Anatomy Of A Grapevine
All cells have the same general organization consisting of a cell wall protoplasm liquid filled region containing living organelles and the vacuole region containing the cell sap. The anatomy of a grapevine plays an important role in the success of a vine prevention of disease and the varietal character of its fruit.
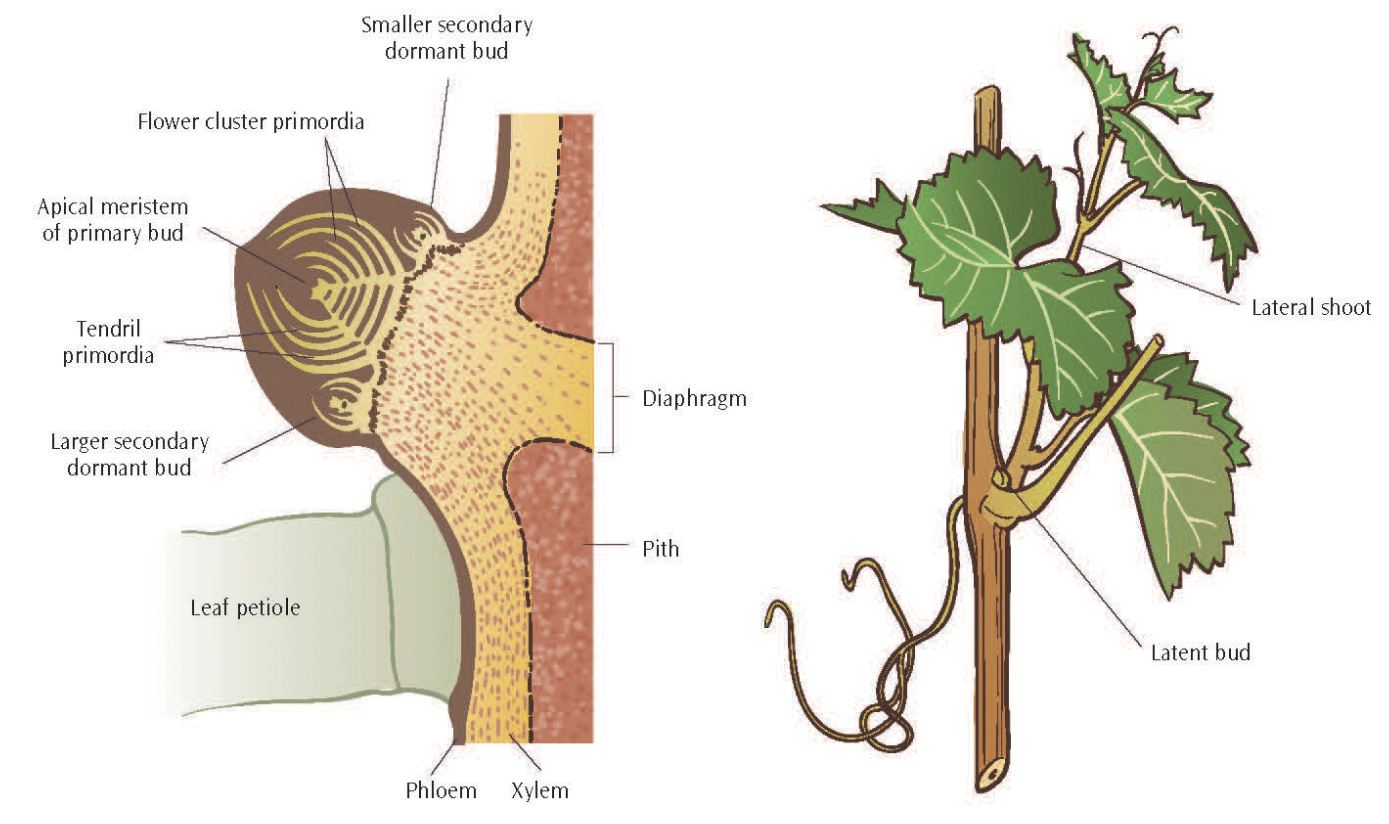 Important Structures Features Of Grapevines Lodi Growers
Important Structures Features Of Grapevines Lodi Growers
Usually the grapevine only produces fruit on canes that grew from the buds of the previous year.
%2C445%2C291%2C400%2C400%2Carial%2C12%2C4%2C0%2C0%2C5_SCLZZZZZZZ_.jpg)
Anatomy of a grapevine. The broad part of a leaf is a. Grapevine structure cells and tissues the basic unit of plant structure and function is the cell. The anatomy of a grape.
Although some grape vines are grown on their own roots. The seeds closest to the inside of the grape are the seeds. Red wines in particular get most of their flavor and spunk from the skins.
Merely pressing red grapes and fermenting the juice results in what the french call blanc de noir meaning white wine from red grapes or literally white from black. The anatomy of the grape the skin the skin of each grape is anywhere from six to 10 cells thick and though it is thin. The parts that make the whole.
This basic cell structure is modified to create different cell types that. Shoots the green stems which develop from primary buds. The roots of a grape vine are multi branched structures that reach.
Grapevine anatomy scion above graft part of vine. Anatomy of a grape vine roots. The pulp pulp comprises the majority of each grape and it rests just under the layer of skin on the grape.
Nutrient and water absorption no roots no grapes. Grapevine is a climber which naturally grows on the trees and bushes high and in wide shapes. Like any other plant also grapevine has its underground and above ground part.
By the spring the canes will have become one year old wood. Eg cabernet sauvignon or riesling rootstock root system for grafted vine roots. Often the images that come to mind when we think of a grapevine are of twisting flaky cocoa colored vines large vibrant overlapping leaves twisting tendrils and heavy hanging bunches of ripe grapes.
Anatomy of a grapevine. In the vineyard its growth is maintained with the pruning in order to control the quantity and quality of the grapes. During the winter the mature shoots turn woody and become the new canes.
 Graphic Showing Anatomy Of A Grape Vine Grape Vine Plant
Graphic Showing Anatomy Of A Grape Vine Grape Vine Plant
 Grapevine Triangle Wines Vines Analytics
Grapevine Triangle Wines Vines Analytics
 Grapes 101 Viticulture And Enology
Grapes 101 Viticulture And Enology
Grapevine Anatomy Soldier Creek Winery
 Anatomy Of A Grapevine Familia Torres
Anatomy Of A Grapevine Familia Torres
 World Of Wine Grapevine Anatomy
World Of Wine Grapevine Anatomy
 Anatomy Of A Grape Vine Garden Guides
Anatomy Of A Grape Vine Garden Guides
 Free Content Virtual Viticulture Academy
Free Content Virtual Viticulture Academy
Grape Cluster And Berries Structure
Grape Cluster And Berries Structure
 Grapevine Anatomy Grape Vine Trellis Grape Vines Vine
Grapevine Anatomy Grape Vine Trellis Grape Vines Vine
 A Illustration Showing The Anatomy Of The Grapevine Woody
A Illustration Showing The Anatomy Of The Grapevine Woody
 Figure 3 From The Peripheral Xylem Of Grapevine Vitis
Figure 3 From The Peripheral Xylem Of Grapevine Vitis
%2C445%2C291%2C400%2C400%2Carial%2C12%2C4%2C0%2C0%2C5_SCLZZZZZZZ_.jpg) Amazon Com The Science Of Grapevines Anatomy And
Amazon Com The Science Of Grapevines Anatomy And
 Fruit Set In Grapevines 101 Penn State Extension Wine
Fruit Set In Grapevines 101 Penn State Extension Wine
Water Uptake Along The Length Of Grapevine Fine Roots
 Lecture 03 Ven2 2018 Pdf Ven2 Lecture 3 Grapevine Anatomy
Lecture 03 Ven2 2018 Pdf Ven2 Lecture 3 Grapevine Anatomy
 Grape Anatomy And Physiology Springerlink
Grape Anatomy And Physiology Springerlink
 Parts Of The Grape Vine Shoots Grapes
Parts Of The Grape Vine Shoots Grapes
 Grape And Wine Metabolites Biotechnological Approaches To
Grape And Wine Metabolites Biotechnological Approaches To
 Second Life Marketplace Vitis Vinifera Anatomy Of A
Second Life Marketplace Vitis Vinifera Anatomy Of A
 Making Wine In The Vineyard Anatomy Of A Grapevine
Making Wine In The Vineyard Anatomy Of A Grapevine
 Parts Of The Grape Vine Flowers And Fruit Grapes
Parts Of The Grape Vine Flowers And Fruit Grapes
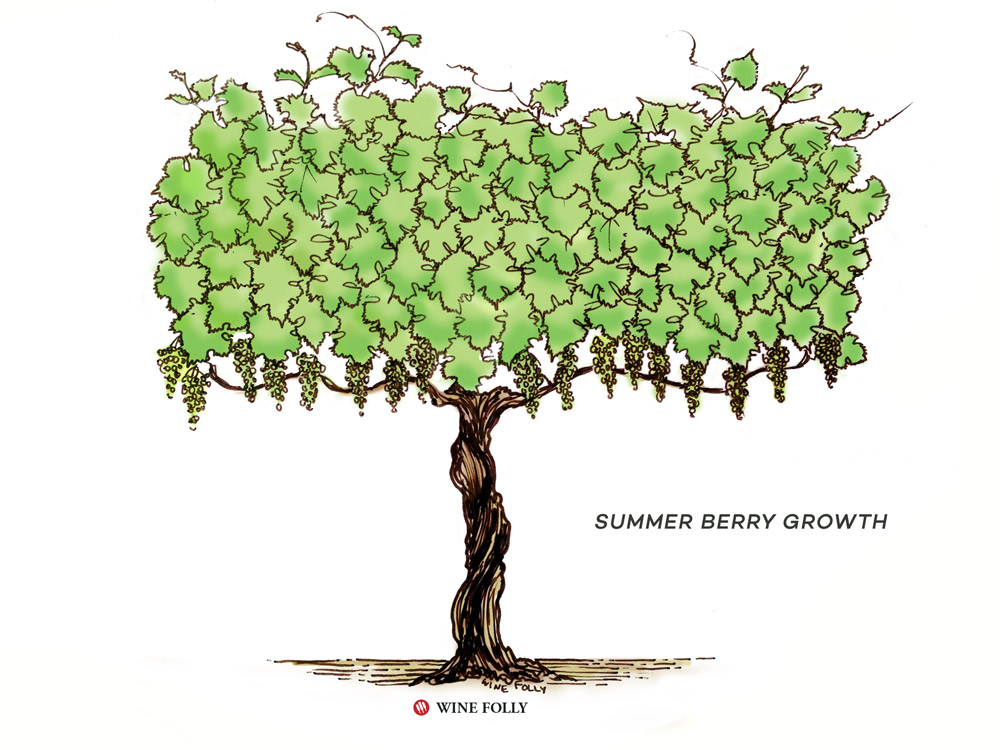 Lifecycle Of A Wine Grapevine Wine Folly
Lifecycle Of A Wine Grapevine Wine Folly


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of A Grapevine"
Posting Komentar