Right Ventricular Anatomy
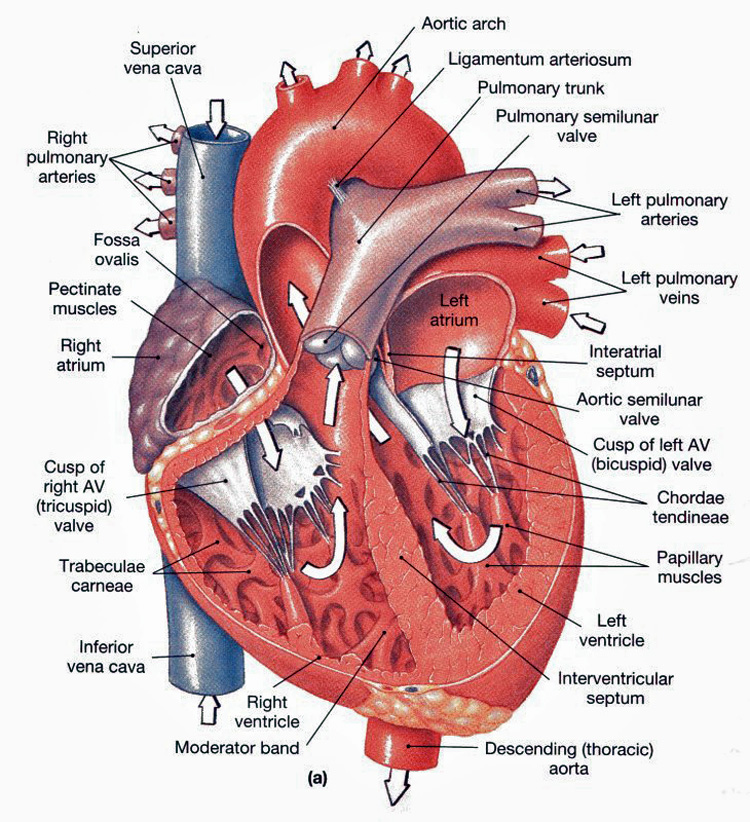
As deoxygenated blood flows into the right atrium it passes through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle which pumps the blood up through. The right ventricle in the normal heart is the most anteriorly situated cardiac chamber since it is located immediately behind the sternum.
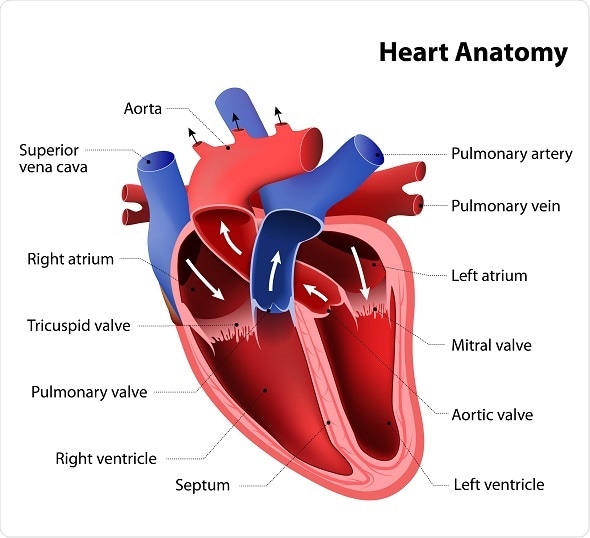
 Heart Anatomy Chambers Valves And Vessels Anatomy
Heart Anatomy Chambers Valves And Vessels Anatomy
The normal rv is anatomically and functionally different from the left ventricle which precludes direct extrapolation of our knowledge of left sided physiopathology to the right heart.

Right ventricular anatomy. The right ventricle is one of the hearts four chambers. It also marks the inferior border of the cardiac silhouette. The right ventricle projects to the left of the right atrium and when viewed in the cardiac short axis plane is semilunar in shape wrapping around the anterolateral aspect of the left ventricle lv.
The point of the chordae tendineae and the papillary muscles is to prevent these cusps to prevent the tricuspid valve from being averted back into the right atrium when the ventricle contracts and the pressure increases and the back flow of blood forces against the tricuspid valve. There is increasing recognition of the crucial role of the right ventricle rv in determining functional status and prognosis in multiple conditions. The mesh surface is the left ventricle.
Septal has attachments to the interventricular septum and. It has thinner walls than the left ventricle due to lower right sided pressures compared to the left ventricle. The moderator band is located in the right ventricular apex that connects the interventricular septum to the anterior papillary muscle.
Posterior originates from the inferior wall of the right ventricle. It is located in the lower right portion of the heart below the right atrium and opposite the left ventricle. Anterior is the largest of the three muscles.
Rv remodelling in diseased hearts can result in profound shape change as in this patient b with dilated rv due to severe pulmonary regurgitation following repair of tetralogy of fallot. When looking within the heart it appears as any other trabecula would except that the moderator band does not. The other important internal features of the right ventricle are the papillary muscles of which there are three.
The right ventricle extends from the right atrium to the apex of the heart. Forms the major portion of the anterior surface of the heart.
 Anatomy Of The Heart Textbook Of Cardiology
Anatomy Of The Heart Textbook Of Cardiology
 Diagnosis And Treatment Of Double Outlet Right Ventricle
Diagnosis And Treatment Of Double Outlet Right Ventricle
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12603/Right_atrium__1_.png) Heart Ventricles Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects
Heart Ventricles Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects
Right Ventricle Cardiovascular Anatomyzone
 Heart Anatomy Right Ventricle 3d Anatomy Tutorial
Heart Anatomy Right Ventricle 3d Anatomy Tutorial
 Ventricles Of The Brain Overview Gross Anatomy
Ventricles Of The Brain Overview Gross Anatomy
Figure 1 A Simplified Quantitative Evaluation Of Right
 Single Ventricle Defects And The Fontan Acha
Single Ventricle Defects And The Fontan Acha
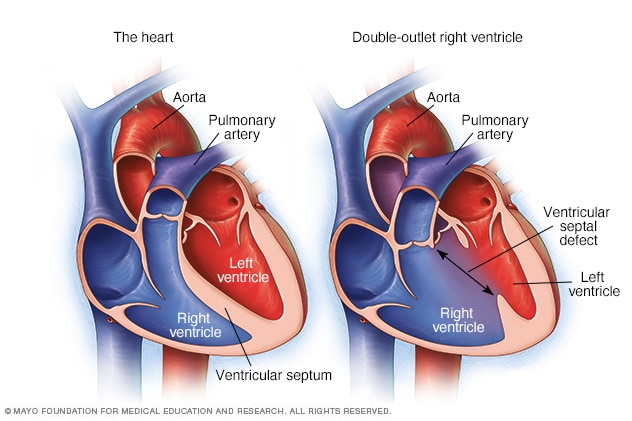 Double Outlet Right Ventricle Overview Mayo Clinic
Double Outlet Right Ventricle Overview Mayo Clinic
 Arvc Genetics Home Reference Nih
Arvc Genetics Home Reference Nih
 Right Ventricular Pulmonary Arterial Coupling Predicts
Right Ventricular Pulmonary Arterial Coupling Predicts
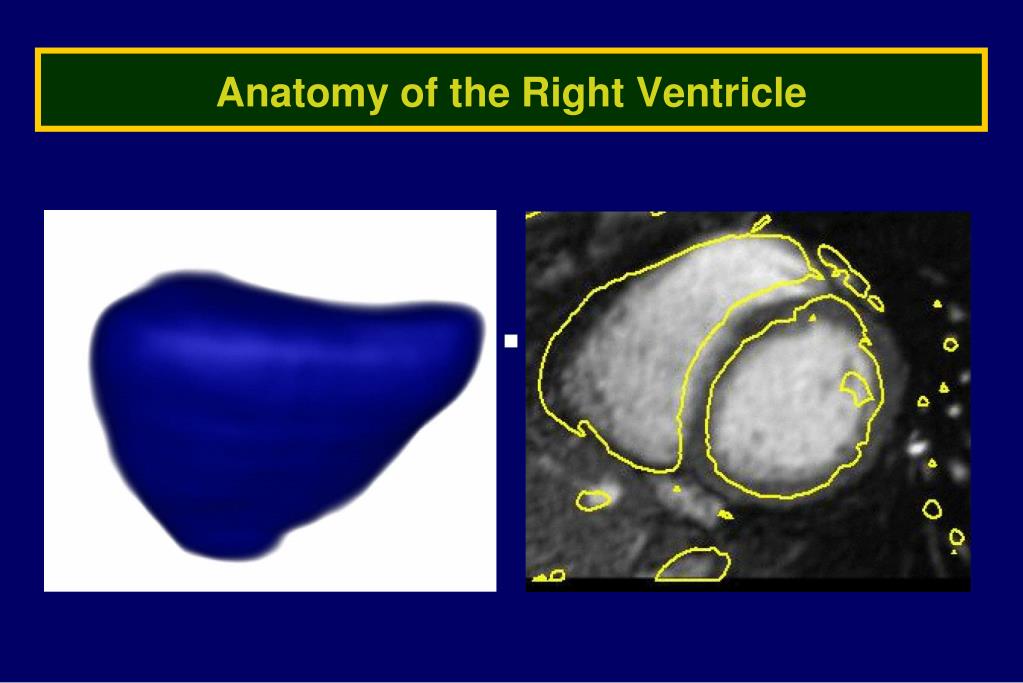 Ppt Assessment Of The Right Ventricle By Echocardiography
Ppt Assessment Of The Right Ventricle By Echocardiography
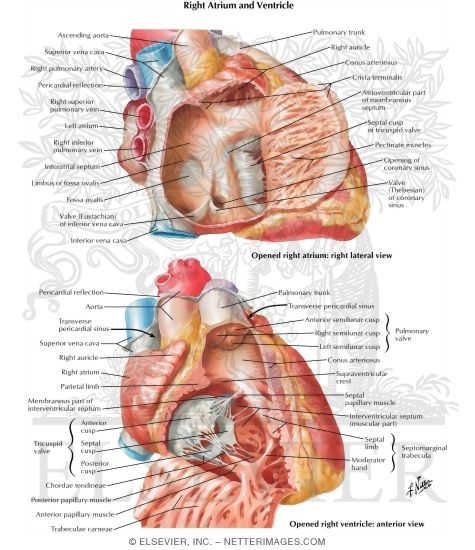 Right Atrium And Right Ventricle
Right Atrium And Right Ventricle
 1000 Ventricle Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
1000 Ventricle Stock Images Photos Vectors Shutterstock
The Heart Cardiovascular System
 Human Anatomy Cardiovascular System Diagram Quizlet
Human Anatomy Cardiovascular System Diagram Quizlet
 Causes Symptoms Of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular
Causes Symptoms Of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular
 Right Ventricle Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Right Ventricle Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
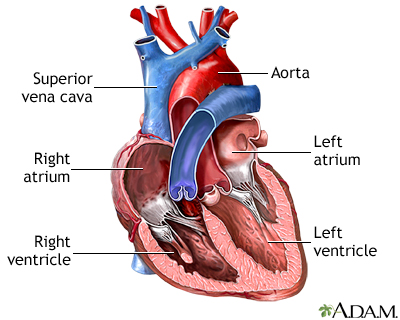 Heart Chambers Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
Heart Chambers Medlineplus Medical Encyclopedia Image
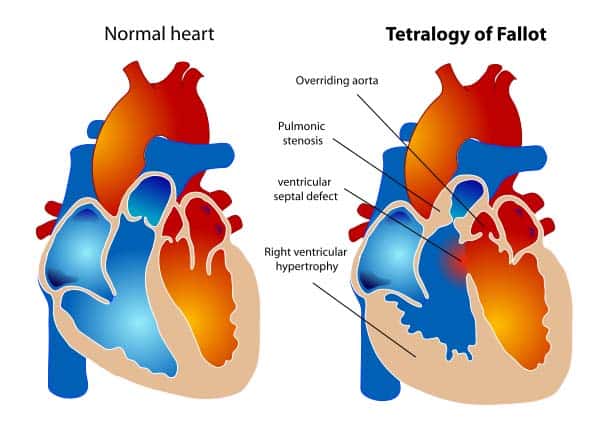 Chambers Of The Heart Atria Ventricles Teachmeanatomy
Chambers Of The Heart Atria Ventricles Teachmeanatomy
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/arteria-pulmonalis-dextra-4/MXb9uFNXQKKSfGVZBThaxg_A._pulmonalis_dexter_01.png) Heart Ventricles Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects
Heart Ventricles Anatomy Function And Clinical Aspects
 Does The Right Ventricle Really Dilate In Ventricular Septal Defect
Does The Right Ventricle Really Dilate In Ventricular Septal Defect
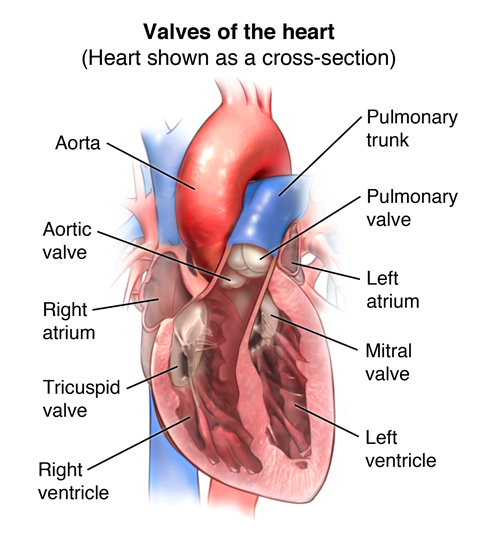
 Anatomical Specimens Of The Right Ventricle Rv A Section
Anatomical Specimens Of The Right Ventricle Rv A Section
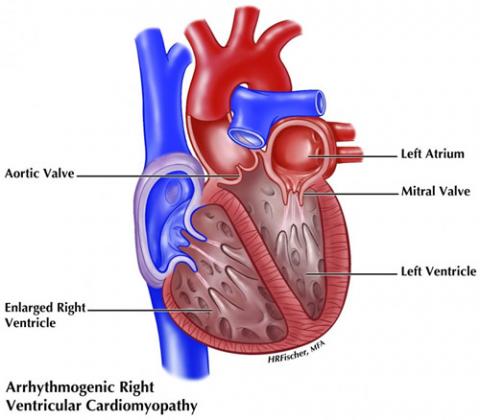 Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Arvc
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Arvc
 Figure 1 From Right Ventricular Septal Pacing A Paradigm
Figure 1 From Right Ventricular Septal Pacing A Paradigm
 Left Vs Right Ventricle Difference Between
Left Vs Right Ventricle Difference Between
 Selective Site Right Ventricular Pacing Heart
Selective Site Right Ventricular Pacing Heart
 How The Healthy Heart Works American Heart Association
How The Healthy Heart Works American Heart Association
 Illustration Picture Of Anatomical Structures Heart
Illustration Picture Of Anatomical Structures Heart

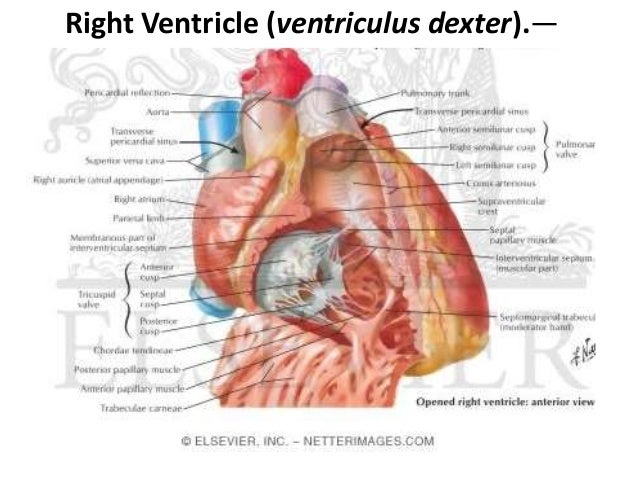
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Right Ventricular Anatomy"
Posting Komentar