Anatomy Of Gingiva
Before the erupting teeth enter the mouth cavity gum pads develop. These are found in the oral cavity or mouth of a human being.
 Gingiva Docx د حسين Muhadharaty
Gingiva Docx د حسين Muhadharaty
The gingiva is the clinical term for gums.

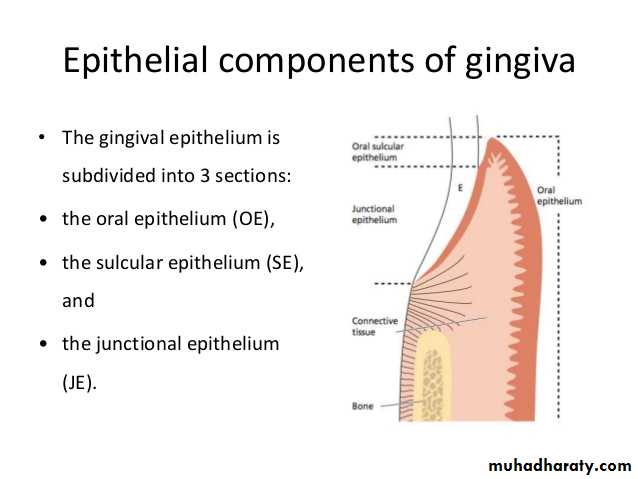
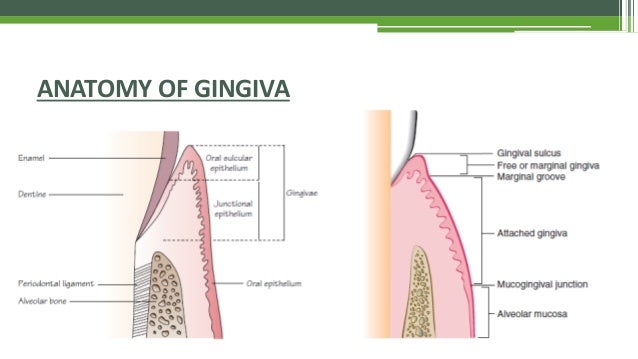
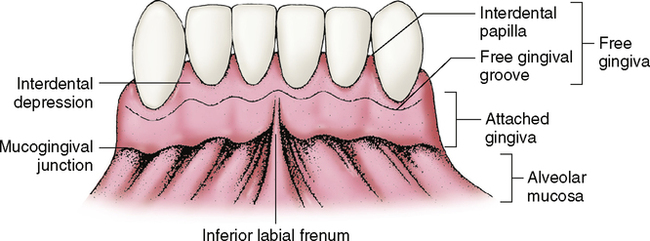
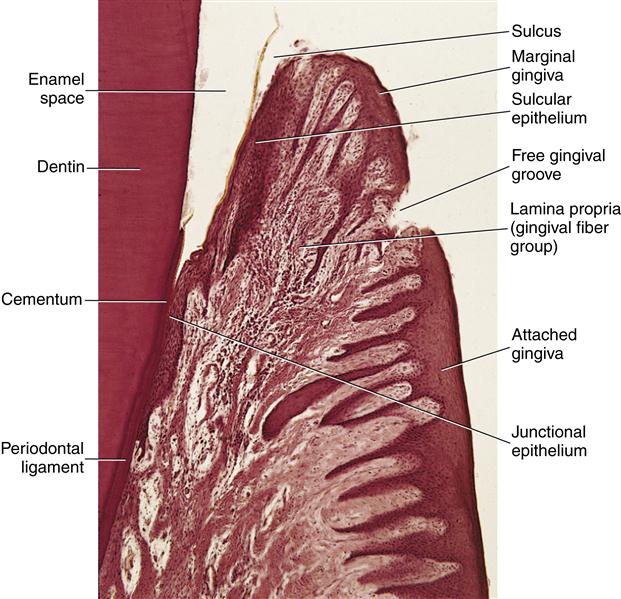
Anatomy of gingiva. Marginal gingiva attached gingiva interdental papilla. The oral mucosa is divided into three types. With the exception of the teeth the mouth is lined by mucous membranes.
1 masticatory mucosa which includes the gingiva and hard palate. This article will highlight the two main types of gingiva. The plaque induced diseases may be associated with endocrine changes medications systemic disease or malnutrition.
Anatomy of the periodontium. These are slight elevations of the overlying oral mucous membrane. Anatomy of gingiva english dr teeth.
Gum also called gingiva plural gingivae in anatomy connective tissue covered with mucous membrane attached to and surrounding the necks of the teeth and adjacent alveolar bone. Each of these periodontal components is distinct in its location tissue architecture biochemical composition and chemical composition but all of these components function together as a single unit. Well get to know the types of gingiva.
Anatomy of a mouth the mouth oral cavity consists of several components including the teeth gingiva gums tongue palate cheeks lips and floor of the mouth. Anatomy histology of the gingival unit and basic oral hygiene continuing education course will examine the characteristics of the gingival unit and discuss basic recommendations necessary for achieving and maintaining the health of the gingiva. It consists of four principal components.
When tooth eruption is complete the gum embraces the neck region of each tooth. And 3 specialized mucosa which is found on the dorsum of the tongue. 2 lining mucosa which consists of the alveolar mucosa soft palate lining of lips cheeks and sublingual area.
Clinical anatomy of the gingival unit. Gingiva periodontal ligament cementum and alveolar bone. What is the description of the tissue on the outer surface of the free gingiva the papillae and the attached gingiva stratified squamous keratinized epithelium is the inner surface of the free gingival margin extending apically keratinized or nonkeratinized.
They consist of mucosal tissue that covers the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible and finish at the neck of each tooth. The american academy of periodontology classifies gingival disease as a major group of periodontal diseases and distinguishes two main subgroups those gingival diseases induced by dental plaque and those attributed to other causes. Unsubscribe from dr teeth.
 Definition Of Gingiva Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms
Definition Of Gingiva Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms
 Clinical Periodontology Introduction Anatomy
Clinical Periodontology Introduction Anatomy
 Gingiva An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Gingiva An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Gingiva Anatomy Dental Hygiene School Dental Assistant
Gingiva Anatomy Dental Hygiene School Dental Assistant
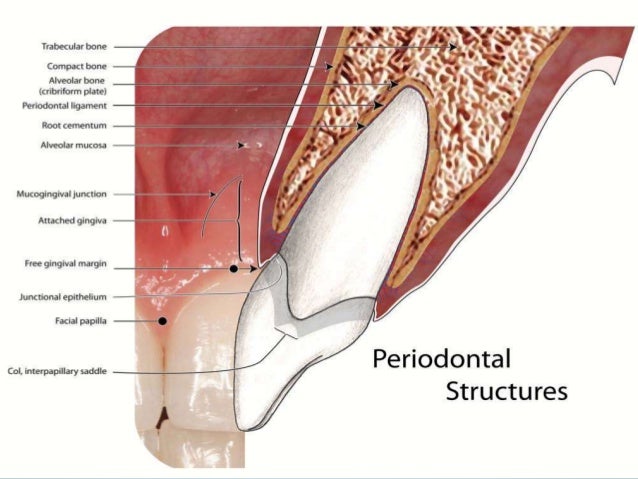
 8 Supporting Structures The Periodontium Pocket Dentistry
8 Supporting Structures The Periodontium Pocket Dentistry
 10 Gingival And Dentogingival Junctional Tissue Pocket
10 Gingival And Dentogingival Junctional Tissue Pocket
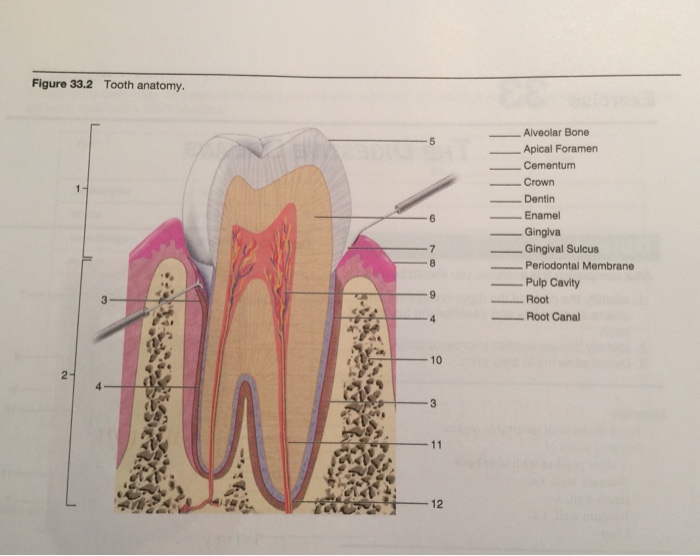
 Tooth Anatomy Structure Function With Pictures
Tooth Anatomy Structure Function With Pictures
 The Periodontium Anatomy Histology Of The Gingival Unit
The Periodontium Anatomy Histology Of The Gingival Unit
Gingival Esthetics An Orthodontic And Periodontal Approach
 Dental Anatomy Stock Photo Image Of Close Gingiva Adult
Dental Anatomy Stock Photo Image Of Close Gingiva Adult
The Abcs Of Veterinary Dentistry G Is For Gingiva
The Abcs Of Veterinary Dentistry G Is For Gingiva
 General Anatomy Terminology Gingiva Root Canal Enamel
General Anatomy Terminology Gingiva Root Canal Enamel
 Anatomy Quiz 2 Gingiva Diagram Quizlet
Anatomy Quiz 2 Gingiva Diagram Quizlet
 The Periodontium Anatomy Histology Of The Gingival Unit
The Periodontium Anatomy Histology Of The Gingival Unit
 Definition Of Gingival Recession And Anatomical
Definition Of Gingival Recession And Anatomical
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4680/KAU7J26FqiSljZhPP7oEDA_Cervix_dentis_02.png) Gingiva Types Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub
Gingiva Types Histology And Clinical Aspects Kenhub



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Gingiva"
Posting Komentar