Horseshoe Crab Anatomy
The entire body of the horseshoe crab is protected by a hard carapace. These are used primarily for finding mates but the horseshoe has many more light sensing organs.
 Anatomy Delaware Bay Horseshoe Crab Survey
Anatomy Delaware Bay Horseshoe Crab Survey
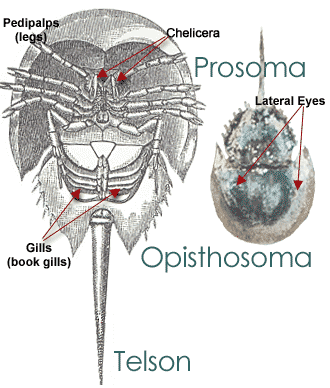
The prosoma the front most section the opisthosoma the mid region and the telson that sword like tail.
Horseshoe crab anatomy. You can also remember them as the cephalothorax which is a fused head and thorax region the abdomen and the tail respectively. The prosoma the opisthosoma and the telson. These are the first ambulatory legs.
An ancient and complex anatomy hides within its domed shell. The atlantic horseshoe crab limulus polyphemus also known as the american horseshoe crab is a species of marine and brackish chelicerate arthropod. A horseshoe crab absorbs oxygen from the water using gills that are divided into.
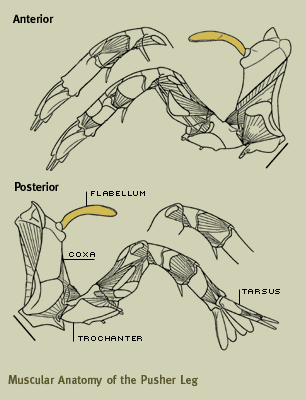
In the adult male the tarsus of these legs are modified as a grasping appendage allowing males to clasp the female during spawning. However they can also feed on algae. The horseshoe crab for many the horseshoe crab is a childhood acquaintance first introduced by a fierce looking shell on a sandy beach.
For ecologists the horseshoe is an important creature a vastly adaptable generalist that predates most species on the planet with a lifecyle that is interlocked with other animals. Horseshoe crabs are generally predators of different species of annelids molluscs as well as of other groups of benthic invertebrates. The horseshoe uses the first pair the chelicera for placing food in its mouth.
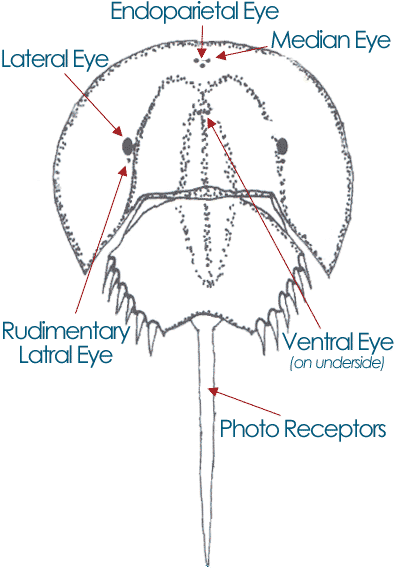
The horseshoe crab has been on earth for 350 million years. These are sometimes referred to as the cephalothorax the abdomen and the tail. A quick glance at the horseshoe will show the crabs two compound lateral eyes unusual because no other living chelicerate possesses compound eyes.
The next pair of appendages are the pedipalps. A look at the underside of the horseshoe reveals six paired appendages. These are sometimes referred to as the cephalothorax the abdomen and the tail.
It has two compound lateral eyes each composed of about 1000 ommatidia plus a pair of median eyes that are able to detect both visible light and ultraviolet light a single endoparietal eye and a pair of rudimentary lateral eyes on the top. The horseshoe crab uses its telson to steer and right itself if it becomes inverted in. There are three divisions to the body of the horseshoe crab.
American horseshoe crab telson. Externally horseshoe crabs can be divided into three sections. Despite their name horseshoe crabs are more closely related to spiders ticks and scorpions than to crabs.
Horseshoe crabs have a total of 10 eyes used for finding mates and sensing light.
 Horseshoe Crab Anatomy Picture Of Coastal Expeditions
Horseshoe Crab Anatomy Picture Of Coastal Expeditions
Imagequiz Biol212 Horseshoe Crab External Anatomy
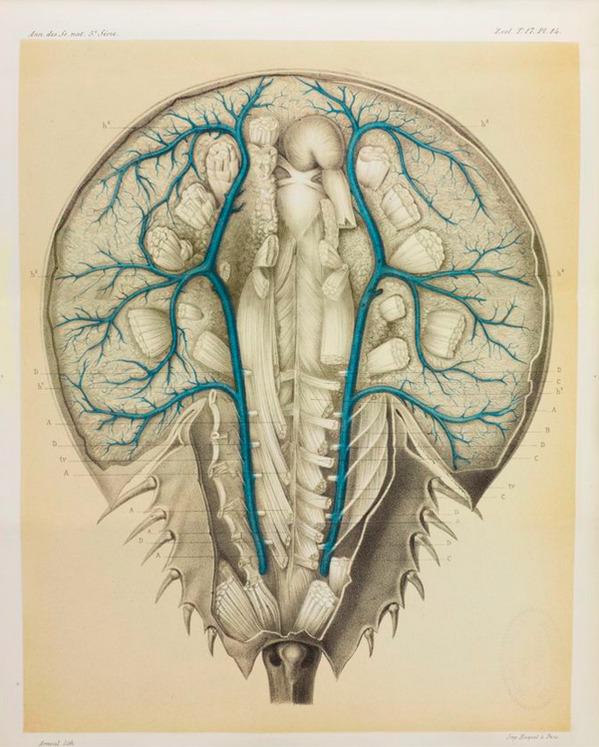 Baby Blue Blood Drive Radiolab Wnyc Studios
Baby Blue Blood Drive Radiolab Wnyc Studios
 Horseshoe Crab Anatomy Carol Vinzant Flickr
Horseshoe Crab Anatomy Carol Vinzant Flickr
Luther Vandross Horseshoe Crab Anatomy
Horseshoe Crabs Everything You Need To Know About This Species
 Mineralization Of Soft Part Anatomy And Invading Microbes In
Mineralization Of Soft Part Anatomy And Invading Microbes In
 Like Pages Of A Book Gills Helen Cheng
Like Pages Of A Book Gills Helen Cheng
 Poster Anatomy Of The Horseshoe Crab
Poster Anatomy Of The Horseshoe Crab
 Horseshoe Crab Marine Biology Biology Horseshoe Crab
Horseshoe Crab Marine Biology Biology Horseshoe Crab
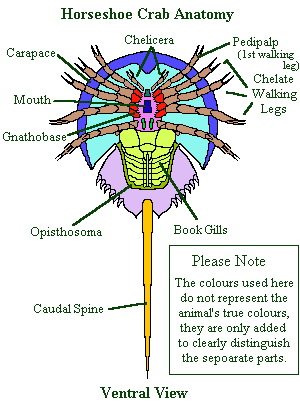 The Earthlife Web Horseshoe Crabs Class Merostomata
The Earthlife Web Horseshoe Crabs Class Merostomata
 Horseshoe Crab Biography Of A Survivor Anthony D
Horseshoe Crab Biography Of A Survivor Anthony D
 Horseshoe Symbiosis The 24 Natural Treasures Of Christmas
Horseshoe Symbiosis The 24 Natural Treasures Of Christmas
 Horseshoe Crab Anatomy Horseshoe Crab Fish Ocean
Horseshoe Crab Anatomy Horseshoe Crab Fish Ocean
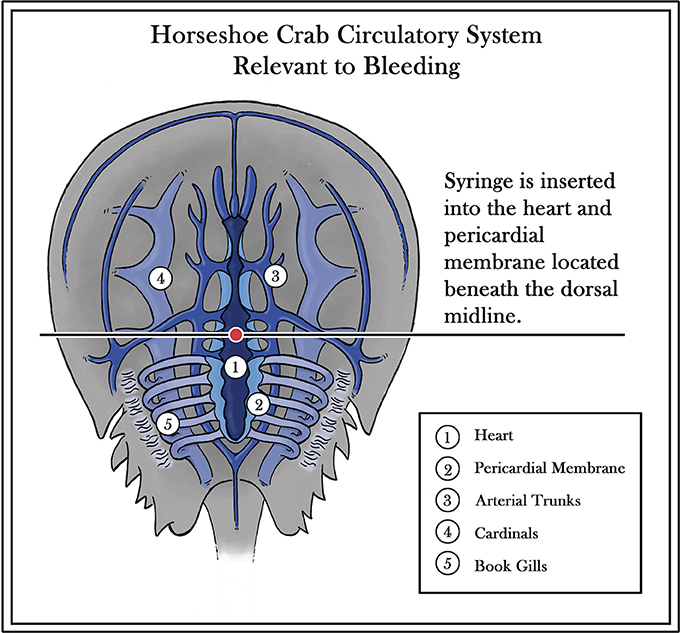 Frontiers The Role Of Horseshoe Crabs In The Biomedical
Frontiers The Role Of Horseshoe Crabs In The Biomedical
 Quiz Worksheet Horseshoe Crab Anatomy Study Com
Quiz Worksheet Horseshoe Crab Anatomy Study Com

Horseshoe Crabs Everything You Need To Know About This Species
 Horseshoe Crabs Marinebio Conservation Society
Horseshoe Crabs Marinebio Conservation Society


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Horseshoe Crab Anatomy"
Posting Komentar