Fatigue Definition Anatomy
Fatigue is a symptom of another disease or condition. Impairment of muscle force production or of shortening speed resulting from repeated andor prolonged activity.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/weird-ms-symptoms-and-phenomena-julies-list-2440790_v4-35a80bda8cf646028103680107dfd7a6.png) Multiple Sclerosis Signs Symptoms And Complications
Multiple Sclerosis Signs Symptoms And Complications
The fatigue may be partial or complete.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/weird-ms-symptoms-and-phenomena-julies-list-2440790_v4-35a80bda8cf646028103680107dfd7a6.png)
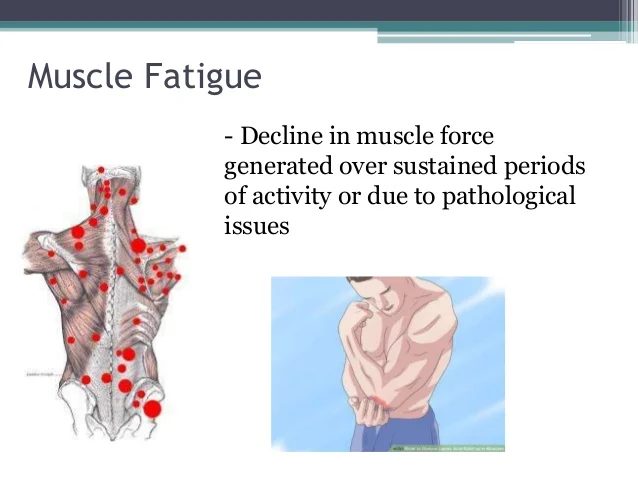
Fatigue definition anatomy. Contraction produces tension the force exerted on the load or object to be moved. Physical fatigue is the transient inability of muscles to maintain optimal physical performance and is made more severe by intense physical exercise. Same principles apply to contraction of a single fiber and a whole muscle.
Fatigue is a normal reaction to intense physical exertion emotional strain or lack of rest. Exhaustion of the energy supply to the muscles of the body however is not an invariable precursor. It may be a symptom of poor physical condition a specific disease or oncoming disease or severe emotional stress.
Sometimes fatigue is psychological in origin. Muscle fatigue defined as the reduced ability to produce muscle tension caused by a decrease in glycogen stores primary cause during excessive exercise. Mental fatigue is a transien.
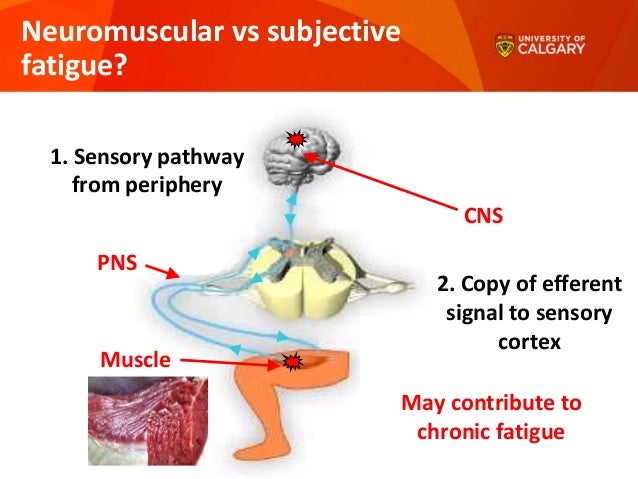
A person who has fatigue feels weak is constantly tired and lacks energy. It is a normal phenomenon if it follows prolonged physical or mental activity and resolves completely with rest. Causes of musle fatigue problems of excitation at the neuromuscular junction insufficient free ca2 at neuromuscular junction.
Such feelings may be generated by muscular effort. Muscle fatigue and oxygen deficit. Start studying human anatomy chapter 6.
Fatigue specific form of human inadequacy in which the individual experiences an aversion to exertion and feels unable to carry on. Synaptic fatigue or short term synaptic depression is an activity dependent form of short term synaptic plasticity that results in the temporary inability of neurons to fire and therefore transmit an input signal. It may be a symptom of one of many medical conditions if it prolonged severe progressive or occurs without provocation.
Contraction doesnt always shorten a muscle. There may be other associated symptoms related to the underlying cause of the chronic fatigue. When it is not relieved by rest it may have a more serious origin.
The reduced capacity of a muscle to perform work as a result of repeated contractions and accumulation of lactic acid in anaerobic cell respiration. Fatigue is a subjective feeling of tiredness. It results when muscle activity exceeds tissue substrate and oxygenation capacity.
Feelings of fatigue may also stem from pain anxiety fear or boredom. Physiology a condition of the muscle in which its capacity to produce maximum voluntary action or to perform a series of repetitive actions is reduced. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
It may be sudden or gradual in onset. Force of duration of contraction vary in response to stimuli of different frequencies and intensities.
 Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
Muscular System Muscles Of The Human Body
 Mechanics Of Skeletal Muscle Ppt Download
Mechanics Of Skeletal Muscle Ppt Download
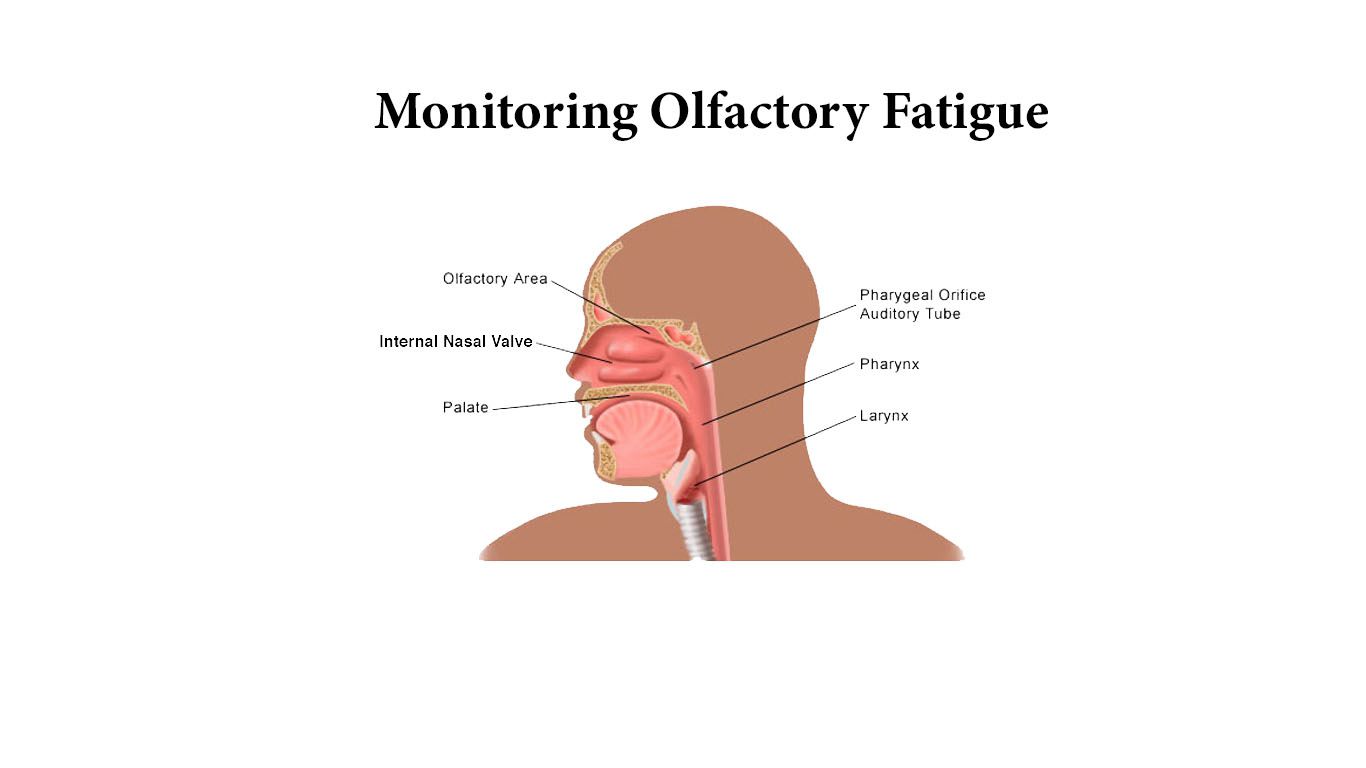 What Is Olfactory Fatigue Do You Have It Chemdaq
What Is Olfactory Fatigue Do You Have It Chemdaq
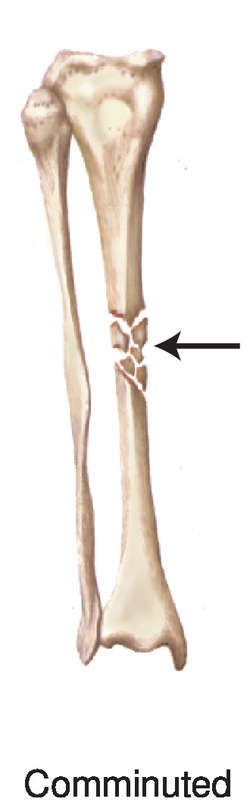 Fatigue Fracture Definition Of Fatigue Fracture By Medical
Fatigue Fracture Definition Of Fatigue Fracture By Medical
 The Effects Of Multiple Sclerosis On Your Body
The Effects Of Multiple Sclerosis On Your Body
 Experiment Emgs During Muscle Fatigue
Experiment Emgs During Muscle Fatigue
 What Are The First Signs Of Fatigue Causes Treatment
What Are The First Signs Of Fatigue Causes Treatment
 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
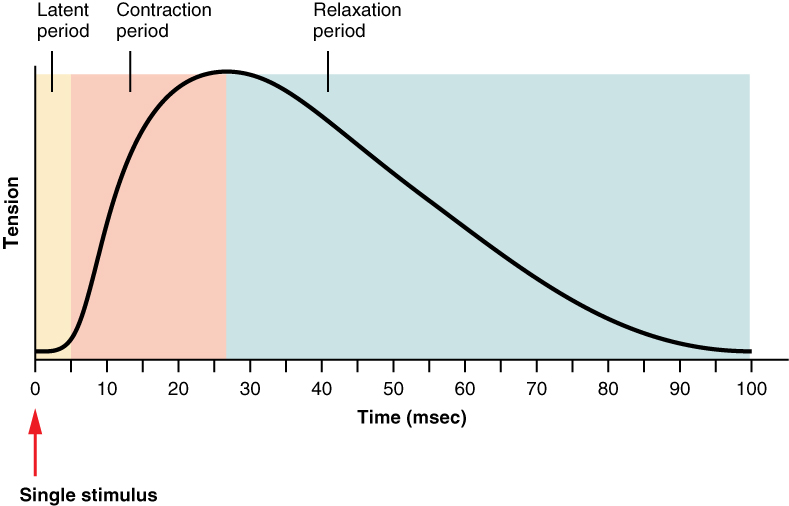 Motor Units And Muscle Twitches
Motor Units And Muscle Twitches
 Experiment Emgs During Muscle Fatigue
Experiment Emgs During Muscle Fatigue

 Trauma And Me Cfs How Understanding The Science Is Making
Trauma And Me Cfs How Understanding The Science Is Making
 Skeletal Muscle Mechanics Dr Abdelrahman Mustafa Lectuerer
Skeletal Muscle Mechanics Dr Abdelrahman Mustafa Lectuerer
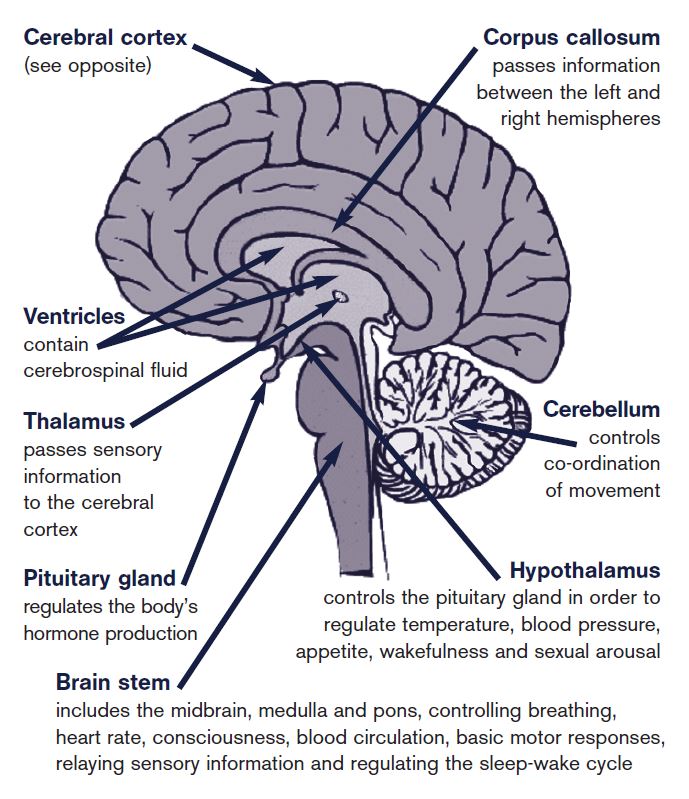
 Weakness Brain Spinal Cord And Nerve Disorders Merck
Weakness Brain Spinal Cord And Nerve Disorders Merck
 24 Signs You Have Chronic Fatigue And Aren T Just Tired
24 Signs You Have Chronic Fatigue And Aren T Just Tired
 The Definition And Causes Of Musculoskeletal Disorders
The Definition And Causes Of Musculoskeletal Disorders
 Pathophysiological And Cognitive Mechanisms Of Fatigue In
Pathophysiological And Cognitive Mechanisms Of Fatigue In
 Chapter 7 Fatigue The Patient History An Evidence Based
Chapter 7 Fatigue The Patient History An Evidence Based
 Nursing Care Plan And Diagnosis Fatigue
Nursing Care Plan And Diagnosis Fatigue
 The Muscles You Never Think About Until They Stop Working
The Muscles You Never Think About Until They Stop Working
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/spine-nerves-illustration-57b389055f9b58b5c2e113c1.jpg) Central Sensitization In Fibromyalgia And Cfs
Central Sensitization In Fibromyalgia And Cfs


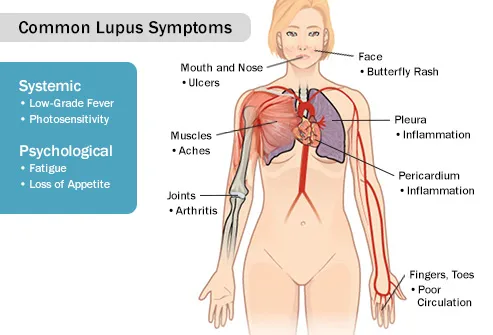


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Fatigue Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar