Anatomy Of Uterus And Ovary
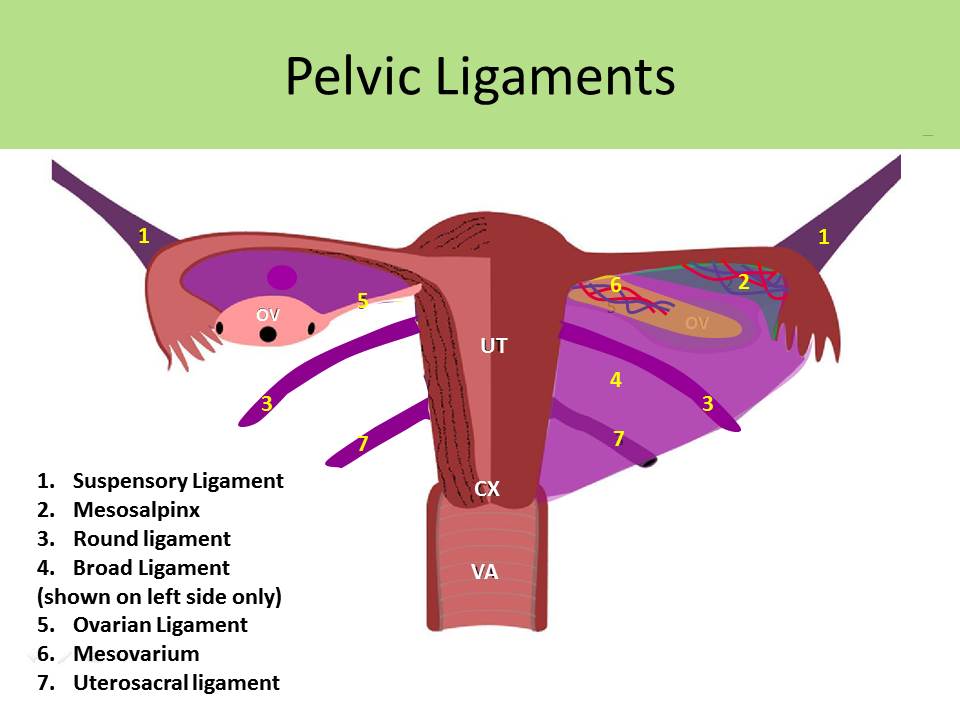
The uterine tubes and the ovaries. Cornu of the uterus by the ovarian ligament the suspensory ligament attaches the ovary to the pelvic wall and carries within its folds the main portion of the ovarian vessels and nerves.
 Female Reproductive Anatomy Reproductive Medbullets Step 1
Female Reproductive Anatomy Reproductive Medbullets Step 1
The ovaries in turn are stabilized by a thin fibrous connection with the outside of the uterus.

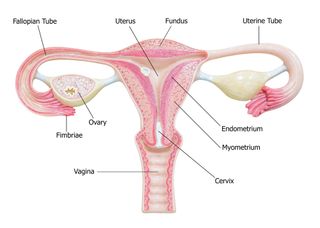
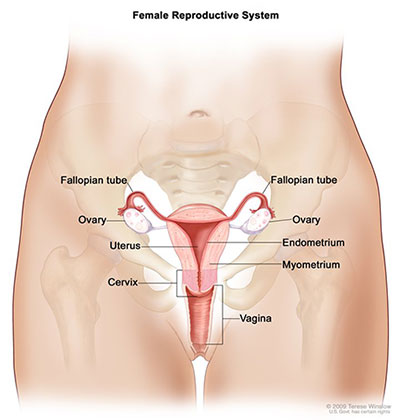
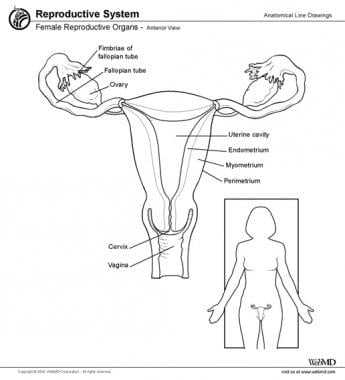
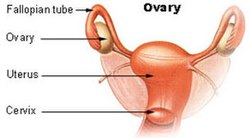
Anatomy of uterus and ovary. The upper part of the uterus above the insertion of the fallopian tubes is called the fundus. These organs work together to produce female sex hormones produce and develop ova egg cells and support the development of a fetus during pregnancy. Anatomy of ovaries the ovaries are the two female reproductive glands which are solid pinkish grey and almold shape entities situated on either side of the uterus and are connected to the uterus by the fallopian tube fig.
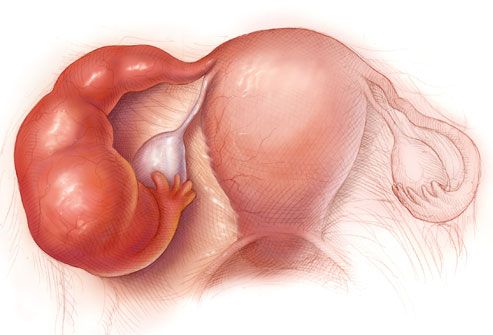
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized ovum implants outside of the uterus usually within the walls of the uterine tubes. The ovaries are paired oval organs attached to the posterior surface of the broad ligament of the uterus by the mesovarium a fold of peritoneum continuous with the outer surface of the ovaries. Neurovascular structures enter the hilum of the ovary via the mesovarium.
Symptoms include abnormal vaginal bleeding amenorrhea breast tenderness lower back pain and pain or pelvic cramps. The suspensory ligament of the ovary infundibular pelvic ligament attaches the ovary to the pelvic sidewall. Located around and on the periphery of the ovarian follicle.
The mesosalpinx covers the fallopian tubes. The intramural part opens into the uterine wall. The uterus is a fibromuscular organ that can be divided into the upper muscular uterine corpus and the lower fibrous cervix which extends into the vagina.
Journey of an egg from the ovaries given the anatomy and location of the ovaries it is easy to imagine the processes of ovulation and reproduction. It is the inferior most extension of the parietal peritoneum and has three divisions based on location. The lateral most aspect of the broad ligament is the mesovarium and overlies the ovaries.
The uterus and ovaries are the most vital organs of the female reproductive system. Help begin and control follicle development by influencing hormone production. The ovarian ligament connects the uterus and ovary.
The posterior portion of the broad ligament forms the mesovarium which supports the ovary and houses its arterial and venous supply. Specifically these cells secrete androgens which are converted into estrogen by the granulosa cells. The broad ligament overlies the uterus fallopian tubes and ovaries.
The right ovary tends to be slightly larger than the left ones.
 Ovaries Facts Function Disease Live Science
Ovaries Facts Function Disease Live Science
 Ultrasound Registry Review General Information
Ultrasound Registry Review General Information
 Ultrasound Registry Review General Information
Ultrasound Registry Review General Information
Female Reproductive System Cleveland Clinic
 07031 01x Normal Anatomy Of The Uterus Anatomy Exhibits
07031 01x Normal Anatomy Of The Uterus Anatomy Exhibits
 The Female Reproductive System Quiz Proprofs Quiz
The Female Reproductive System Quiz Proprofs Quiz
 Benign Uterine Growths Symptoms Treatments Causes
Benign Uterine Growths Symptoms Treatments Causes
 Pelvic Floor Anatomy With Uterus Anatomy Images Medical
Pelvic Floor Anatomy With Uterus Anatomy Images Medical
 The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
 Female Reproductive Anatomy Reproductive Medbullets Step 1
Female Reproductive Anatomy Reproductive Medbullets Step 1
 Pathological Uterus And Ovary Anatomical Model Human Female
Pathological Uterus And Ovary Anatomical Model Human Female
 Seer Training Salpingo Ovarian Peritoneal Functional Anatomy
Seer Training Salpingo Ovarian Peritoneal Functional Anatomy
 Pelvic Uterine Pain 18 Possible Causes Of Pelvic Pain In
Pelvic Uterine Pain 18 Possible Causes Of Pelvic Pain In
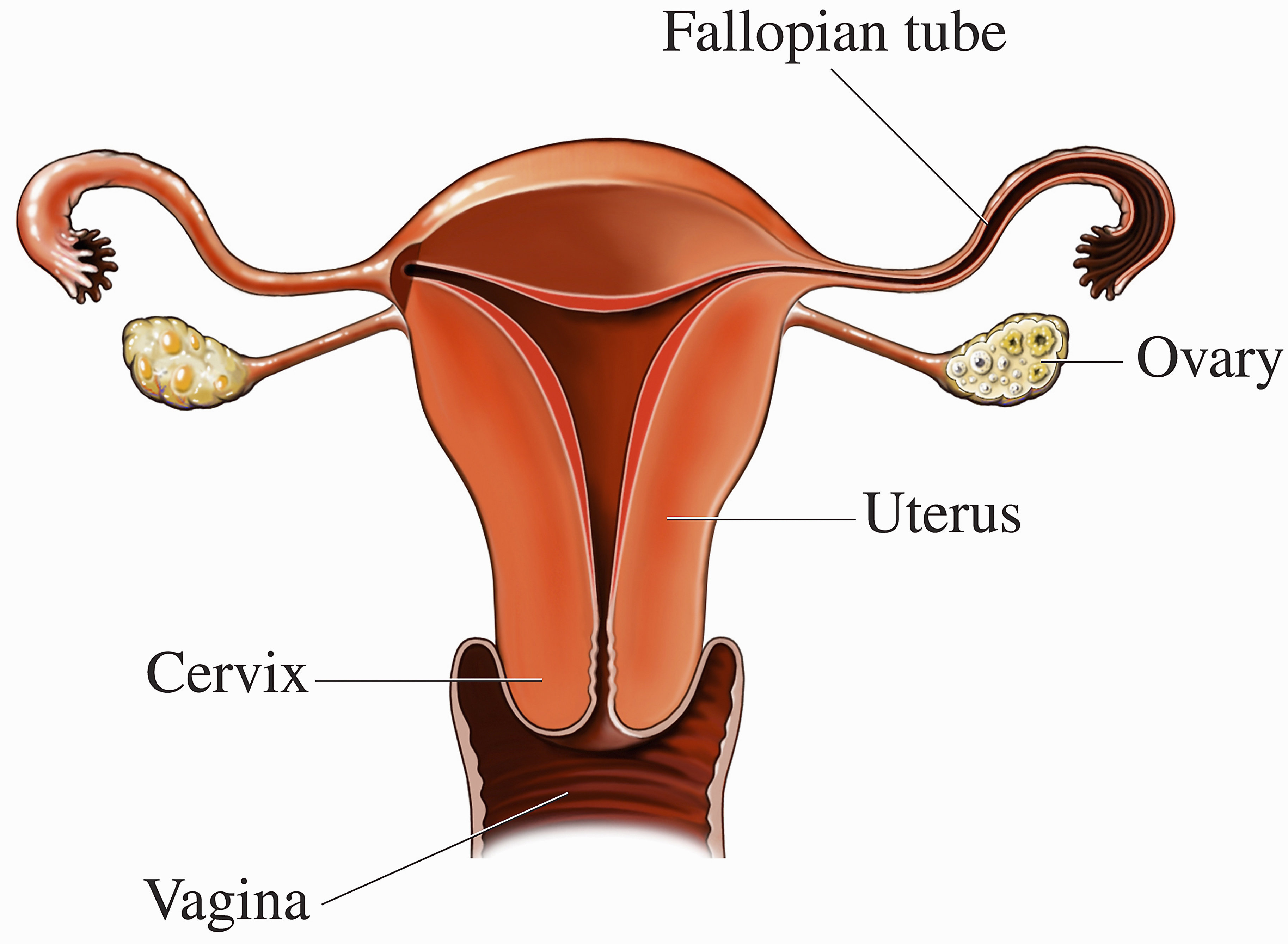 Ovaries You And Your Hormones From The Society For
Ovaries You And Your Hormones From The Society For
 Transvaginal Ultrasound Uses And What To Expect
Transvaginal Ultrasound Uses And What To Expect
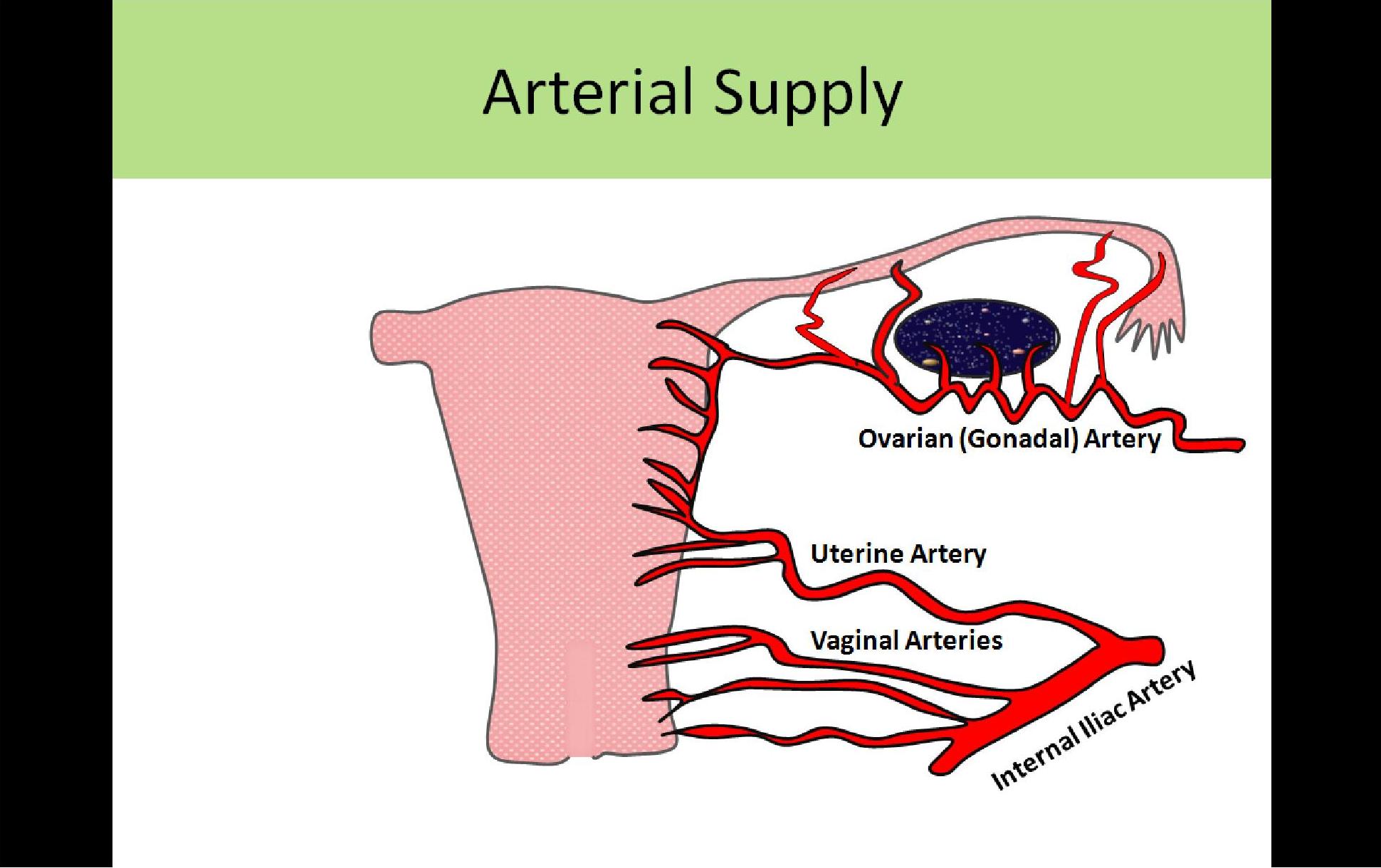 Ultrasound Registry Review General Information
Ultrasound Registry Review General Information
 Uterus And Ovaries Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
Uterus And Ovaries Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
 Fallopian Tube Anatomy Function Britannica
Fallopian Tube Anatomy Function Britannica
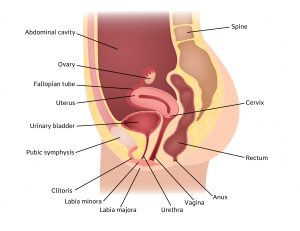 Pelvic And Genital Anatomy Frequently Asked Questions
Pelvic And Genital Anatomy Frequently Asked Questions
 Female Reproductive System Gynecological Medical Banner Woman S
Female Reproductive System Gynecological Medical Banner Woman S
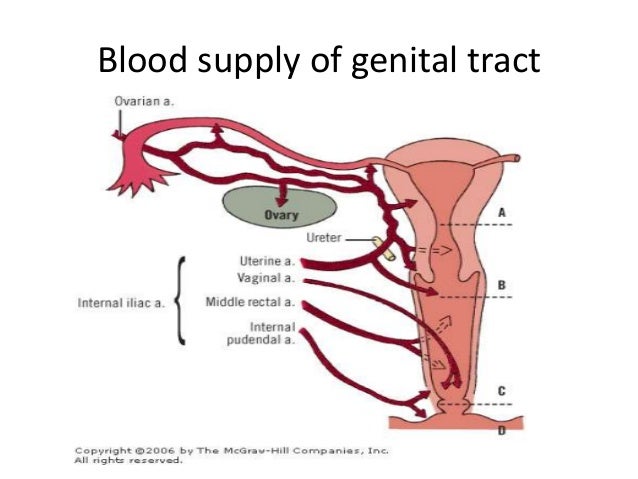
 Uterine Blood Supply Elearning
Uterine Blood Supply Elearning
 Uterus Ovaries And Bladder Posterior Canvas Print
Uterus Ovaries And Bladder Posterior Canvas Print
 Ovarian Low Malignant Potential Tumors Treatment Mhealth Org
Ovarian Low Malignant Potential Tumors Treatment Mhealth Org
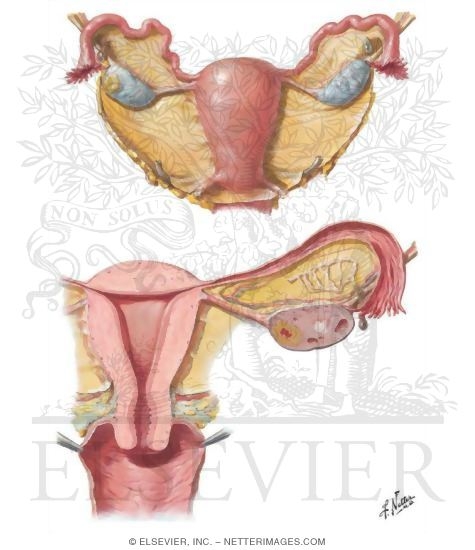 Uterus Ovaries And Uterine Tubes
Uterus Ovaries And Uterine Tubes
 Uterus Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants
Uterus Anatomy Overview Gross Anatomy Natural Variants


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Uterus And Ovary"
Posting Komentar