Anatomy Of Hernia
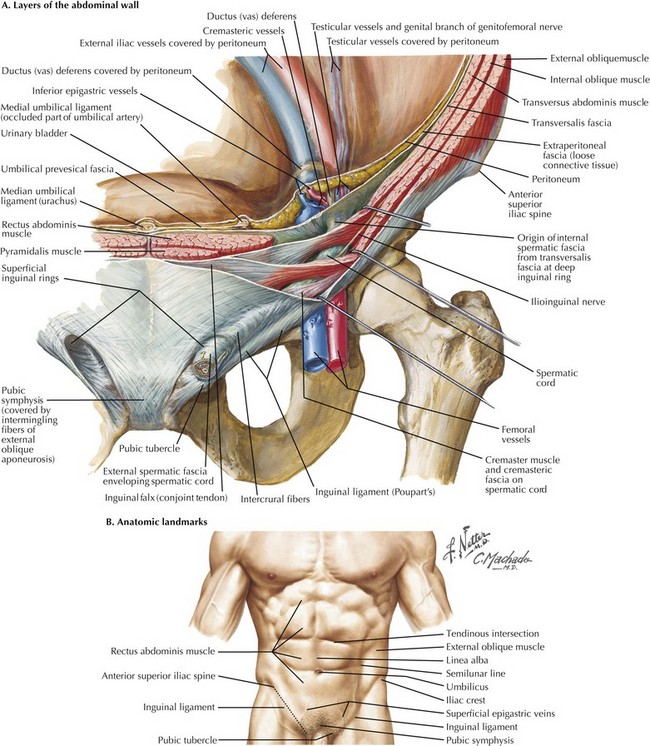
These layers are a bit different between the umbilical region and the groin but overall the basic layers are the same. It can be fat bowel or in some cases the genitourinary tract.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/2024/vMYj0g4ulLNt5QdwnotiYw_Diaphragm_02.png) Hiatal Hernia Symptoms And Management Kenhub
Hiatal Hernia Symptoms And Management Kenhub
The majority of hernias form in the weaker areas of the abdominal wall where there is no muscle present and typically occur in the linea alba.
Anatomy of hernia. The abdominal wall a sheet of tough muscle and tendon that runs down from the ribs to the legs at the groins acts as the bodys corset. The two types of hiatal hernias are sliding and paraesophageal. The 2 types of inguinal.
25 in males and 2 in females 75 of hernias groin hernias 23rd indirect and 13rd direct. Abdominal wall hernias and relevant surgical techniques. This weakness may be inherent as in the case of inguinal femoral and umbilical hernias.
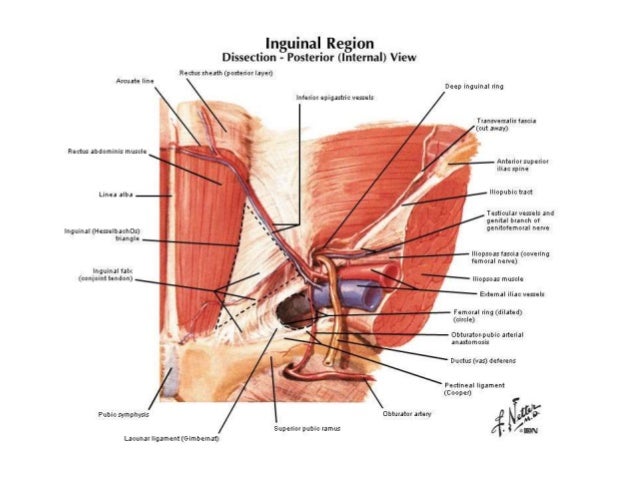
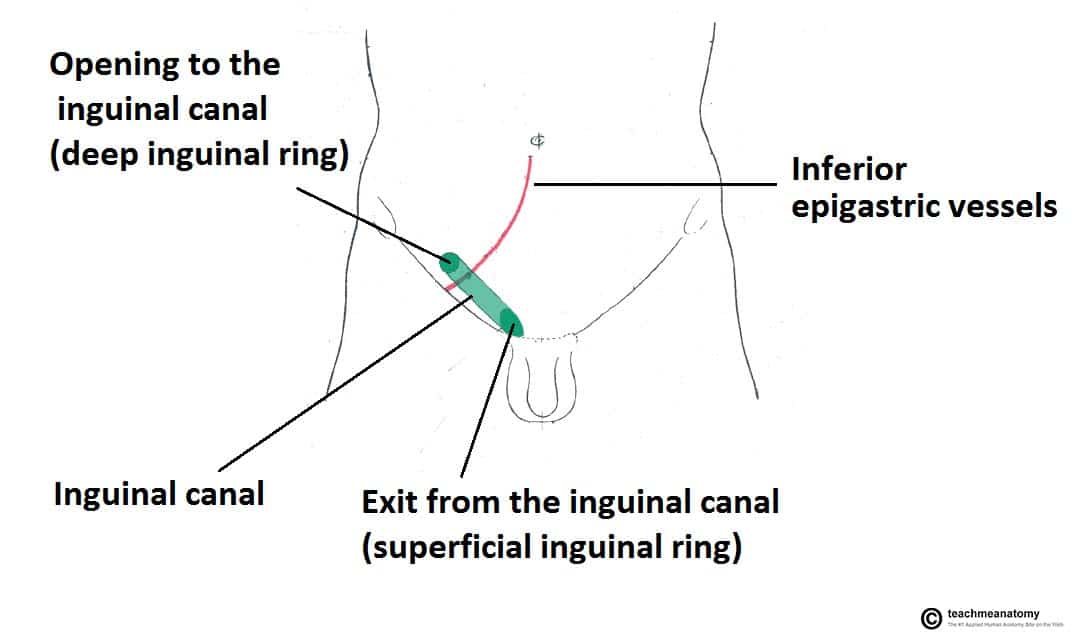
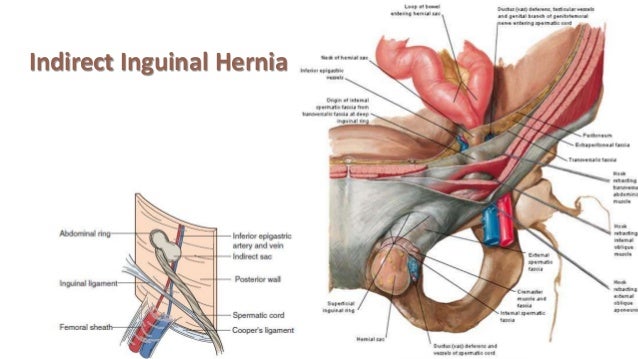
Hernias involving the inguinal canal can be divided into two main categories. Within the boundaries of this area you can find the external iliac artery and vein. Indirect where the peritoneal sac enters the inguinal canal through the deep inguinal ring.
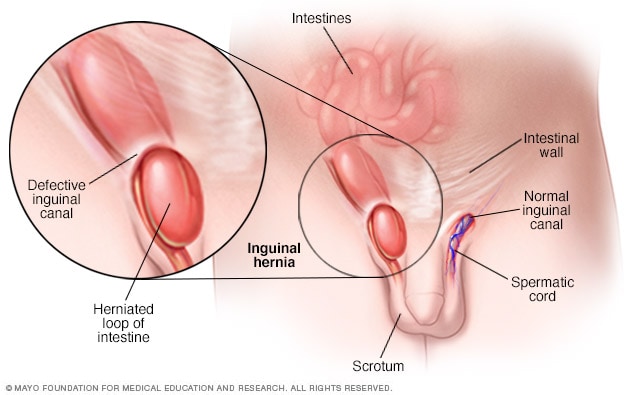
The most common location for hernia is the abdomen. The most common types of hernia are inguinal inner groin incisional resulting from an incision femoral outer groin umbilical belly button and hiatal upper stomach. A hernia occurs when an organ or fatty tissue squeezes through a weak spot in a surrounding muscle or connective tissue called fascia.
An inguinal hernia is the protrusion of intra abdominal contents through a defect in the abdominal wall. The upper part of the stomach usually protrudes upwards but it can also be the small intestine transverse colon or omentum. Hernia a condition in which part of an organ is displaced and protrudes through the wall of the cavity containing it.
A ventral hernia is a disruption or hole in the abdominal wall and can be classified as primary occurring de novo or incisional hernias caused by previous incision and surgery. Hernia anatomy the layers of the abdominal wall the first concept to understand is the basic layers of the abdominal wall. Direct where the peritoneal sac enters the inguinal canal though the posterior wall of the inguinal canal.
Its function amongst other things is to hold in the abdominal contents principally the intestines. During a laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair the dangerous triangle the triangle of doom refers to a triangular area bound by the vas deferens the testicular vessels and the peritoneal fold. A hiatal hernia is a protrusion of the abdominal contents into the thorax through an enlarged esophageal hiatus caused by a weakness or opening in the diaphragm.
A hernia is caused by the protrusion of a viscus in the case of groin hernias an intra abdominal organ through a weakness in the abdominal wall.
 Surgical Anatomy Of Inguinal Hernia
Surgical Anatomy Of Inguinal Hernia
 14 Inguinal Hernia General Anatomy Titles Incision Academy
14 Inguinal Hernia General Anatomy Titles Incision Academy
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/8025/The_Hernia.png) Inguinal Canal Anatomy Contents And Hernias Kenhub
Inguinal Canal Anatomy Contents And Hernias Kenhub
 Umbilical Hernia Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair Belly
Umbilical Hernia Laparoscopic Inguinal Hernia Repair Belly
 Inguinal Hernia Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
Inguinal Hernia Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic
 Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Basicmedical Key
Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Basicmedical Key
 Surgical Options In The Management Of Groin Hernias
Surgical Options In The Management Of Groin Hernias
 The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
 Abdominal Hernia Anatomy Of Female Lateral View Medical
Abdominal Hernia Anatomy Of Female Lateral View Medical
Laparoscopic Totally Extra Peritoneal Tep Inguinal Hernia
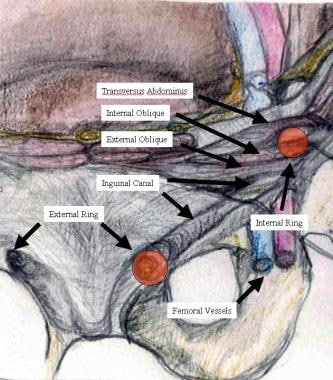 Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Practice Essentials Background
Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Practice Essentials Background
Anatomy Of A Hernia Simplified Version Holistic Hernia
 Surgical Anatomy Of Inguinal Hernia
Surgical Anatomy Of Inguinal Hernia
 Figure 1 From Clinical Practice Groin Hernias In Adults
Figure 1 From Clinical Practice Groin Hernias In Adults
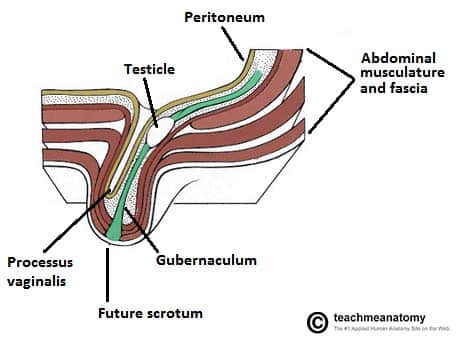 The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
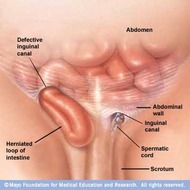 Mayo Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Anatomical Landmarks
Mayo Open Inguinal Hernia Repair Anatomical Landmarks
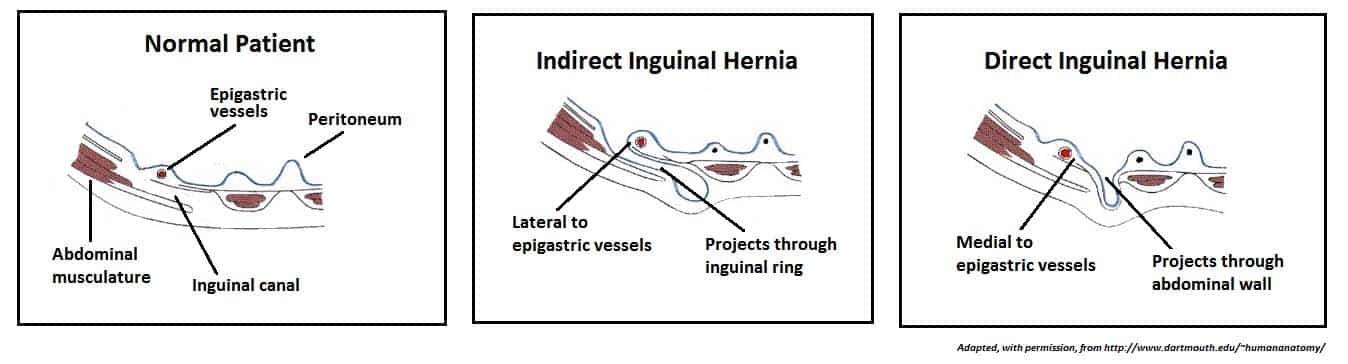 The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
The Inguinal Canal Boundaries Contents Teachmeanatomy
 Free Art Print Of A Human Anatomy Strangulated Hernia
Free Art Print Of A Human Anatomy Strangulated Hernia
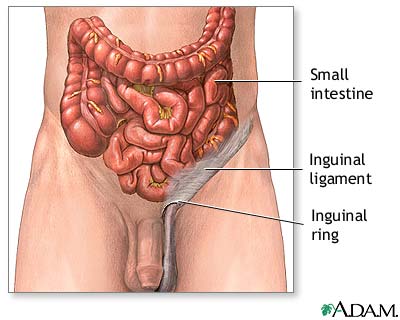 Inguinal Hernia Repair Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
Inguinal Hernia Repair Series Normal Anatomy Medlineplus
 Simplified Anatomy Of A Midline Incisional Hernia And
Simplified Anatomy Of A Midline Incisional Hernia And
What Is A Hernia A Laparoscopic Surgeon Tells All The
Clinical Anatomy Of The Abdominal Wall Hernia Surgery Oa

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Hernia"
Posting Komentar