Meningeal Anatomy
Connected to the dura mater on the side closest to the cns. The meningeal coverings the brain and spinal cord are covered by layers of connective tissue called meninges from the greek word meninx which means membrane.
 Anatomy Of The Brain Protection
Anatomy Of The Brain Protection
On a dry specimen the groove is easy to see.
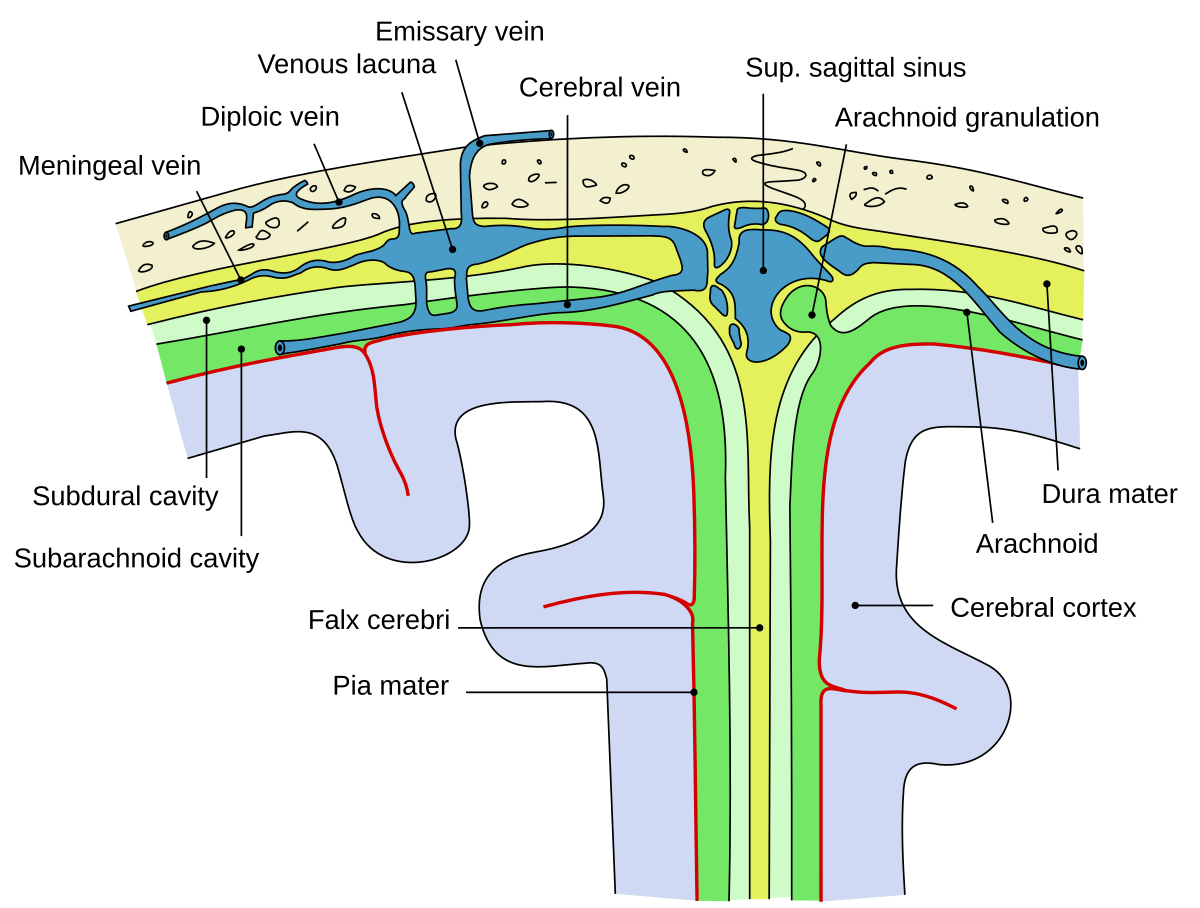
Meningeal anatomy. This middle layer of the meninges connects the dura mater and pia mater. Distally the meninges form a strand of fibrous tissue the filum terminale which attaches to the vertebral bodies of the coccyx. The meningeal layer folds up to form dural infoldings that divide the cranial cavity into different compartments.
It is a very thin membrane composed of fibrous tissue covered on its outer surface by a sheet of flat cells thought to be impermeable to fluid. Cranial meninges spinal meninges. There are three layers to the meninges.
The innermost layer the pia mater hugs the spinal cord and. The meninges refer to the membranous coverings of the brain and spinal cord. The largest infolding the falx cerebri is found in the longitudinal cerebral fissure.
Meninges layers dura mater. It is the meningeal envelope that firmly adheres to the surface of the brain and spinal cord following all of the brains contours the gyri and sulci. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.
The middle meningeal artery runs in a groove on the inside of the cranium. The outermost membrane this is the thickest of the three layers and has both an outer. It acts as an anchor for the spinal cord and meninges.
The meninges is a collective term for the three membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord are are covered in separate articles. It acts as an anchor for the spinal cord and meninges. This can clearly be seen on a lateral skull x ray where it may be mistaken for a fracture of the skull.
The pia mater is the meningeal envelope that firmly adheres to the surface of the brain and spinal cord. There are three layers of meninges known as the dura mater arachnoid mater and pia mater. This infolding separates the occipital lobes of the.
In fishes only a single layer the primitive meninx is present. This outer layer connects the meninges to the skull and vertebral column. This thin inner layer of the meninges is in direct contact with and closely covers.
 Regional Anatomy Meninges At Texas Woman S University
Regional Anatomy Meninges At Texas Woman S University
 Semester 3 A1 Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
Semester 3 A1 Anatomy Flashcards Quizlet
 Advances In Meningeal Immunity Trends In Molecular Medicine
Advances In Meningeal Immunity Trends In Molecular Medicine
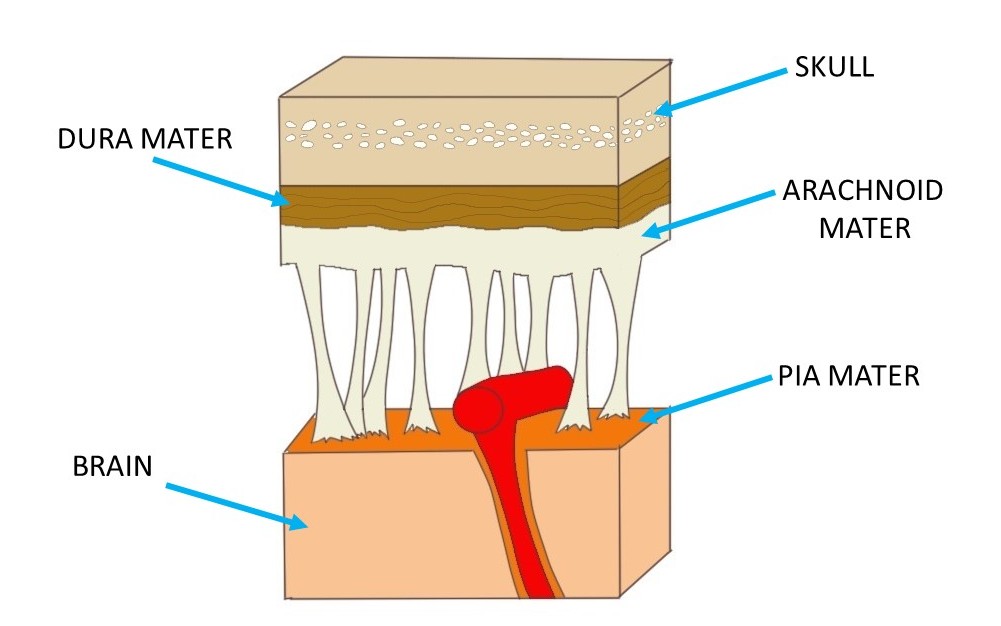 Know Your Brain Meninges Neuroscientifically Challenged
Know Your Brain Meninges Neuroscientifically Challenged
 Humb1004 Study Guide Winter 2018 Final Dural Venous
Humb1004 Study Guide Winter 2018 Final Dural Venous
 Spinal Cord And Meningeal Layers Diagram Quizlet
Spinal Cord And Meningeal Layers Diagram Quizlet
 Scalp Skull And Meninges The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
Scalp Skull And Meninges The Big Picture Gross Anatomy
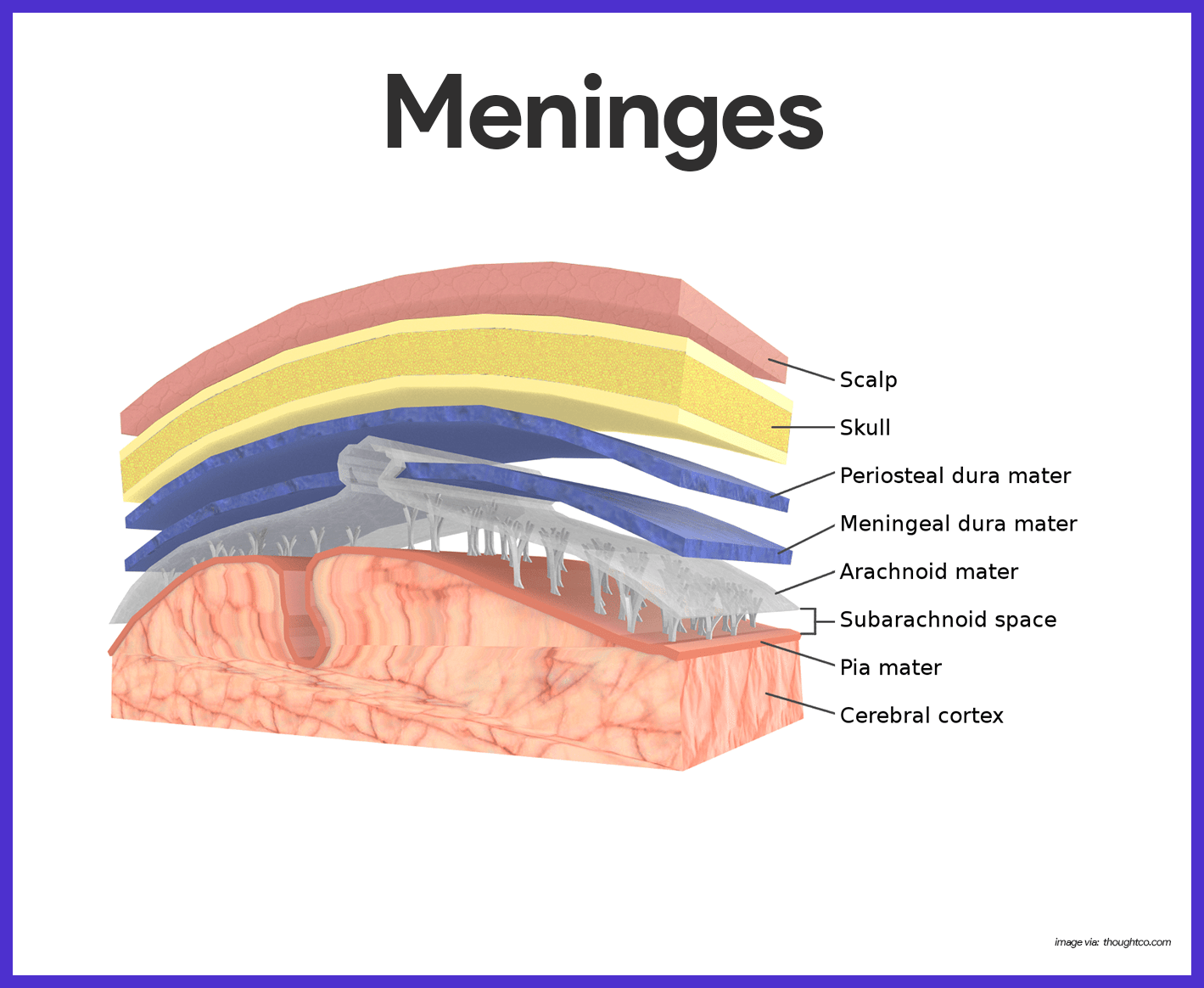 Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
Nervous System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs
 Illustrations Fig 1198 Gray Henry 1918 Anatomy Of The
Illustrations Fig 1198 Gray Henry 1918 Anatomy Of The
 Meningeal Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Meningeal Artery An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/dura-mater/euBIk5FhFHJiCVQaFaXBKA_Dura_mater_01.png) Meninges Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Function
Meninges Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Function
 Significance Of Biological Membranes For Accurate
Significance Of Biological Membranes For Accurate
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/456/lu5kV9M3yLK6FA6RJoGpew_spinal-membranes-and-nerve-roots_english.jpg) Meninges Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Function
Meninges Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Anatomy Function
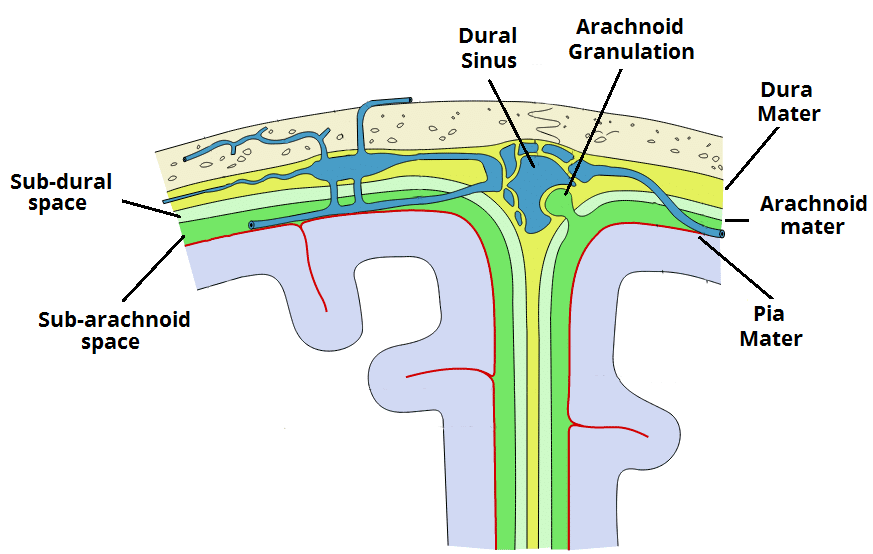 The Meninges Dura Arachnoid Pia Teachmeanatomy
The Meninges Dura Arachnoid Pia Teachmeanatomy
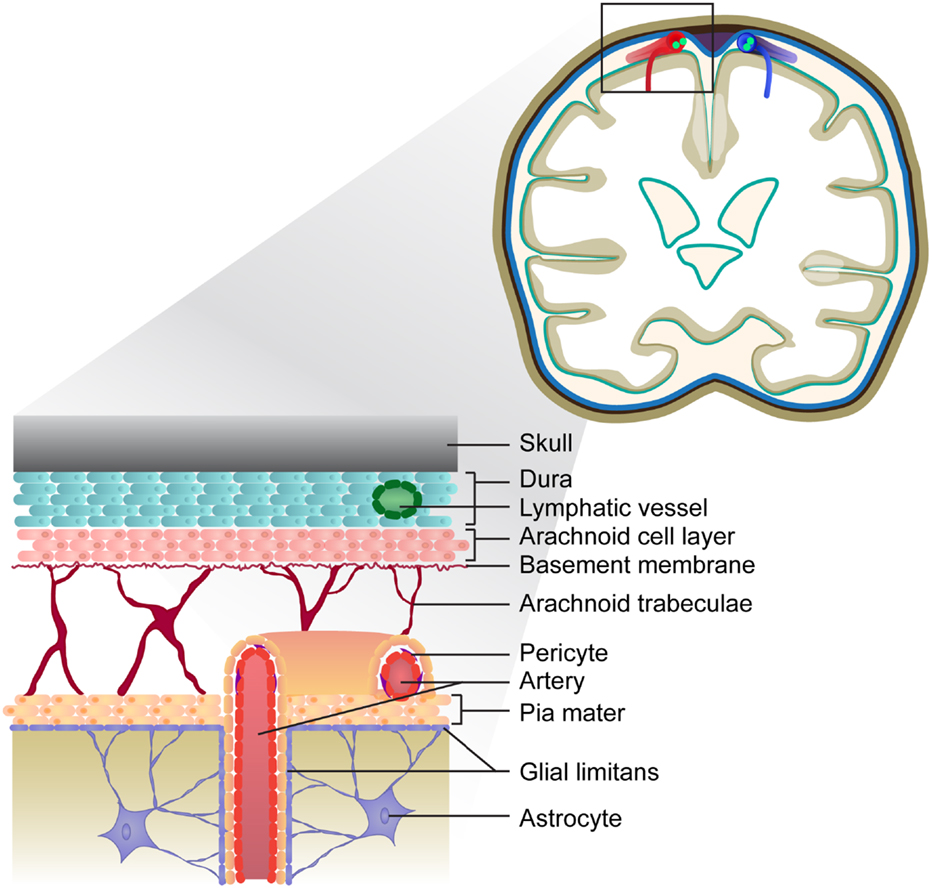 Frontiers Meningeal Tertiary Lymphoid Tissues And Multiple
Frontiers Meningeal Tertiary Lymphoid Tissues And Multiple
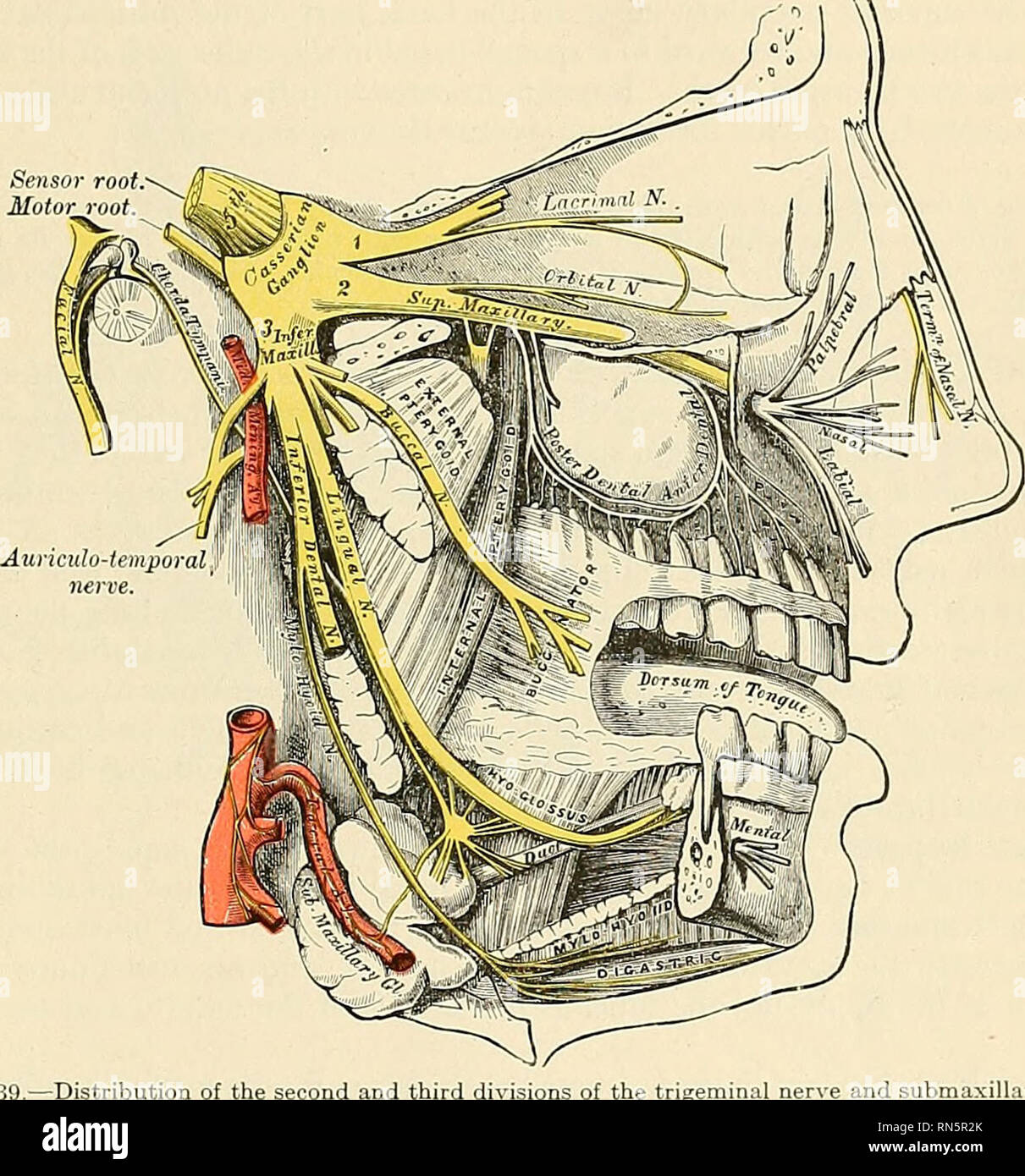 Anatomy Descriptive And Applied Anatomy The Fifth
Anatomy Descriptive And Applied Anatomy The Fifth
The Meninges Treat The Athlete
 Middle Meningeal Artery Wikipedia
Middle Meningeal Artery Wikipedia
 Regional Anatomy Meninges At Texas Woman S University
Regional Anatomy Meninges At Texas Woman S University
 How Meningitis Causes Neck Pain And Stiffness
How Meningitis Causes Neck Pain And Stiffness
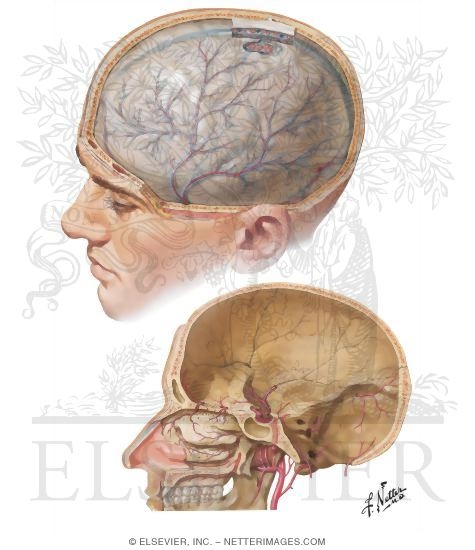 Meningeal Arteries Dura Mater And Middle Meningeal Artery
Meningeal Arteries Dura Mater And Middle Meningeal Artery
 Posterior Meningeal Artery Wikipedia
Posterior Meningeal Artery Wikipedia
What Is The Difference Between Meninges Of Brain And Spinal

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Meningeal Anatomy"
Posting Komentar