Knee Soft Tissue Anatomy
Accurate and timely diagnosis increases the likelihood of fully restoring normal and pain free use of the affected knee. The pair of collateral ligaments keeps the knee from moving too far side to side.
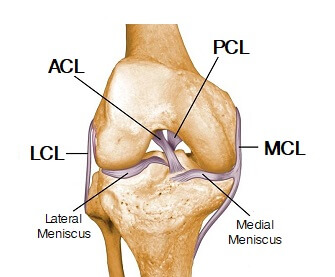 Knee Joint Anatomy Motion Knee Pain Explained
Knee Joint Anatomy Motion Knee Pain Explained
The cruciate ligaments crisscross each other in the center of the knee.

Knee soft tissue anatomy. Tendons ligaments and other soft tissues of the knee joint the knee joint relies on a variety of ligaments tendons and soft tissue structures to maintain flexibility stability and strength. Ligaments are tough fibrous connective tissues which link bone to bone made of collagen. Soft tissue knee injuries are some of the most common and clinically challenging musculoskeletal disorders seen in the emergency department.
Tendonitis refers to an acute inflammation in the tendon often following an injury whereas a tendinosis is chronic and often lacks inflammation. Ligaments are ropy fibrous bands of tissue that connect bones to other bones. The condyles of the femur and of the tibia come in close proximity to form the main structure of the joint.
The acl is located in the center of the knee joint and runs from the femur thigh bone to the tibia shin bone through the center of the knee. Anatomy of the knee. Inside the capsule is the synovial membrane which is lined by the synovium a soft tissue structure that secretes synovial fluid the lubricanr of the knee.
Patellar tendinosis also known as jumpers knee this is an overuse injury characterized by repeated microscopic tears of the tendon and degeneration of the normal collagen structure. The image below depicts the normal anatomy of the knee. Soft tissue anatomy anterior cruciate ligament acl the anterior cruciate ligament acl is the major stabilizing ligament of the knee.
The most common ligament injuries are acl tears mcl tears. In knee joint anatomy they are the main stabilising structures of the knee acl pcl mcl and lcl preventing excessive movements and instability. Bones and soft tissues the main parts of the knee joint are the femur tibia patella and supporting ligaments.
Medial Patellofemoral Ligament Reconstruction Kogarah Nsw
 What Is Arthrofibrosis Knee Doctor Near Me Dr Roger Chams
What Is Arthrofibrosis Knee Doctor Near Me Dr Roger Chams
 Hip Thigh And Knee Ppt Download
Hip Thigh And Knee Ppt Download
 Knee Joint Anatomy Bones Ligaments Muscles Tendons Function
Knee Joint Anatomy Bones Ligaments Muscles Tendons Function
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11078/bones-knee-tibia-fibula_english.jpg) Leg And Knee Anatomy Bones Muscles Soft Tissues Kenhub
Leg And Knee Anatomy Bones Muscles Soft Tissues Kenhub
 The Knee Anatomy Injuries Treatment And Rehabilitation
The Knee Anatomy Injuries Treatment And Rehabilitation
 Deep And Superficial Mcl And Acl Double Bundle Anatomy
Deep And Superficial Mcl And Acl Double Bundle Anatomy
 Knee Joint Anatomy Pictures And Information
Knee Joint Anatomy Pictures And Information
 Iliotibial Band Syndrome Wikipedia
Iliotibial Band Syndrome Wikipedia
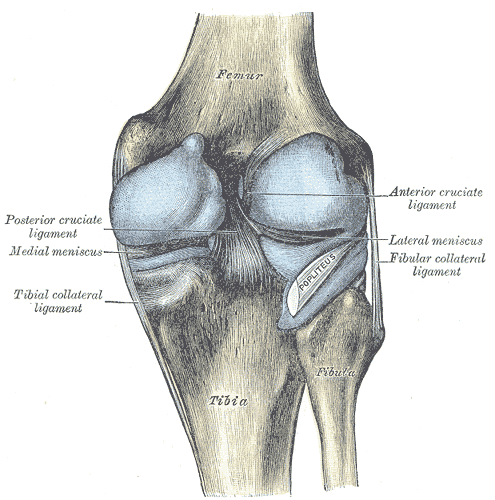 Posterior Knee Pain Physiopedia
Posterior Knee Pain Physiopedia
 A Guide To Your Knees Well Guides The New York Times
A Guide To Your Knees Well Guides The New York Times
 Knee Joint Anatomy Pictures And Information
Knee Joint Anatomy Pictures And Information
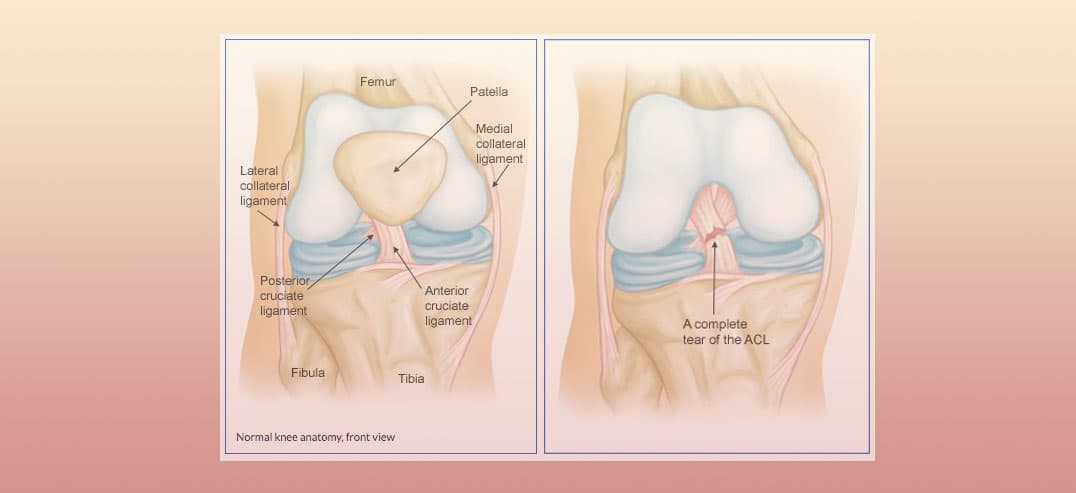 Knee Sprain Aka Anterior Cruciate Ligament Sprain
Knee Sprain Aka Anterior Cruciate Ligament Sprain
 Knee Arthroscopy Ackland Sports Medicine
Knee Arthroscopy Ackland Sports Medicine
 Novobrace Tendonitis Desmitis And Soft Tissue Injury
Novobrace Tendonitis Desmitis And Soft Tissue Injury
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Morphopedics
 Soft Tissue Injuries What Are They How Can You Best Recover
Soft Tissue Injuries What Are They How Can You Best Recover
 Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
Joints Ligaments And Connective Tissues Advanced Anatomy
.ashx)
 The Knee Resource Patellar Dislocation Subluxation
The Knee Resource Patellar Dislocation Subluxation
 Knee Arthroscopy Orthoinfo Aaos
Knee Arthroscopy Orthoinfo Aaos
 Physical Examination Of The Knee Musculoskeletal Key
Physical Examination Of The Knee Musculoskeletal Key
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11077/175_176_177_178_179_tibia_extensors_nn.png) Leg And Knee Anatomy Bones Muscles Soft Tissues Kenhub
Leg And Knee Anatomy Bones Muscles Soft Tissues Kenhub
Soft Tissue Knee Patient Information Gavin Mchugh
 Evaluation Of Patients Presenting With Knee Pain Part I
Evaluation Of Patients Presenting With Knee Pain Part I
 Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Orthoinfo Aaos
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome Orthoinfo Aaos
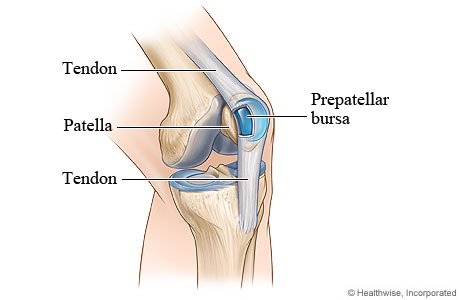 Tiny Bursa Balloons To Bursitis Direct Orthopedic Care
Tiny Bursa Balloons To Bursitis Direct Orthopedic Care
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Knee Soft Tissue Anatomy"
Posting Komentar