Agonist Definition Anatomy
Another example is the dumbbell curl at the elbow. Drug a substance that is used as a medicine or narcotic.
 Agonist Vs Antagonist Drugs December 2019
Agonist Vs Antagonist Drugs December 2019
It is the group of muscles that contract to move a.
Agonist definition anatomy. 111 describe the roles of agonists antagonists and synergists interactions of skeletal muscles in the body the moveable end of the muscle that attaches to the bone being pulled is called the muscles insertion and the end of the muscle attached to a fixed stabilized bone is called the origin. Agonists are also interchangeably referred to as prime movers since they are the muscles considered primarily responsible for generating or controlling a specific movement. The muscle that contracts while the other relaxes.
However the term is often defined incorrectly to mean all the muscles that have a role in producing a movement. Hip flexion keeps the upper body from falling backwards when standing erect. Because of this agonists are known as the prime movers.
The biceps and triceps are antagonistic muscles. By this definition stabilizers neutralizers and fixators are also agonists. Agonist definition a person engaged in a contest conflict struggle etc especially the protagonist in a literary work.
Agonist a muscle that contracts while another relaxes. Agonist agonists plural someone involved in a contest or battle as in an agon. It be an or a particular receptor promoting a receptor mediated biological response by competing substance or substance at receptor.
The agonist muscle group is also referred to as the prime mover because it is the muscle group that provides the main pull to create a movement. Biochemistry a molecule that can combine with a receptor on a cell to produce a physiological reaction. An agonist is a muscle that is capable of increasing torque in the direction of a limbs movement and thus produce a concentric action.
When bending the elbow the biceps are the agonist. A chemical in on or receptors receptors by structural of receptors ligand s. Antagonistic muscle physiology a muscle that opposes the action of another.
The agonist in a movement is the muscle s that provides the major force to complete the movement. In the bicep curl which produces flexion at the elbow the biceps muscle is the agonist as seen in the image below. The elbow flexor group is the agonist shortening during the lifting phase elbow flexion.
Anatomy a a particular movement to a of movement in a by contracting.
 11 The Muscular System Objectives Human Anatomy Physiolgoy
11 The Muscular System Objectives Human Anatomy Physiolgoy
 Gastrocnemius Muscle Anatomy Britannica
Gastrocnemius Muscle Anatomy Britannica
 Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Agonists For Endometriosis Nejm
Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone Agonists For Endometriosis Nejm
 Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Physiopedia
Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Physiopedia
 Antagonist Muscle Definition Examples
Antagonist Muscle Definition Examples
 Adrenergic Agonists Antagonists
Adrenergic Agonists Antagonists
 Muscles Of The Upper Arm Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab
Muscles Of The Upper Arm Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab

 Receptor Theory Basic Concepts In Pharmacology What You
Receptor Theory Basic Concepts In Pharmacology What You
 Irene S Myomassology Institute Anatomy Lecture Review Guide
Irene S Myomassology Institute Anatomy Lecture Review Guide
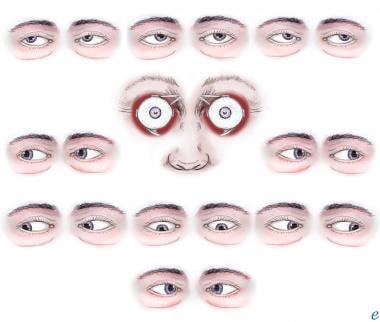 Extraocular Muscle Actions Eye Movements Rectus Muscles
Extraocular Muscle Actions Eye Movements Rectus Muscles
 Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Online Student
Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Online Student

Competitive And Non Competitive Antagonists Deranged
 Anatomical Terms Of Muscle Wikipedia
Anatomical Terms Of Muscle Wikipedia
 Extraocular Muscles And Movements
Extraocular Muscles And Movements
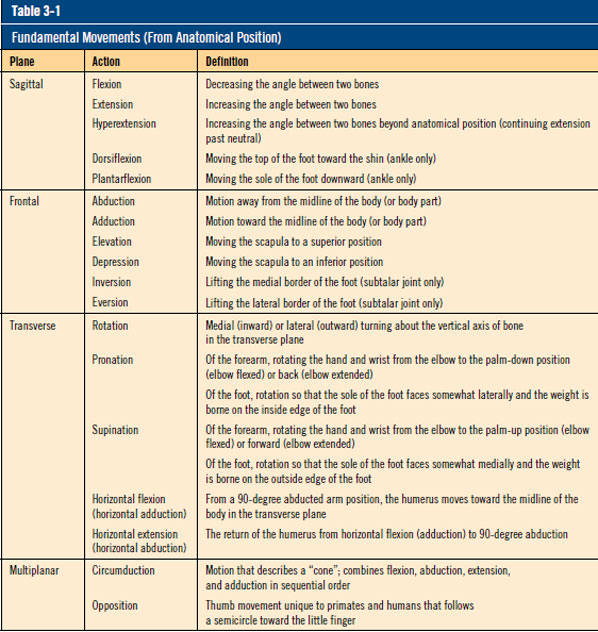 Ace S Essentials Of Exercise Science Helper
Ace S Essentials Of Exercise Science Helper
 Flexion And Extension Record Your Antagonistic Muscles
Flexion And Extension Record Your Antagonistic Muscles
 Agonist Antagonist Muscle Groups Illustration Skeletal
Agonist Antagonist Muscle Groups Illustration Skeletal





Belum ada Komentar untuk "Agonist Definition Anatomy"
Posting Komentar