Anatomy Muscle Contraction
Anatomy muscle contraction. A muscle that is attached to the bones of the skeleton and pro muscle of the heart involuntary muscle found inside many internal organs of the bo thin filaments.
 Process Of Muscle Contraction Anatomy Physiology 210
Process Of Muscle Contraction Anatomy Physiology 210
Professor dave explains 89443 views.
Anatomy muscle contraction. The next muscle contraction will be greater than the previous muscle contraction. The force of muscle contraction depends on. The signal an impulse called an action potential travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron.
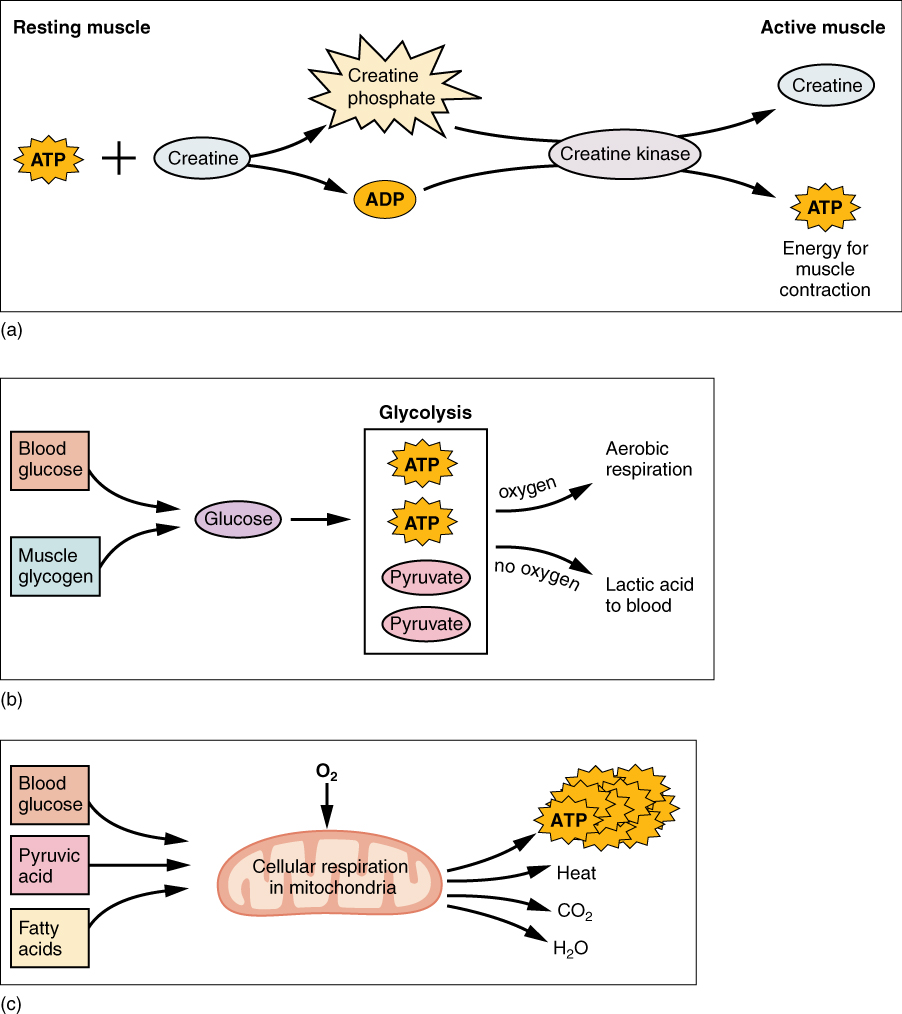
Based on the all or none law of muscle contraction a muscle cell that receives a signal that is below threshold or a weak signal to contract will not contract if you look inside a sarcomere you will see. A contractile protein that makes up the thick small bridge like structures on myosin. Muscle contraction during exercise is divided into three categories depending on how the muscle contacts and whether it is lengthening or shortening.
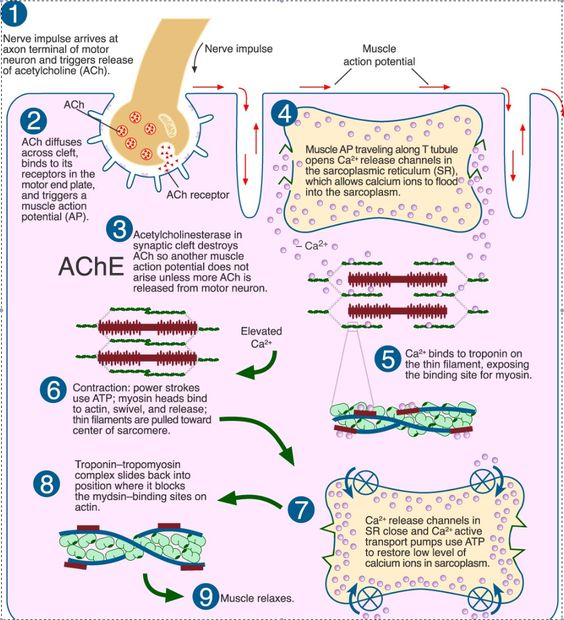
This stimulates the sarcoplasmic reticulum to release calcium into the muscle cell. A contractile filament that is part of the thi thick filaments. Previous 413 next please select an option in order to make atp.
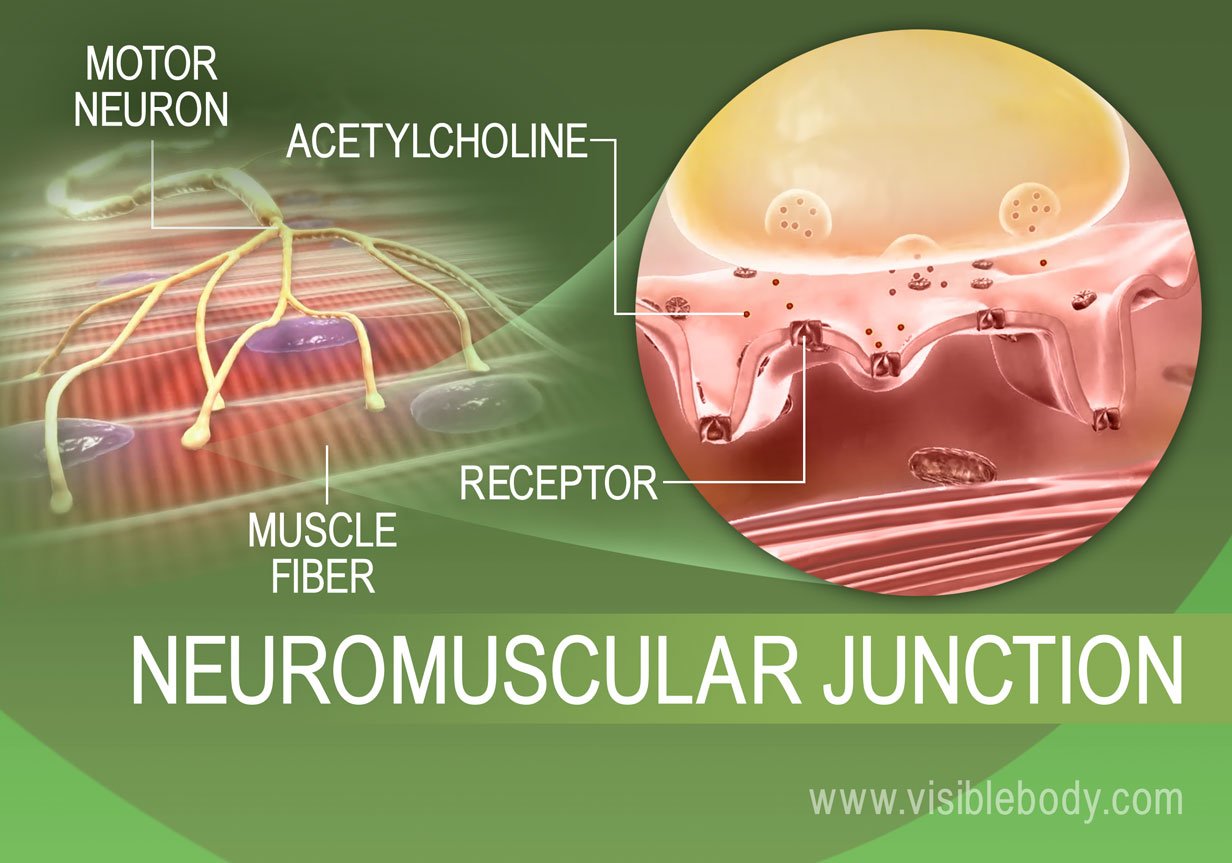
The motor nerve stimulates an action potential impulse to pass down a neuron to the neuromuscular junction. A muscle contraction is triggered when an action potential travels along the nerves to the muscles. Group of muscle fibers innervated by a single neuron.
Anatomy muscle muscle contraction. Muscle contraction is described by the sliding filament model of contraction. Ach is the neurotransmitter that binds at the neuromuscular junction nmj to trigger depolarization and an action potential travels along the sarcolemma to trigger calcium release from sr.
Skeletal muscles consist of numerous motor units and therefore stimulating more motor units creates a stronger contraction. Sarcomeres action potential and the neuromuscular junction duration. The next muscle contraction will be weaker than the previous muscle contraction.
There wont be a second muscle contraction until all the calcium ions are reabsorbed. The mechanism of muscle contraction. Calcium floods into the muscle cell binding with troponin allowing actin and myosin to bind.
The actin and myosin cross bridges bind and contract using atp as energy atp is an energy compound that all cells use to fuel their activity this is discussed. Here we explain isotonic isometric isokinetic concentric and eccentric muscle contractions. Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal.
The degree of contraction of a skeletal muscle is influenced by the number of motor units being stimulated with a motor unit being a motor neuron plus all of the muscle fibers it innervates. A motor neuron its axon terminals and all of the skeletal muscle fibers it stimulates.
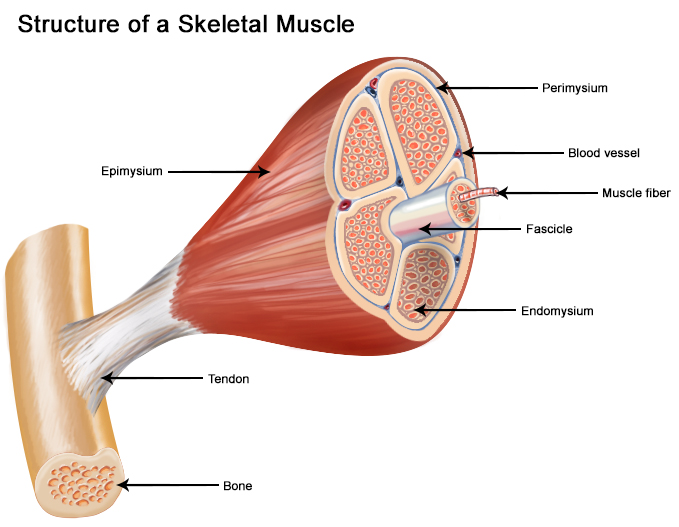
 Seer Training Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
Seer Training Structure Of Skeletal Muscle
 Muscle Contraction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
Muscle Contraction Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
 Solved Case 2 5 Smooth Muscle Contraction Mh Is A 26 Yea
Solved Case 2 5 Smooth Muscle Contraction Mh Is A 26 Yea
 Let S Move The Events Of Muscular Contraction Crazy Cool
Let S Move The Events Of Muscular Contraction Crazy Cool
 10 3 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
10 3 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
 Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Online
Sliding Filament Model Of Muscle Contraction Online
The Skeletal Muscle Contraction Cycle Course Hero
 Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
Muscle Contractions Learn Muscular Anatomy
 Biceps Muscle Anatomy Britannica
Biceps Muscle Anatomy Britannica
 Muscle Definition Function Types And Structure Biology
Muscle Definition Function Types And Structure Biology
 Muscle Fiber Contraction In Two Hours Muscle Types Of
Muscle Fiber Contraction In Two Hours Muscle Types Of
 Muscle Contractions 3d Muscle Lab
Muscle Contractions 3d Muscle Lab
 Lab 4 Respiratory Anatomy Muscle Contractions Diagram Quizlet
Lab 4 Respiratory Anatomy Muscle Contractions Diagram Quizlet
 Muscle Contraction Process Hd Animation
Muscle Contraction Process Hd Animation
 Muscle Contraction Not In My Colour
Muscle Contraction Not In My Colour
 Is Lifting A Glass Of Water To Your Mouth Considered An
Is Lifting A Glass Of Water To Your Mouth Considered An
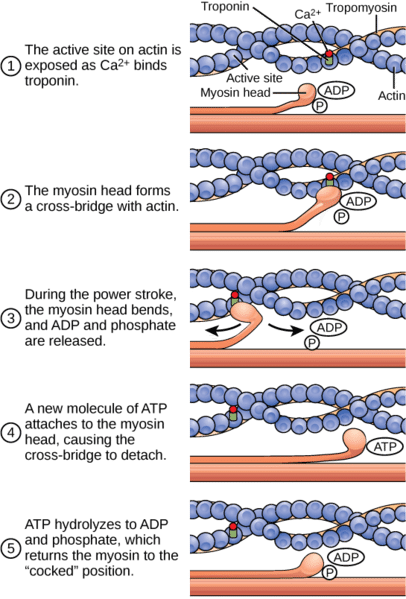 Ultrastructure Of Muscle Skeletal Sliding Filament
Ultrastructure Of Muscle Skeletal Sliding Filament
 Chapter 9 5 Whole Muscle Contraction Bio201
Chapter 9 5 Whole Muscle Contraction Bio201
 Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
Muscle Fiber Contraction And Relaxation Anatomy And
 Structures Superficial Anatomy And Physiology
Structures Superficial Anatomy And Physiology
 10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology
10 2 Skeletal Muscle Anatomy Physiology
 Muscle Contraction Unit 13 Skeletal System Human Anatomy
Muscle Contraction Unit 13 Skeletal System Human Anatomy

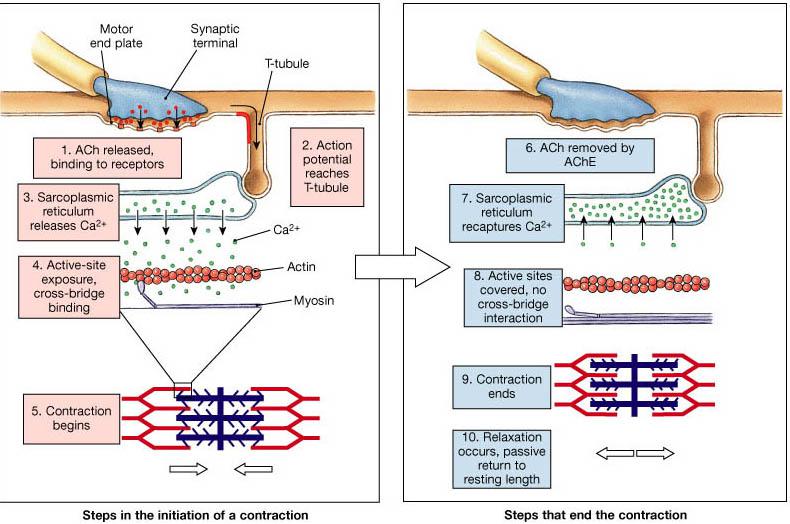
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Muscle Contraction"
Posting Komentar