Anatomy Of A Spider
Unlike other insects the most populous type of arthropods spiders have bodies divided into two segments or tagmata singular. A beautiful image showing the internal anatomy of a spider.
The anatomy of spiders includes many characteristics shared with other arachnids.
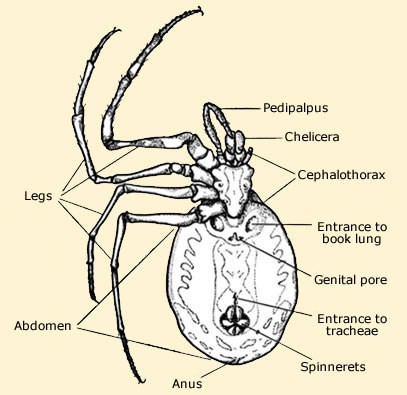
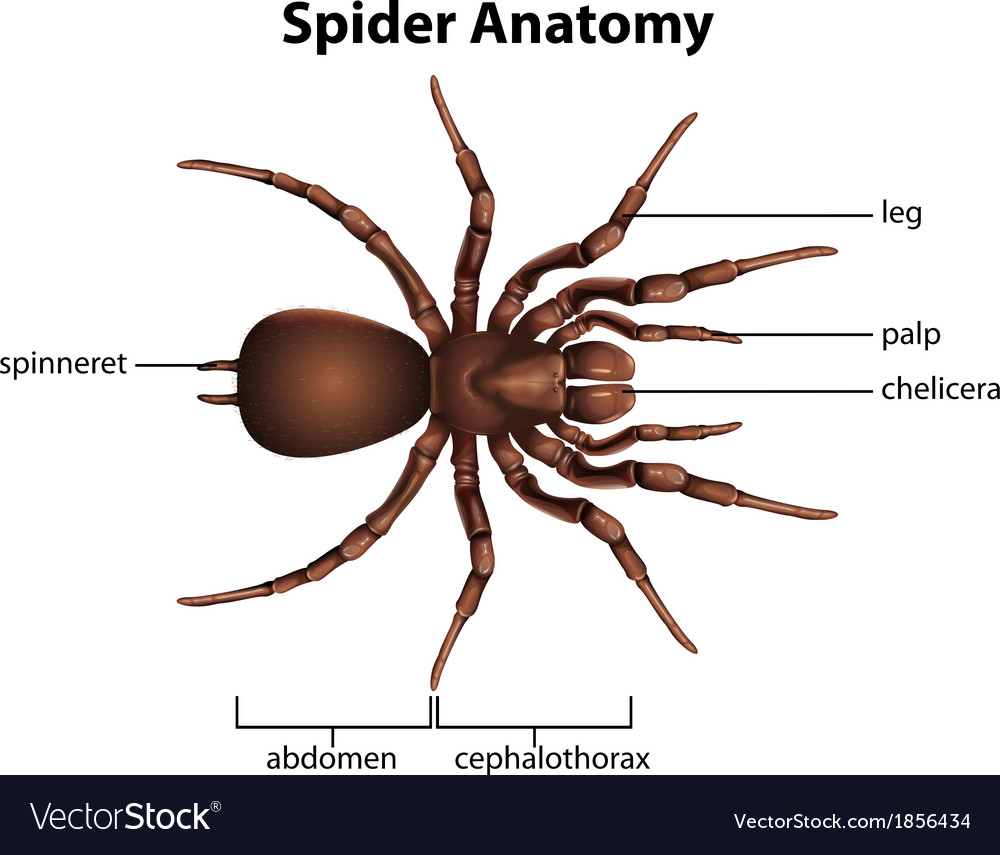
Anatomy of a spider. Even a relatively large spider can have fangs with very sharp points. The abdomen is the posterior of the two body regions of a spider. Arthropod animal with eight legs and an unsegmented body.
At the front of the cephalothorax we find. In spiders the first pair of appendages the chelicerae are like two segment fingers the outer segment being a hollow fang that injects venom virtually all spiders have poison glands though some are far more venomous than others. These characteristics include bodies divided into two tagmata sections or segments eight jointed legs no wings or antennae the presence of chelicerae and pedipalps simple eyes and an exoskeleton which is periodically shed.
The bodies of spiders range in size from about 1 mm up to 9 cm. The anatomy of a spider is very interesting. Non complex sight organ of a spider.
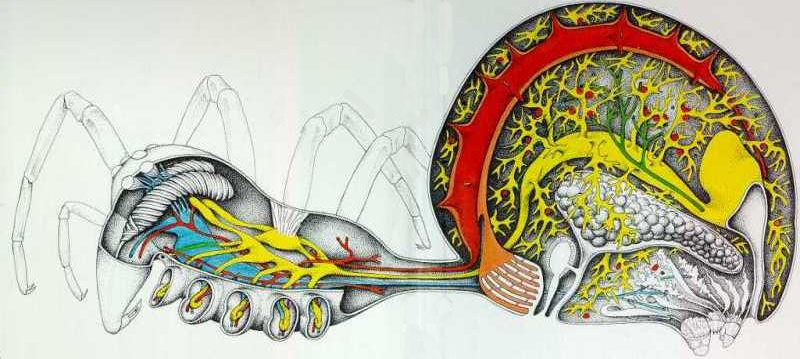
Spider eyes and other senses. Seat of the mental capacities of a spider. Internal anatomy of a spider.
Non complex sight organ of a spider. All spiders have 8 legs 2 body parts cephalothorax and abdomen fang like chelicerae and antenna like pedipalps click on the terms below to learn more about each body part. Everything else is self explanatory.
The smallest of full grown spiders can be less than 4 mm. These are the cephalothorax formed by a fusion of the head and thorax cephalon means headbrain and the abdomen. Spiders have 8 legs.
Sucking part of the digestive tract. They range from large stocky burrowers to petite colourful web builders to everything in between. Venom producing glandular organ of a spider.
This sets them apart from insects which have only 6 legs. They are designed to help them move with ease and to conserve energy. The body of spiders is divided in two major parts.
A spiders body is divided into two regions prosoma anterior part and ophisthosoma the posterior part. There are around 4000 species of spiders in australia and the diversity of species is truly incredible. These are also called prosoma front body and opisthosoma rear body respectively.
This jumping spiders main centre eyes are very close together. While all have the basic features listed above it is not always easy to see or distinguish them. Prosoma contains head antenna and the legs.
Even though there is plenty of variation when you look at the size and colors of spiders they all have general characteristics.
 Spider Anatomy For Artists John Muir Laws
Spider Anatomy For Artists John Muir Laws
 Coxal Glands Arachnids Spider Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty
Coxal Glands Arachnids Spider Anatomy Stock Vector Royalty
 Spiders Of Missouri Missouri S Natural Heritage
Spiders Of Missouri Missouri S Natural Heritage
 Spider Joe On Twitter Anatomy Of A Spider Found In The
Spider Joe On Twitter Anatomy Of A Spider Found In The
 Anatomy Of A Spider Canvas Print
Anatomy Of A Spider Canvas Print
 A Spider Anatomy Include All Name
A Spider Anatomy Include All Name
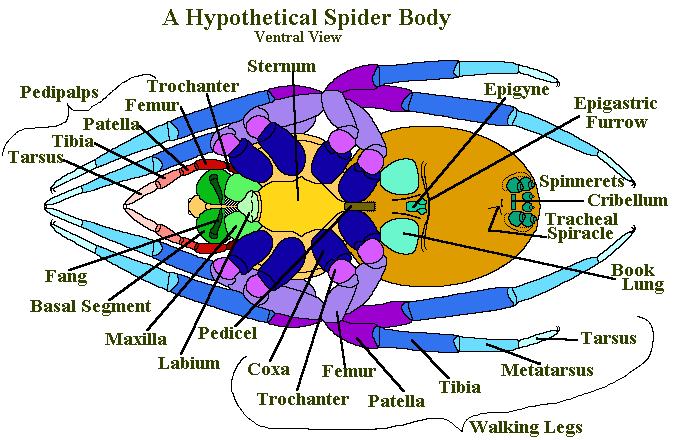 The Earthlife Web Spider Anatomy
The Earthlife Web Spider Anatomy
 Photo Art Print Anatomy Of A Spider Europosters
Photo Art Print Anatomy Of A Spider Europosters
 Vintage Argiope Spider Anatomy Classroom Chart From Turtox
Vintage Argiope Spider Anatomy Classroom Chart From Turtox
 Class Arachnida Spider Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
Class Arachnida Spider Anatomy Diagram Quizlet
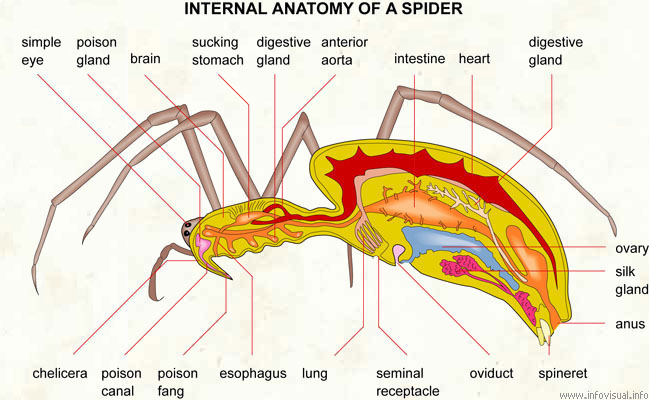 Internal Anatomy Of A Spider Visual Dictionary
Internal Anatomy Of A Spider Visual Dictionary
 Spider Anatomy Worksheet Education Com
Spider Anatomy Worksheet Education Com
 Spider Anatomy Diagram Picture Of Spider
Spider Anatomy Diagram Picture Of Spider
 Proper Anatomy Of The Spider Proper Anatomy Know Your Meme
Proper Anatomy Of The Spider Proper Anatomy Know Your Meme
Spider Anatomy Spiders Biology And Biodiversity
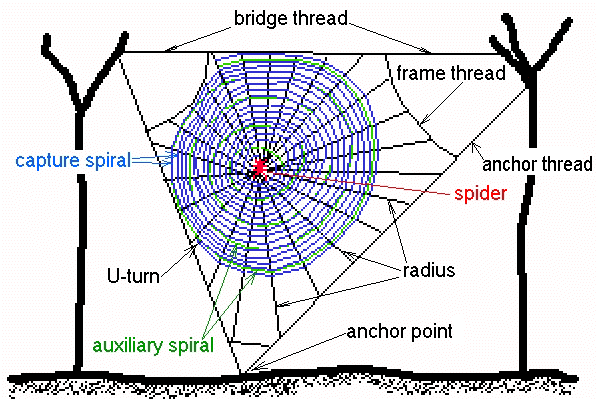 Anatomy Of A Spiderweb Dissection Connection
Anatomy Of A Spiderweb Dissection Connection
 12 Different Types Of Spiders Found In Houses Around The World
12 Different Types Of Spiders Found In Houses Around The World
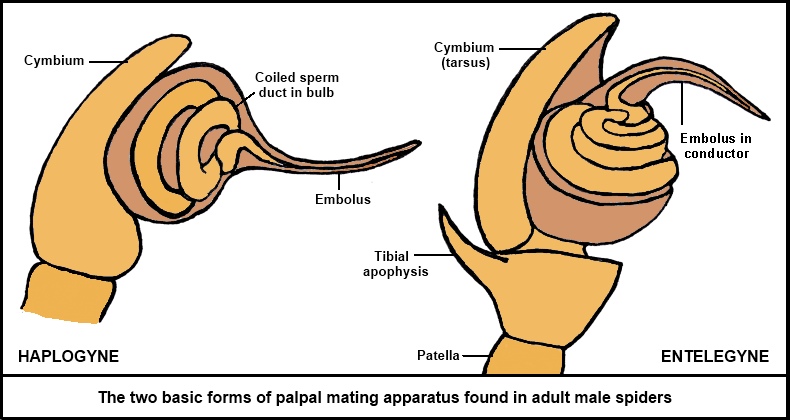 All About Spiders Types Of Spiders Life Cycle Etc
All About Spiders Types Of Spiders Life Cycle Etc
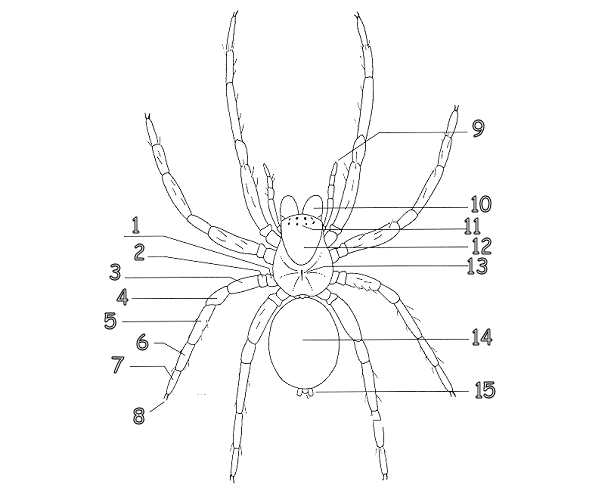
Jumping Spider External Anatomy
Spider Anatomy About Spiders Online Biology Dictionary
 Spider Anatomy A Simple Body Plan Of A Common Huntsman Spi
Spider Anatomy A Simple Body Plan Of A Common Huntsman Spi
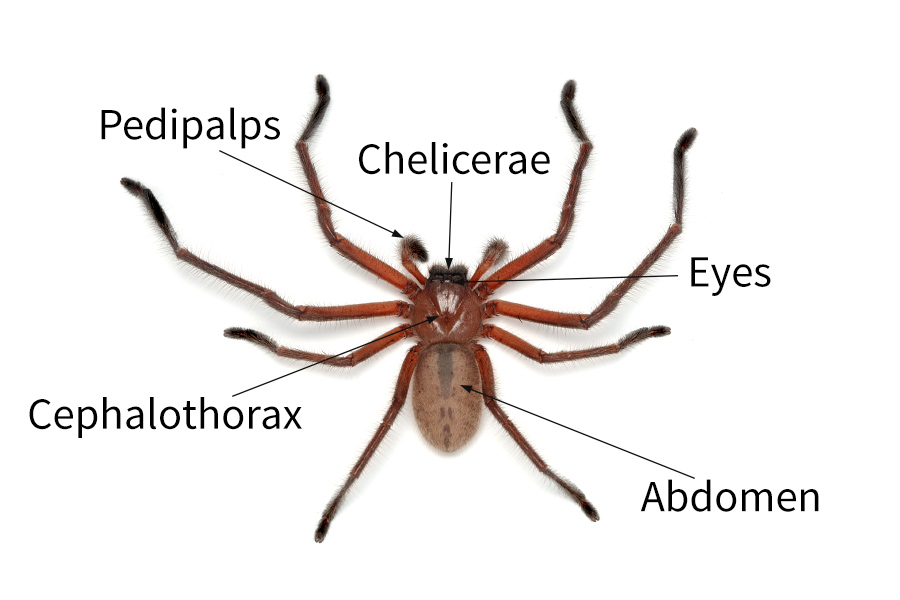




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of A Spider"
Posting Komentar