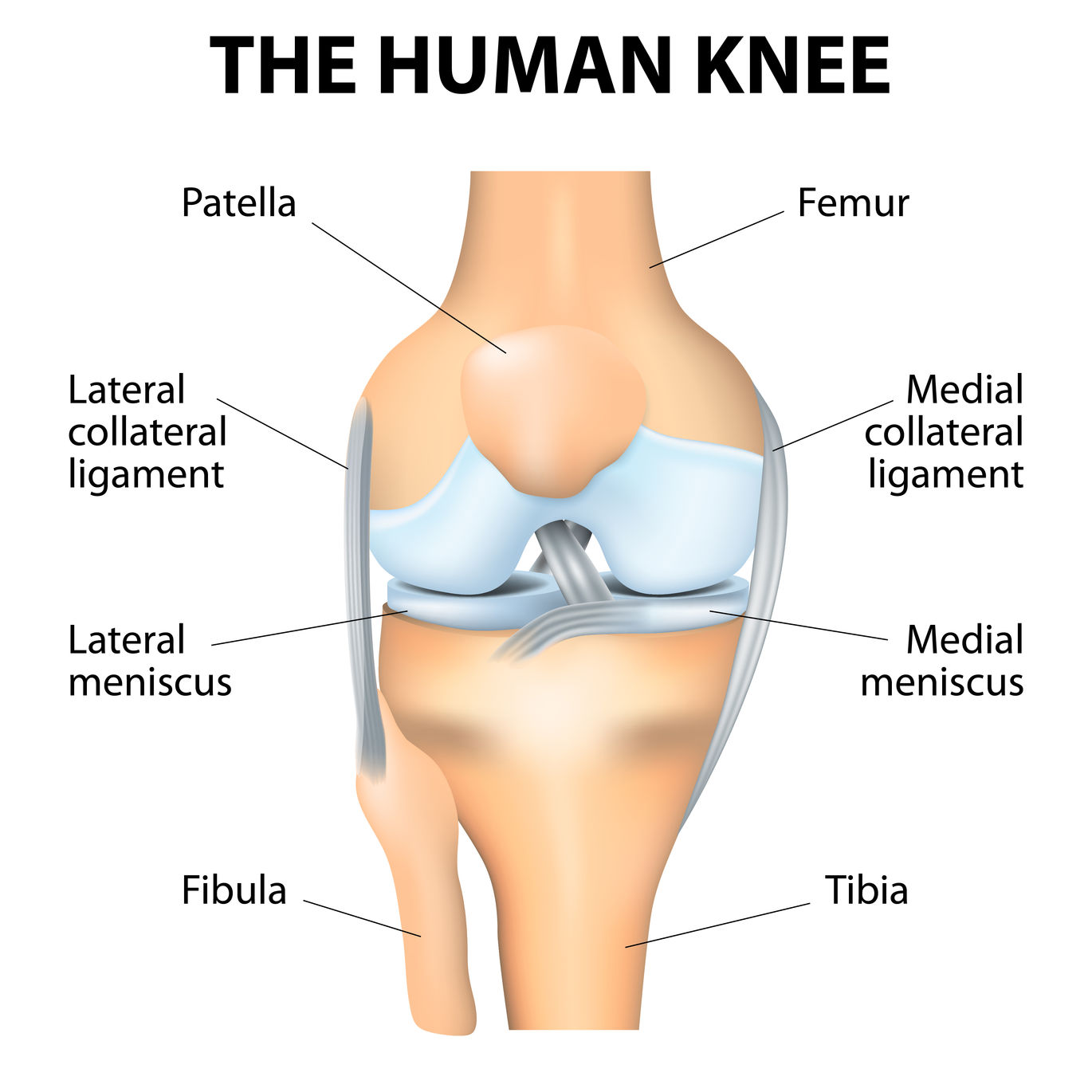 Patellar Instability Anatomy And Causes Jeffrey H Berg
Patellar Instability Anatomy And Causes Jeffrey H Berg
 Knee Injuries For Parents Nemours Kidshealth
Knee Injuries For Parents Nemours Kidshealth
 Amazon Com Semtomn Canvas Wall Art Print Patella Knee Joint
Amazon Com Semtomn Canvas Wall Art Print Patella Knee Joint
 Patella Approach Mid Axial Longitudinal Approach Ao
Patella Approach Mid Axial Longitudinal Approach Ao
 The Knee Anatomy Injuries Treatment And Rehabilitation
The Knee Anatomy Injuries Treatment And Rehabilitation
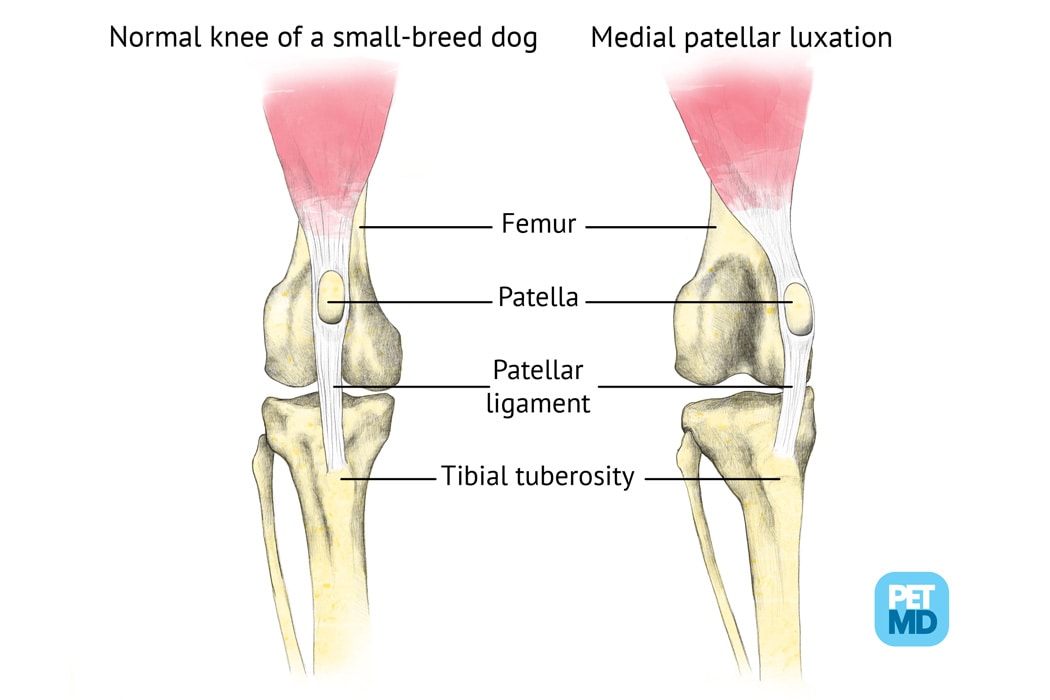 Patellar Luxation In Dogs Medical Diagram
Patellar Luxation In Dogs Medical Diagram
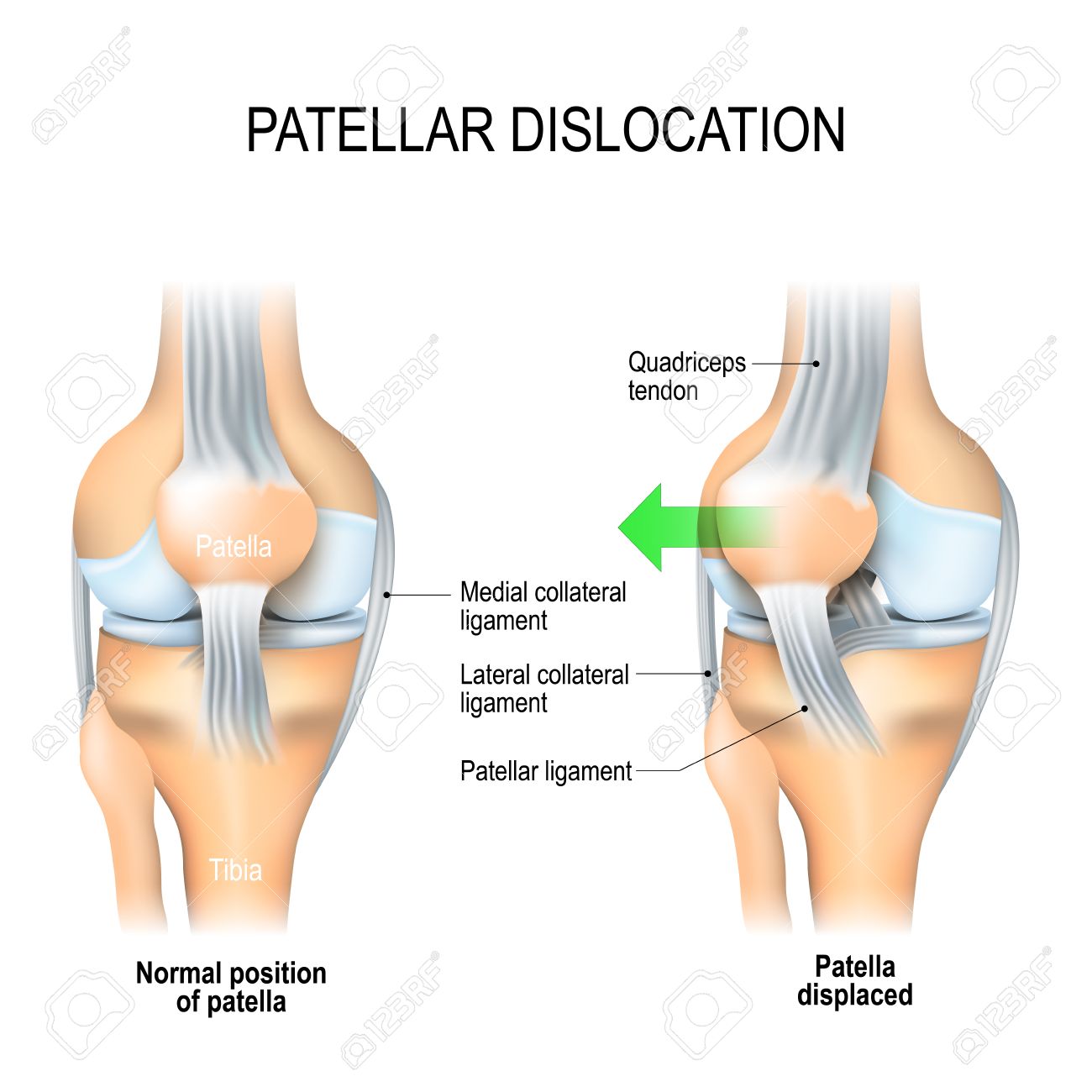 Patellar Dislocation Normal Position Of Kneecap And Patella
Patellar Dislocation Normal Position Of Kneecap And Patella
 Knee Pain Due To Patellofemoral Disorders Treatments Hss
Knee Pain Due To Patellofemoral Disorders Treatments Hss
 The Patella Anatomy Of The Patella Physiology Of The
The Patella Anatomy Of The Patella Physiology Of The
 Basic Anatomy Of The Patella Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Basic Anatomy Of The Patella Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
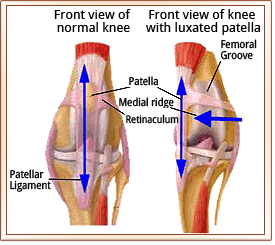 Patellar Luxation Metropolitan Veterinary Associates
Patellar Luxation Metropolitan Veterinary Associates
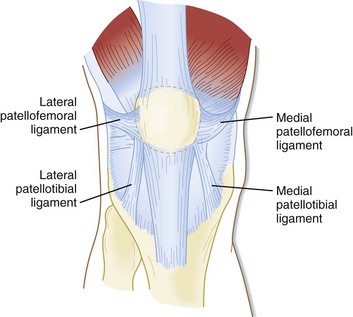 Patellofemoral Joint Physiopedia
Patellofemoral Joint Physiopedia
 Patellofemoral Joint An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Patellofemoral Joint An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
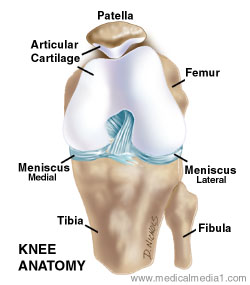 Anatomy Of The Knee Joint Paley Orthopedic Spine Institute
Anatomy Of The Knee Joint Paley Orthopedic Spine Institute
:watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/patella-5/dDgJWgQNyzceGp9ye8CfmA_Patella_01.png) Patella Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Patella Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Functional Anatomy Of The Knee Movement And Stability
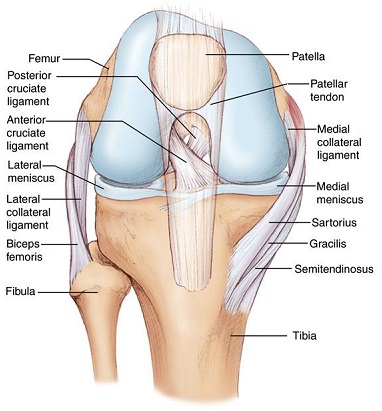 Knee Surgeon Chicago Prp Treatment Chicago Patellar
Knee Surgeon Chicago Prp Treatment Chicago Patellar
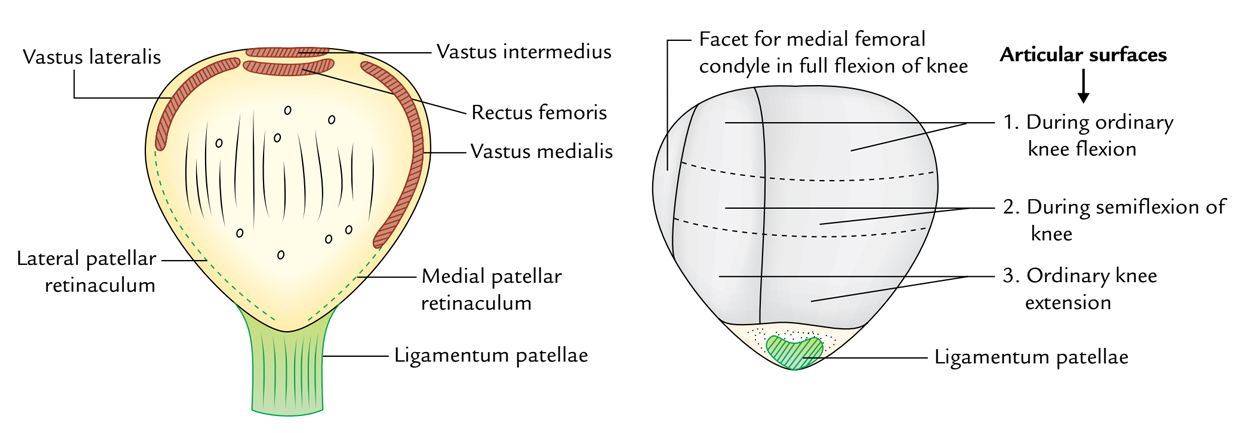 Easy Notes On Patella Knee Cap Learn In Just 3 Minutes
Easy Notes On Patella Knee Cap Learn In Just 3 Minutes



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of The Patella"
Posting Komentar