Anatomy Of Forearm
Eight in the palm side and 12 in the back side. The radius is located on the side of the forearm closest to the thumb.
 The Basic Anatomy Of The Human Forearm The Red Areas
The Basic Anatomy Of The Human Forearm The Red Areas
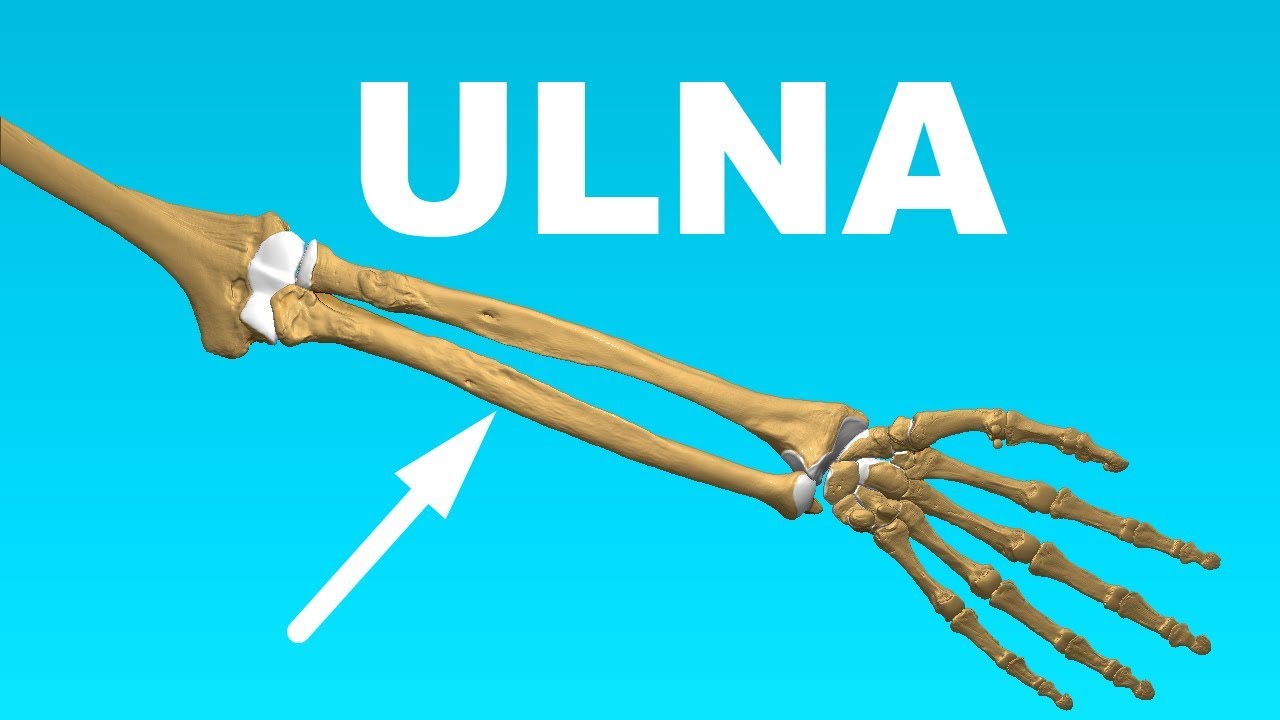
Its two major bones are the radius and the ulna.
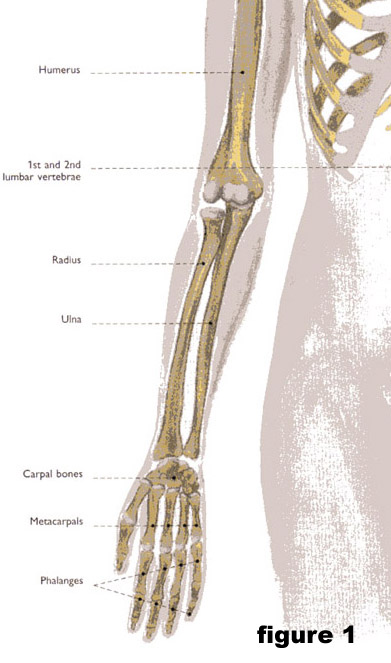
Anatomy of forearm. The forearm consists of two long bones. Deep fascia attachment along the posterior border of the ulna. Anatomy of arm in arm part is then called the forearm.
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The ulna is located medially and is both longer and larger than the radius which runs parallel to it laterally. The flexor digitorum superficialis is the only muscle.
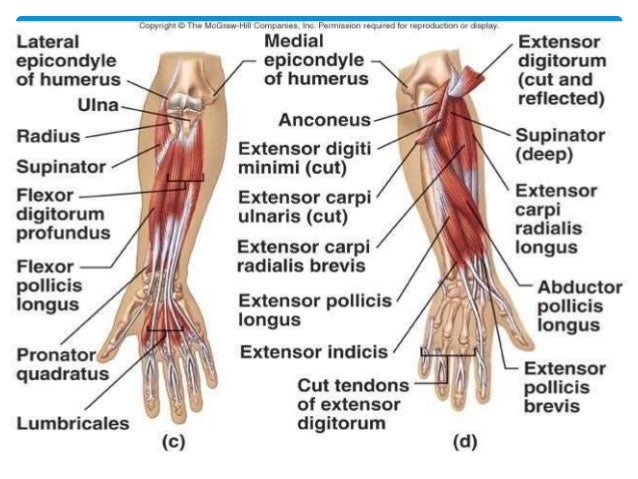
These forearm bones articulate with each other in two locations. These two bones are held together by the intervening interosseous membrane. Muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm superficial compartment.
Sigmoidsemilunar trochlear notch anteriorly composed of coronoid process posteriorly. Beneath the skin and the fat stored just beneath the skin are 20 muscles. The forearm is the lower portion of the arm found between the elbow and wrist joints.
In brachiating tree swinging primates the arm is unusually long. The forearm is the area between the elbow joint and the wrist. The superficial muscles in the anterior compartment are.
The structures dividing the forearm into these compartments are as follows. All land vertebrates have this bone. Radius in radius the two bones of the forearm when viewed with the palm facing forward.
The radius and the ulna. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb but which in anatomy technically means only the region of the upper arm whereas the lower arm is called the forearm. Started in 1995 this collection now contains 6591 interlinked topic pages divided into a tree of 31 specialty books and 721 chapters.
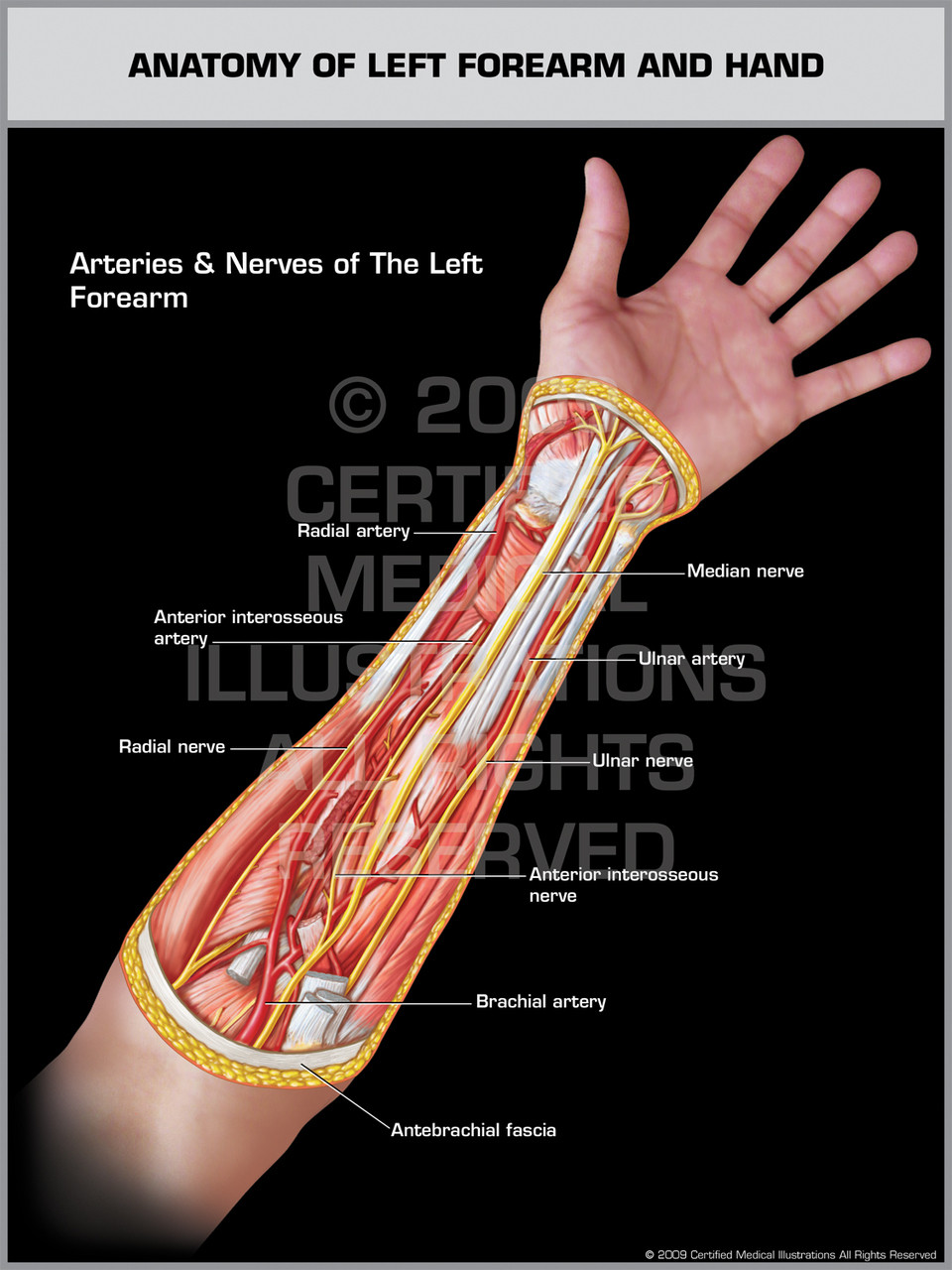
Supplying these muscles are several major arteries and nerves namely the ulnar artery and median. Lateral intermuscular septum that extends from the anterior border of the radius to the deep fascia around the upper limb. Content is updated monthly with systematic literature reviews and conferences.
Anatomy of forearm 1. Function and structure of. Anatomy of forearm essex lopresseti injury plastic deformation of forearm approaches to forearm.
Additionally the biceps brachii operates as a supinator of the forearm by rotating the radius and moving the palm of the hand anteriorly. Bon articulations and ligament muscles nerve and blood vessels anatomy. On the posterior side of the upper arm is the triceps brachii which acts as an extensor of the forearm at the elbow and the humerus at the shoulder.
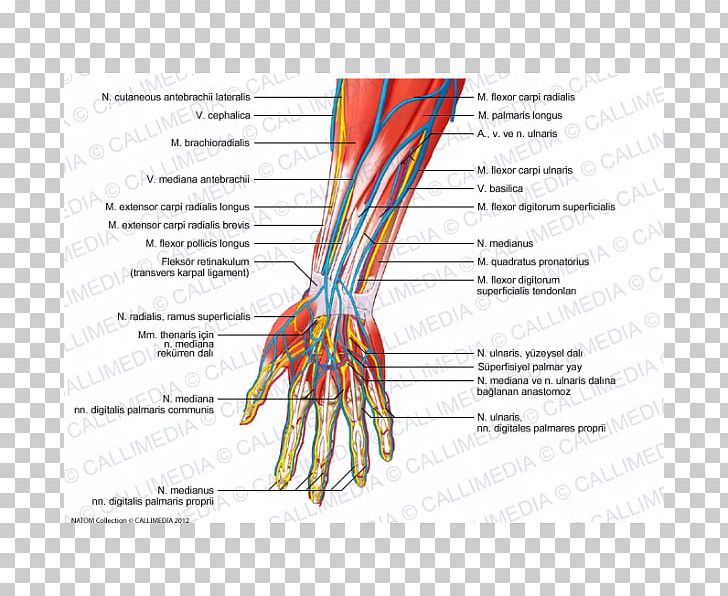 Forearm Radial Nerve Human Anatomy Png Clipart Anatomy
Forearm Radial Nerve Human Anatomy Png Clipart Anatomy
 Elbow Forearm Atlas Of Anatomy
Elbow Forearm Atlas Of Anatomy
 Muscles That Rotate The Forearm Acland S Video Atlas Of
Muscles That Rotate The Forearm Acland S Video Atlas Of
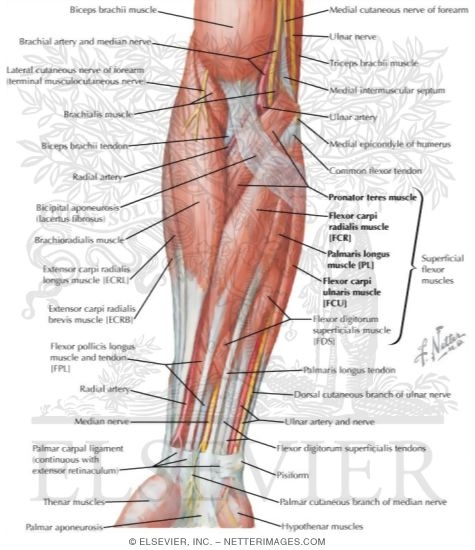 Muscles Of Forearm Superficial Layer Anterior View
Muscles Of Forearm Superficial Layer Anterior View
 Anatomy Of Forearm Muscles Anterior View Middle Poster
Anatomy Of Forearm Muscles Anterior View Middle Poster
 Iv Myology 7e The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Gray
Iv Myology 7e The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Gray
Forearm Radiographic Anatomy Wikiradiography
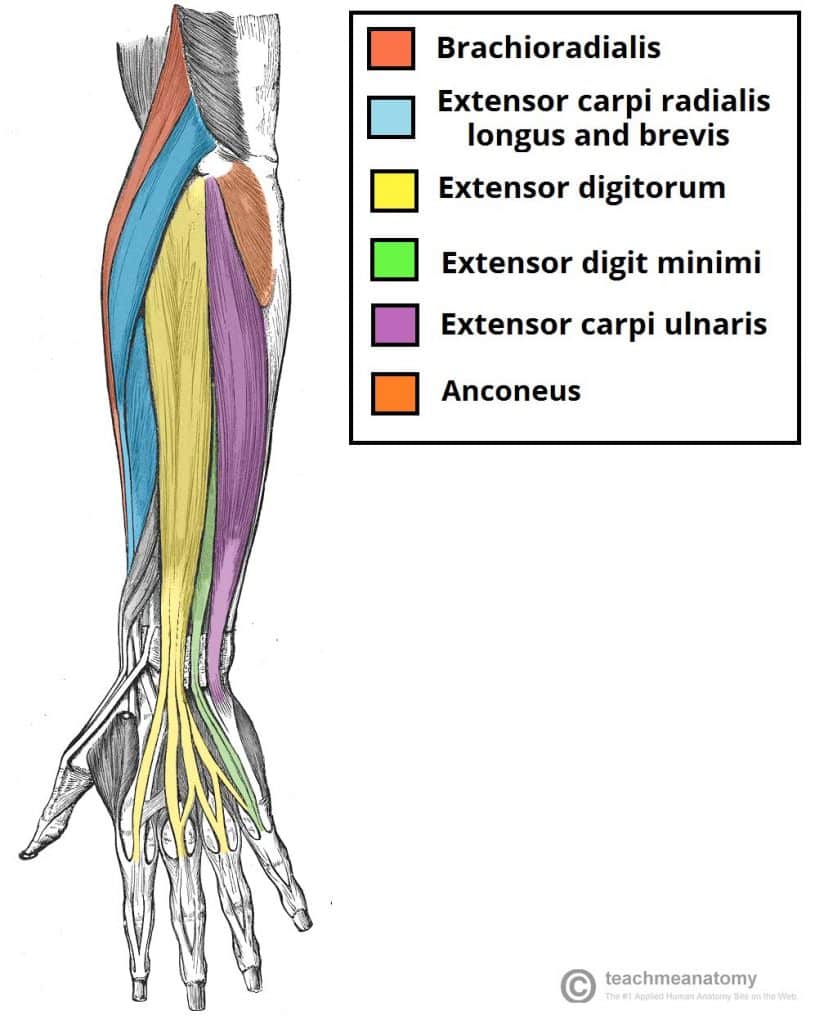 Muscles Of The Posterior Forearm Superficial Deep
Muscles Of The Posterior Forearm Superficial Deep
 Forearm Muscles Anatomy Support Movement
Forearm Muscles Anatomy Support Movement
 Anatomy Of Human Forearm Muscles Deep
Anatomy Of Human Forearm Muscles Deep
 Surface Anatomy Of The Forearm
Surface Anatomy Of The Forearm
 The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Human Anatomy
The Muscles And Fasciae Of The Forearm Human Anatomy
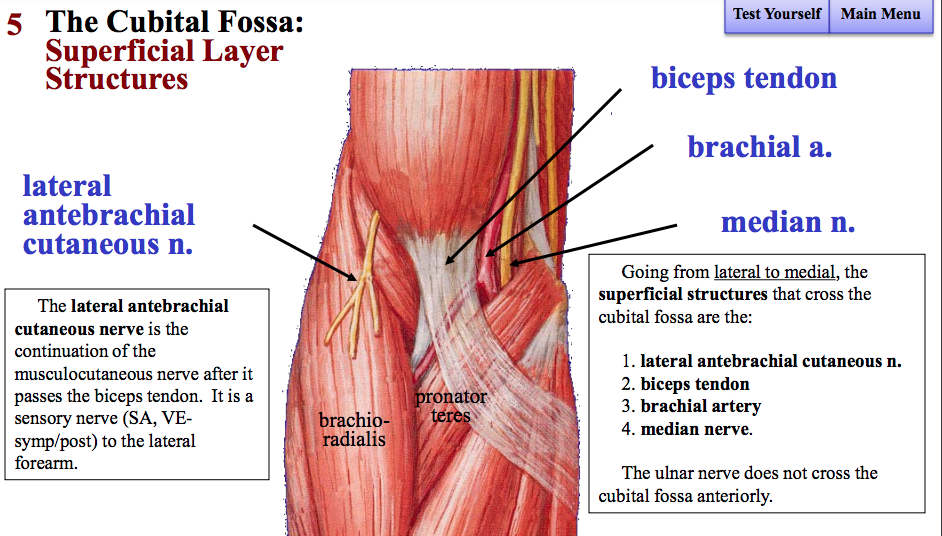
 Human Anatomy For The Artist The Ventral Forearm What Are
Human Anatomy For The Artist The Ventral Forearm What Are
 Anatomy Of Forearm Wrist And Hand Health And Fitness Wall Chart Poster Chartex Ltd
Anatomy Of Forearm Wrist And Hand Health And Fitness Wall Chart Poster Chartex Ltd
 Elbow Forearm Atlas Of Anatomy
Elbow Forearm Atlas Of Anatomy
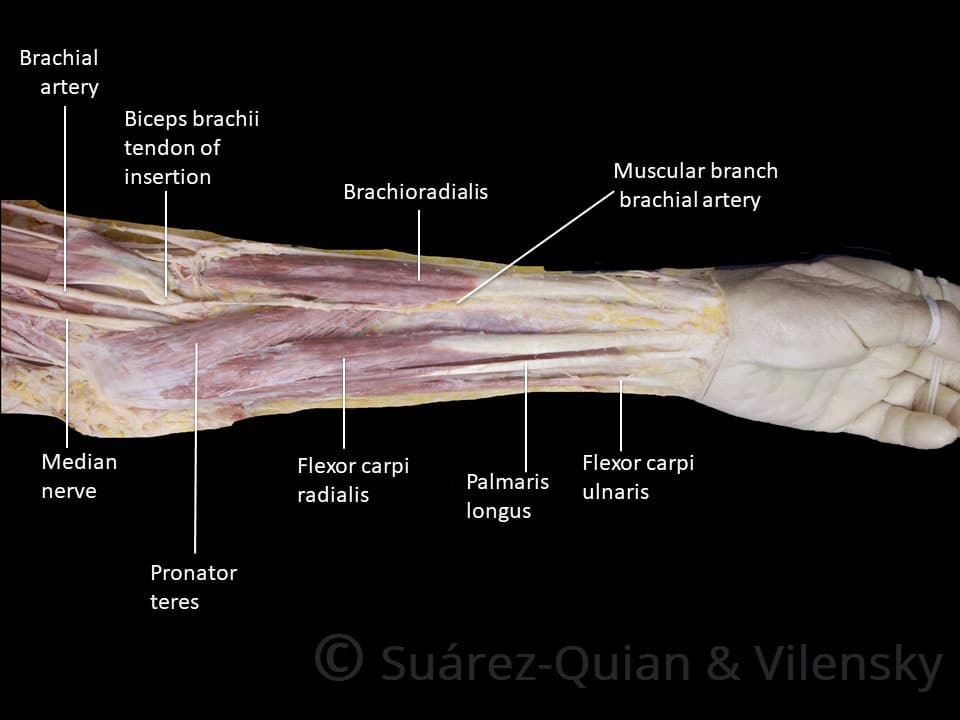 Muscles Of The Anterior Forearm Flexion Pronation
Muscles Of The Anterior Forearm Flexion Pronation
 Anatomy Forearm Hand Elbow Print Sra3 12x18 Conqueror Laid
Anatomy Forearm Hand Elbow Print Sra3 12x18 Conqueror Laid
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/253/EbSgbtSfLFUdccIX9rSQ_forearm-flexor-muscles_english.jpg) Diagram Pictures Flexors Of The Forearm Anatomy Kenhub
Diagram Pictures Flexors Of The Forearm Anatomy Kenhub
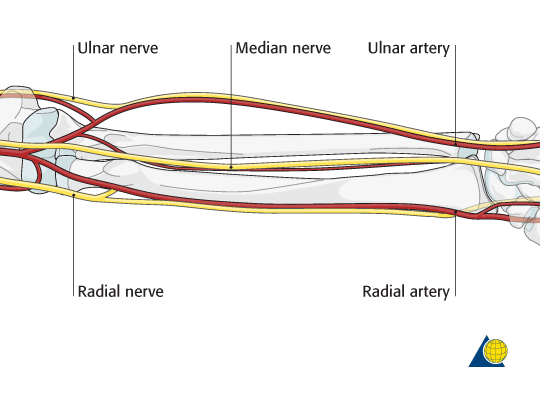 Common Forearm Nerve Blocks Core Em
Common Forearm Nerve Blocks Core Em
 Forearm Muscles Of Anterior Compartment Superficial Middle
Forearm Muscles Of Anterior Compartment Superficial Middle
 Amazon Com Anatomy Forearm Elbow Tendons Print Sra3 12x18
Amazon Com Anatomy Forearm Elbow Tendons Print Sra3 12x18
 Forearm Blood Supply Anatomy Orthobullets
Forearm Blood Supply Anatomy Orthobullets
 Anatomy Of The Volar Forearm Part 1 Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
Anatomy Of The Volar Forearm Part 1 Everything You Need To Know Dr Nabil Ebraheim
 Anterior Forearm Deep Anatomy Gray S Illustration
Anterior Forearm Deep Anatomy Gray S Illustration
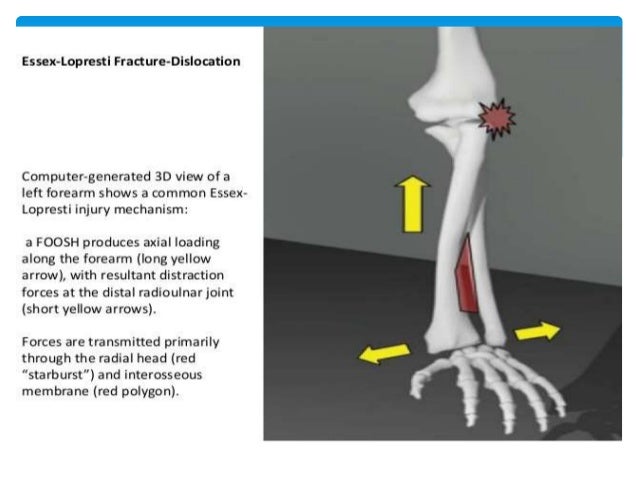
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Forearm"
Posting Komentar