Ultrasound Neck Anatomy
Optimal positioning and exposure of the neck for ultrasound of the thyroid and parathyroid glands a b and lateral neck for lymph node examination and mapping c. A common neck ultrasound is ultrasound of the thyroid which uses sound waves to produce pictures of the thyroid gland within the neck.
Find out more from alaska family sonograms.

Ultrasound neck anatomy. It does not use ionizing radiation. A neck ultrasound is performed to diagnose potential problems of the thyroid lymph nodes and carotid arteries. These include the masseter muscle the zygomatic arch and the outer cortex of the ramus of the mandible and the suprazygomatic portion of the temporalis muscle.
The infrahyoid region of the neck includes the visceral anterior cervical posterior cervical carotid retropharyngeal and perivertebral spaces. The carotid space in the suprahyoid region of the neck contains the internal carotid artery the internal jugular vein cranial nerves ix to xii and the sympathetic plexus. While the vast majority of patients are supine on the exam table with a pillow supporting the shoulders to allow gentle neck extension keep in mind that some patients have beautiful anatomy d that allows ultrasound exam even in a sitting position.
Anterior neck anatomy false vocal cords true vocal cords paraglottic fat. Head and neck anatomy is important when considering pathology affecting the same area. An enlarged cervical lymph node is the most commonly encountered neck lump.
Because most lesions in the neck are site specific once a lesion has been located specific ultrasound features can be used to establish the diagnosis. In radiology the head and neck refers to all the anatomical structures in this region excluding the central nervous system that is the brain and spinal cord and their associated vascular structures and encasing membranes ie the meninges. The visceral space contains the thyroid parathyroid glands larynx hypopharynx the cervical trachea and esophagus the recurrent laryngeal nerve.
In the infrahyoid neck it is surrounded by the anterior cervical space anteriorly by the visceral and retropharyngeal spaces medially and by the perivertebral and posterior cervical spaces posteriorly. Only some parts of the masticator space can be explored sonographically. This can be confirmed from ultrasound guided fnac allowing appropriate clinical management and treatment.
 Thyroid Normal Ultrasoundpaedia
Thyroid Normal Ultrasoundpaedia
 The Radiology Assistant Infrahyoid Neck
The Radiology Assistant Infrahyoid Neck
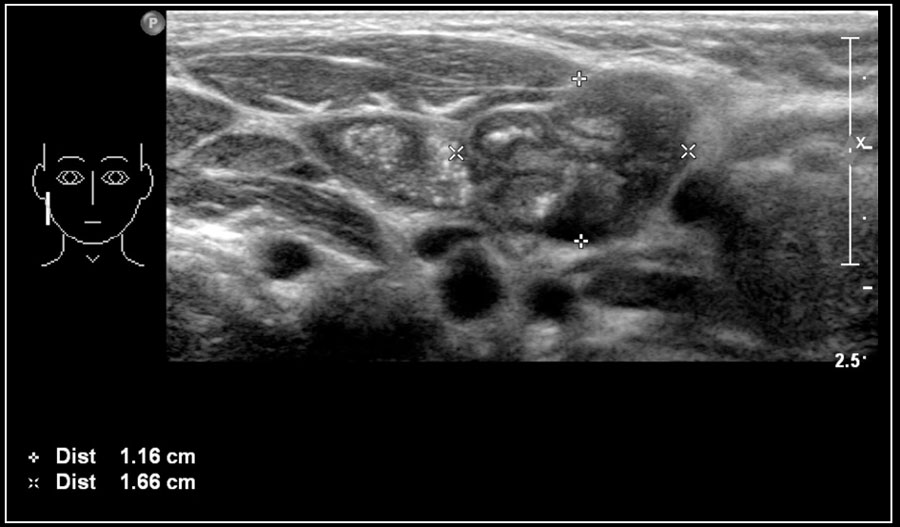 The Radiology Assistant Neck Masses In Children
The Radiology Assistant Neck Masses In Children
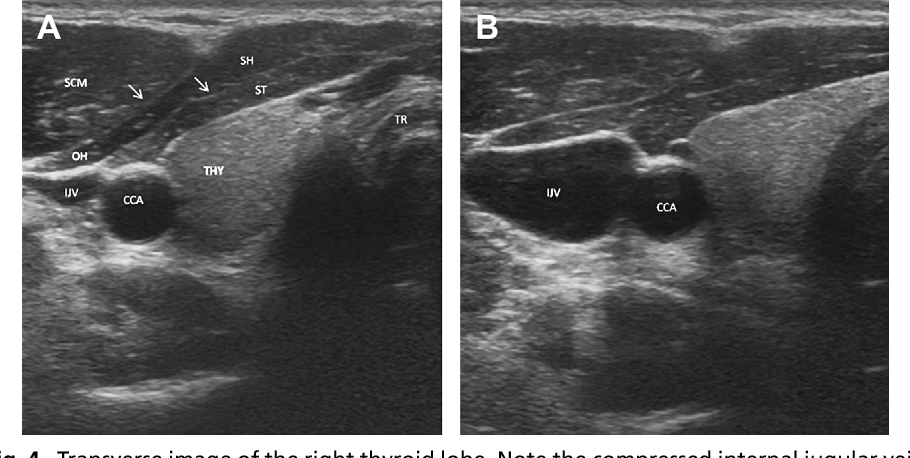 Figure 7 From Head And Neck Anatomy And Ultrasound
Figure 7 From Head And Neck Anatomy And Ultrasound
 Pdf Ultrasound Comparison Of External And Internal Neck
Pdf Ultrasound Comparison Of External And Internal Neck
 Figure 7 From Head And Neck Anatomy And Ultrasound
Figure 7 From Head And Neck Anatomy And Ultrasound
 Normal Thyroid Gland Transverse Ultrasound Through The Neck
Normal Thyroid Gland Transverse Ultrasound Through The Neck
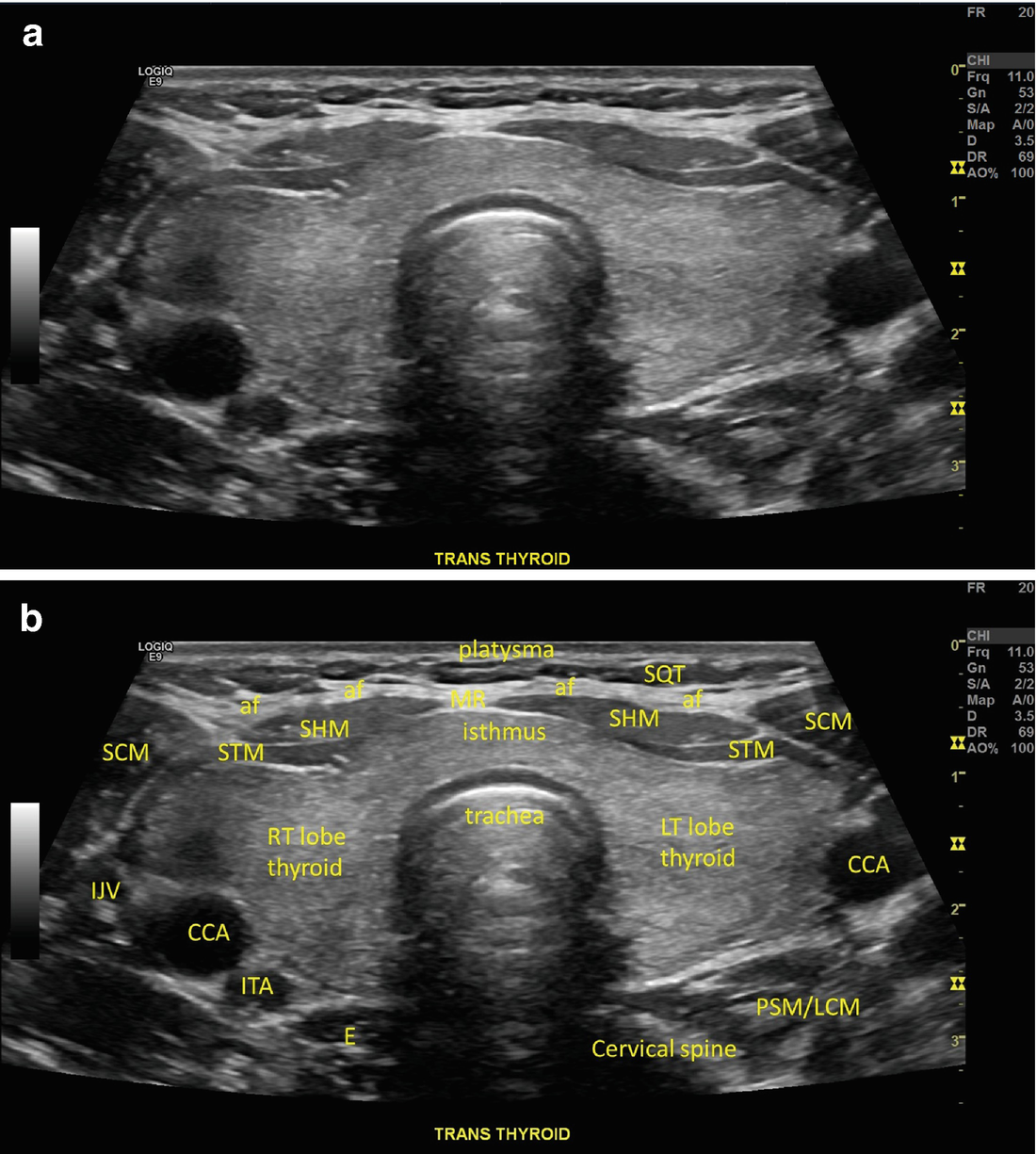 Normal Neck Anatomy And Method Of Performing Ultrasound
Normal Neck Anatomy And Method Of Performing Ultrasound
 The Radiology Assistant Infrahyoid Neck
The Radiology Assistant Infrahyoid Neck
 Figure 7 From Head And Neck Anatomy And Ultrasound
Figure 7 From Head And Neck Anatomy And Ultrasound
 The Radiology Assistant Neck Masses In Children
The Radiology Assistant Neck Masses In Children
 Ultrasound Guided Cervical Plexus Block Nysora
Ultrasound Guided Cervical Plexus Block Nysora
 Chapter 25 Overview Of The Neck The Big Picture Gross
Chapter 25 Overview Of The Neck The Big Picture Gross
 Ultrasound Guided Cervical Plexus Block Nysora
Ultrasound Guided Cervical Plexus Block Nysora
 Ecr 2019 C 2688 High Resolution Cutaneous Ultrasound Of
Ecr 2019 C 2688 High Resolution Cutaneous Ultrasound Of
 The Radiology Assistant Infrahyoid Neck
The Radiology Assistant Infrahyoid Neck
 Figure 7 From Head And Neck Anatomy And Ultrasound
Figure 7 From Head And Neck Anatomy And Ultrasound
 Pocket Atlas Of Normal Ultrasound Anatomy Radiology Pocket
Pocket Atlas Of Normal Ultrasound Anatomy Radiology Pocket
 Cervical Nerves In Impingement Regions Anatomy Scanned With
Cervical Nerves In Impingement Regions Anatomy Scanned With
 Normal Carotids Ultrasound How To
Normal Carotids Ultrasound How To
 Head And Neck 4 3 Salivary Glands Case 4 3 3 Pleomorphic
Head And Neck 4 3 Salivary Glands Case 4 3 3 Pleomorphic
New Advances In Diagnostic Imaging Might Reveal The Source



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Ultrasound Neck Anatomy"
Posting Komentar