Vein Anatomy Arm
The basilic vein originates from the dorsal venous network of the hand and ascends the medial aspect of the upper limb. The cephalic and basilic veins are major superficial veins of the forearm.
 Shoulder Thumb Vein Arm Augsdelms Arm
Shoulder Thumb Vein Arm Augsdelms Arm
Making its way through the basilic vein is the median basilica vein located in the lower part of the elbow which works as a communicator in the arm.

Vein anatomy arm. Blood clots develop when blood cells known as platelets or thrombocytes become activated due to a vein injury or disorder. The major superficial veins of the upper limb are the cephalic and basilic veins. The deep veins for the most part accompany arteries within the fascial sleeve whereas the superficial veins lie for most of their course outside the fascial sleeve.
The arteries deliver freshly oxygenated blood to muscles and bone. Continue from the axillary vein checking in transverse that the basilic and brachial veins of the upper arm are compressible. From the radial side lateral side of the forearm the cephalic vein runs up from the anatomical snuffbox along the preaxial border of the upper limb.
Within the tight sleeve of the deep fascia as is seen in the lower limbs. The veins return oxygen. The vessels of the arms are part of the circulatory system which provides nutrients to the tissues.
At the border of the teres major the vein moves deep into the arm. Blockages occur due to blood clots that develop in either superficial veins or deep veins most often in the legs or arms. This becomes still more effective.
Upper arm veins brachial basilic the basilic vein is the larger and is more superficial. Muscular contractions press on the veins and form a very effective mechanism of venous return. Deep veins and superficial veins.
Usually single but may be duplicated. Vein problems are typically the result of a blockage or defect. As you reach the proximal arm the axillary vein will divide into the basilic and brachial veins.
Continuing upwards through the forward part of the elbow the cephalic vein makes its way through the valley created by the biceps brachii and the brachioradialis on either side of it. They are located within the subcutaneous tissue of the upper limb. The veins of the arm may be divided into two groups.
 Circulatory Routes Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
Circulatory Routes Boundless Anatomy And Physiology
 Finger Foot Human Leg Vein Human Anatomy Png Clipart
Finger Foot Human Leg Vein Human Anatomy Png Clipart
 Thumb Elbow Arm Anatomy Vein Png 600x600px Watercolor
Thumb Elbow Arm Anatomy Vein Png 600x600px Watercolor
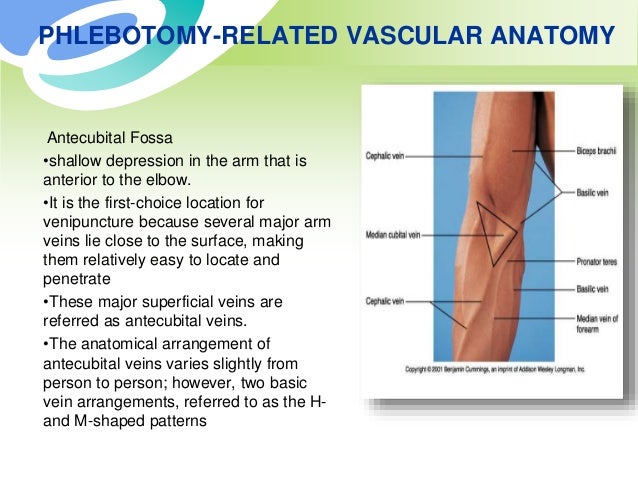 Phlebotomy Related Vascular Anatomy
Phlebotomy Related Vascular Anatomy
 Veins Of The Arm Anatomy Study Buddy
Veins Of The Arm Anatomy Study Buddy
 Arm Dvt Normal Ultrasoundpaedia
Arm Dvt Normal Ultrasoundpaedia
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Arm
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcore Em
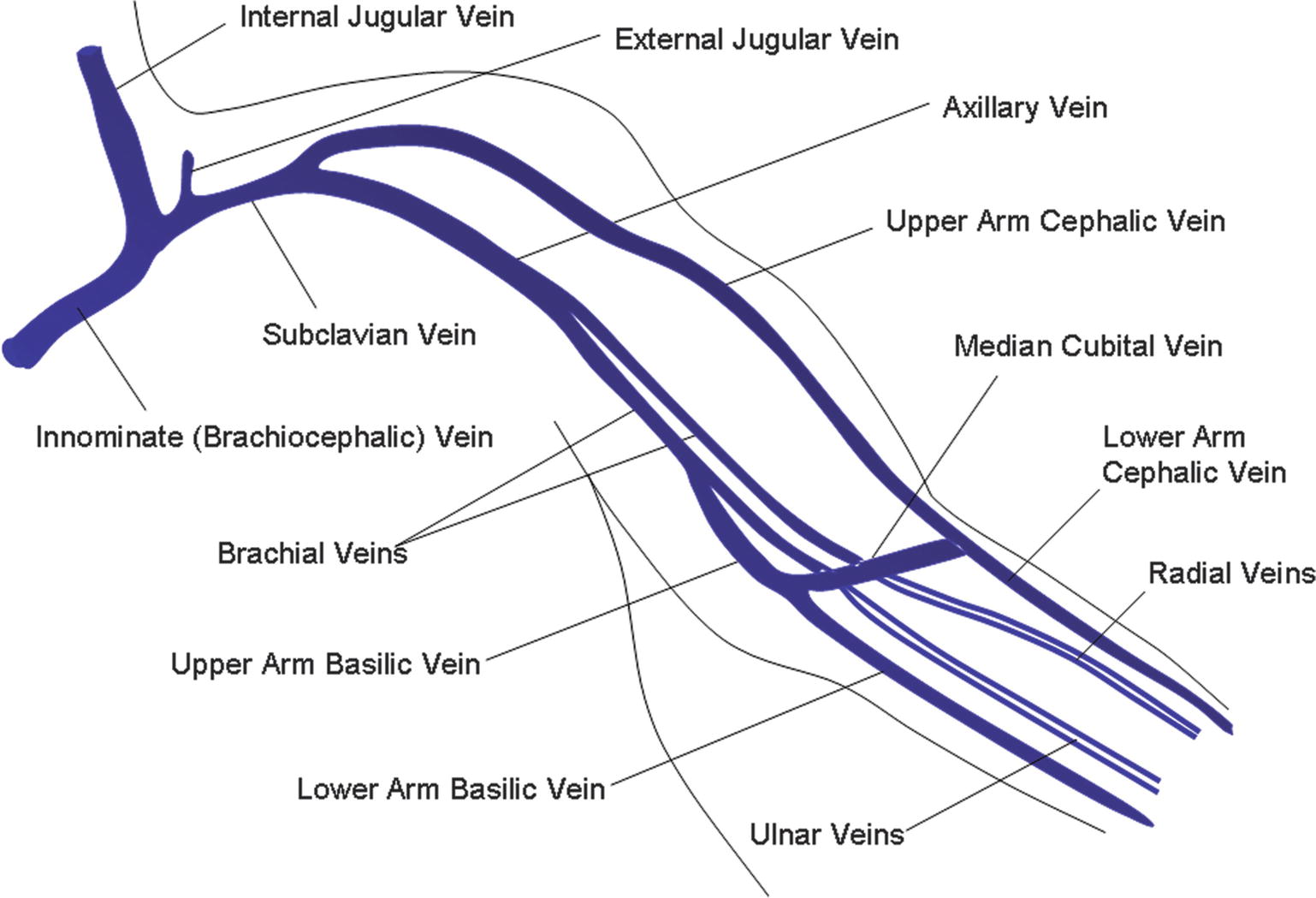 Upper Extremity Venous Thrombosis Thoracic Key
Upper Extremity Venous Thrombosis Thoracic Key
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/771/PoKFfwUGXrJ4sytwNutLA_upper-arm-nerves-vessels_english.jpg) Cephalic Vein Anatomy And Clinical Points Kenhub
Cephalic Vein Anatomy And Clinical Points Kenhub
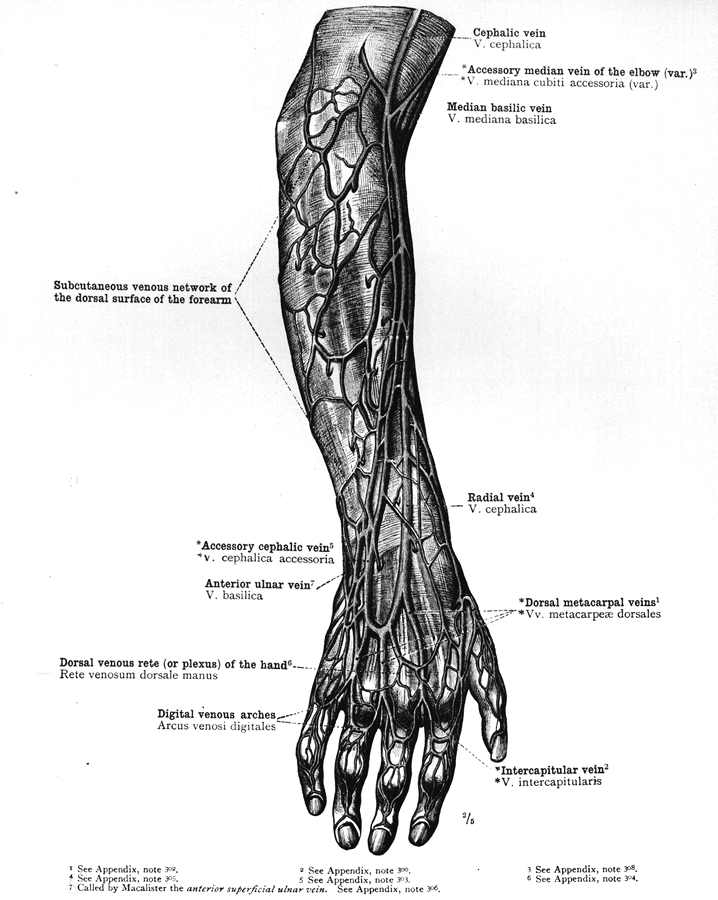 Anatomy Atlases Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Human Anatomic
Anatomy Atlases Illustrated Encyclopedia Of Human Anatomic
 Anatomy Veins Of The Hand And Forearm Critical Care
Anatomy Veins Of The Hand And Forearm Critical Care
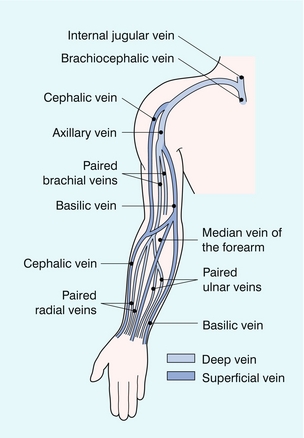 The Peripheral Veins Clinical Gate
The Peripheral Veins Clinical Gate
 Vein Elbow Forearm Anatomy Artery Png Clipart Abdomen
Vein Elbow Forearm Anatomy Artery Png Clipart Abdomen
 Names Of Veins In The Arm Anatomy And Physiology Medical
Names Of Veins In The Arm Anatomy And Physiology Medical
 Anatomy Of Gsv And Ssv With Common Variants Of Ssv Gsv
Anatomy Of Gsv And Ssv With Common Variants Of Ssv Gsv
 Cephalic Vein Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Cephalic Vein Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
 Nerves Blood Vessels And Lymph Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
Nerves Blood Vessels And Lymph Advanced Anatomy 2nd Ed
 Chapter 33 Venous And Intraosseous Access In Adults
Chapter 33 Venous And Intraosseous Access In Adults
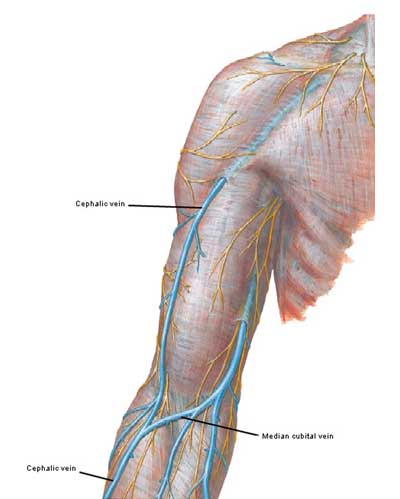 Frank Netter Page 8 Outlander Anatomy
Frank Netter Page 8 Outlander Anatomy
Upper Extremity Veins Human Anatomy
 Brachial Veins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Brachial Veins An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Cephalic Vein Circulatory System Anatomy Human Body Arm
Cephalic Vein Circulatory System Anatomy Human Body Arm
 Medical Illustration Of Arteries Veins And Lymphatic System In Hand And Arm Poster
Medical Illustration Of Arteries Veins And Lymphatic System In Hand And Arm Poster
 Arm Anatomy Part 1 Muscles Arteries And Veins
Arm Anatomy Part 1 Muscles Arteries And Veins

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Vein Anatomy Arm"
Posting Komentar