Ecg Anatomy
Heart muscle that is irritated conducts electricity differently than heart muscle that is normal. A double membrane that covers the outside of the heart.
 Chest Leads Ecg Lead Placement Normal Function Of The
Chest Leads Ecg Lead Placement Normal Function Of The
Ecg exigency and cardiovascular curveball ecg clinical cases.

Ecg anatomy. The ecg measures the electrical activity of the heart. Ecg library basics waves intervals segments and clinical interpretation. The electrodes are wires that you attach to the patient to record the ecg.
Most often the ecg assessment includes the following. Abnormal conduction may be apparent. These electrodes allow leads to be calculated.
A quivering ventricular muscle that is unable to pump blood. Thick muscular wall that separates the heart into right and l. What is an ecg.
Basic cardiac anatomy anatomy of the heart introduction to electrocardiology and ecg interpretation cardiac electrophysiology. Lead refers to an imaginary line between two ecg electrodes. Ecg a to z by diagnosis ecg interpretation in clinical context.
Middle layer of the heart that is made of muscle tissue. 100 ecg quiz self assessment tool for examination practice. An ecg is recorded by placing electrodes on the surface of the skin.
The electrocardiogram or ecg is a simple diagnostic test which records the electrical activity of the heart over a set time period via this exam tips post helps us to understand the anatomy and physiology behind the ecg and how to interpret it. There are 12. Anatomy of the heart ecg.
The letters ecg stand for electro cardiogram. This electrical activity controls the heart beat. Determination of the rate assessment of the rhythm evaluation of the electrical conduction patterns.
Focus topic heart anatomy and physiology the human heart is a hollow cone shaped muscular organ roughly the size of its owners fist that weighs approximately 9 to 12 oz 250 350 g size of the human heart. What is happening when the ventricles are filling. Action potentials and electrical vectors.
Ecg reference sites and books the best of the rest. A smooth layer of cells that lines the inside of the heart b. How it all works electrodes.
The 12 lead ecg.
Cardiocollege E Xpert Ecg E Learning
 Partonomy Of Anatomy For The Ecg The Lines Represent Part
Partonomy Of Anatomy For The Ecg The Lines Represent Part
 Ecg Educator Blog Coronary Artery Anatomy
Ecg Educator Blog Coronary Artery Anatomy
 Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 141 Ischemia
Ecg Interpretation Ecg Interpretation Review 141 Ischemia
 Understanding An Ecg Geeky Medics
Understanding An Ecg Geeky Medics
 Acute Chronic Knowledge Acquisition Case Study Ecg And
Acute Chronic Knowledge Acquisition Case Study Ecg And
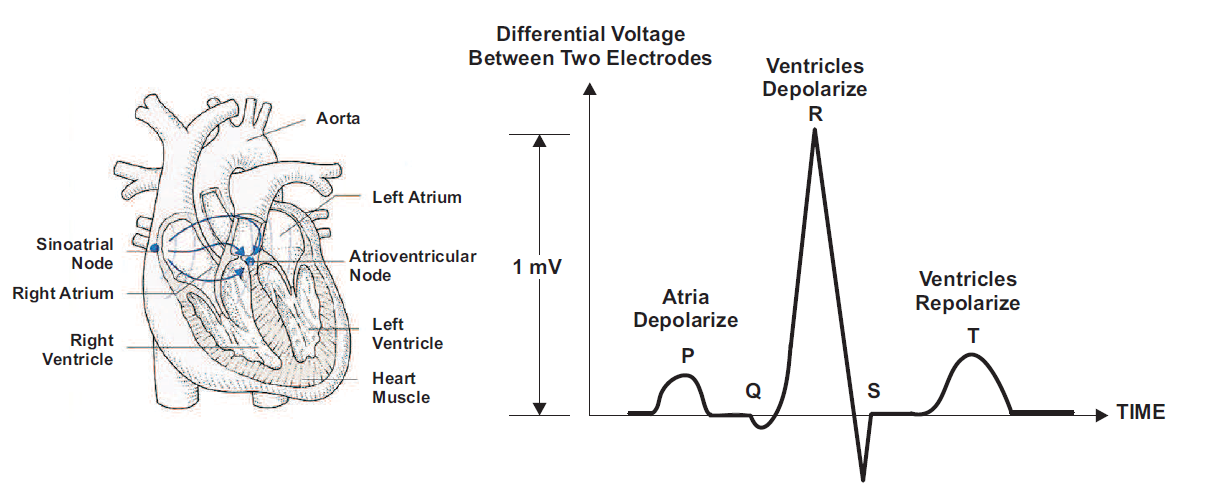 Smart Sensing With Ultra Low Power Mcus Part 4 Holter
Smart Sensing With Ultra Low Power Mcus Part 4 Holter
 Ekg Pqrst Rhythm Strip Wave Quiz Anatomy Pathophysiology
Ekg Pqrst Rhythm Strip Wave Quiz Anatomy Pathophysiology
 Coronary Anatomy And Corresponding Ecg Leads Chalk Talk
Coronary Anatomy And Corresponding Ecg Leads Chalk Talk
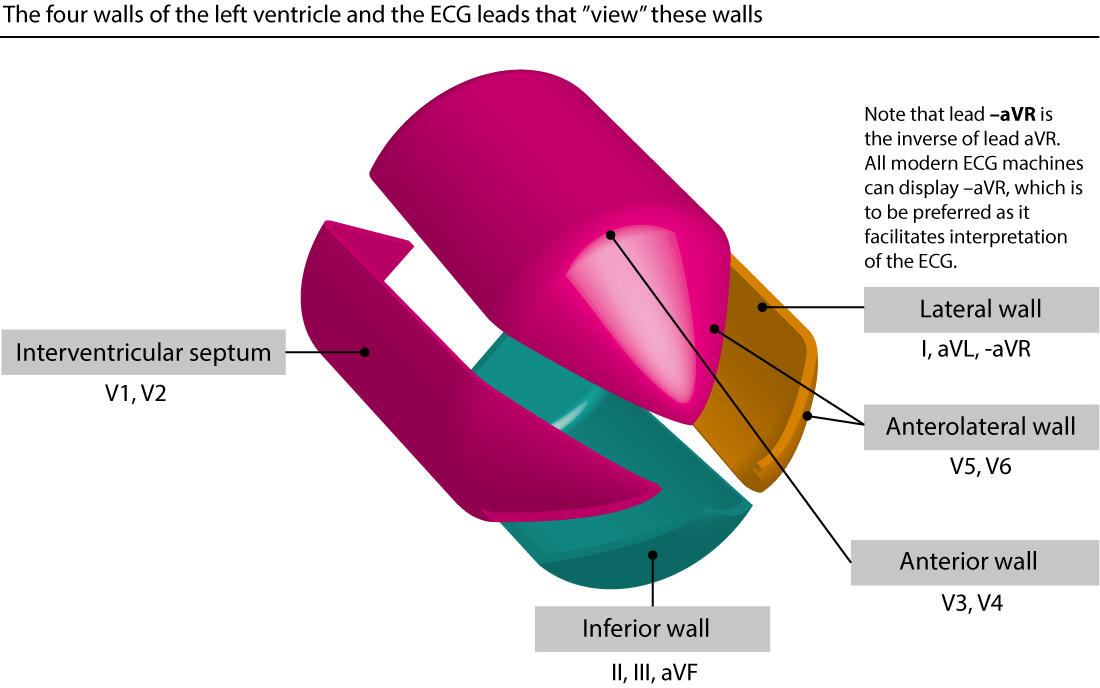 The Ecg Leads Electrodes Limb Leads Chest Precordial
The Ecg Leads Electrodes Limb Leads Chest Precordial
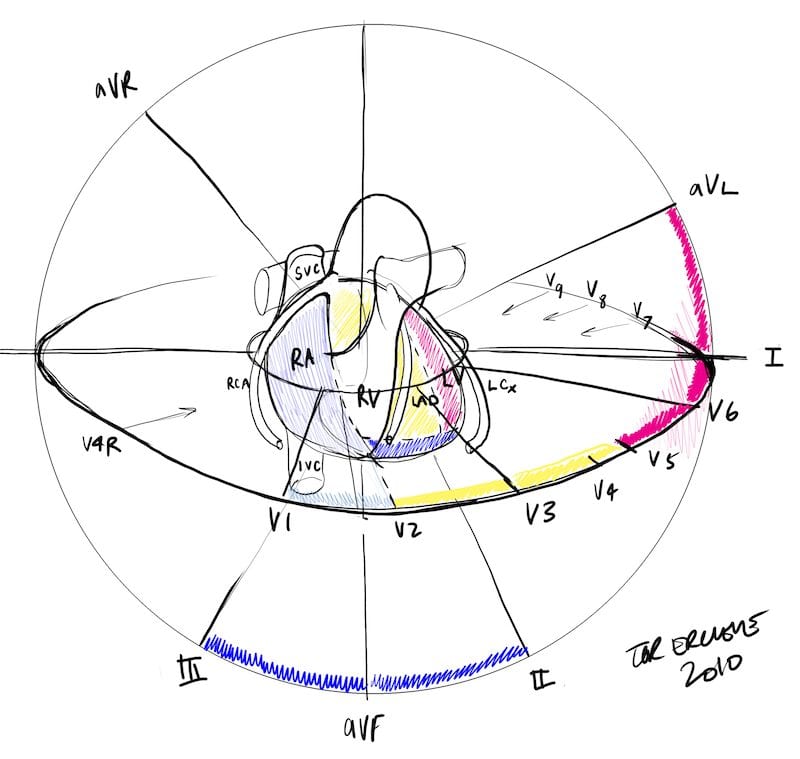 Mi Localization Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Anatomy Basics
Mi Localization Litfl Medical Blog Ecg Anatomy Basics
 A Schematic Representation Of The Heart Anatomy B Ecg
A Schematic Representation Of The Heart Anatomy B Ecg
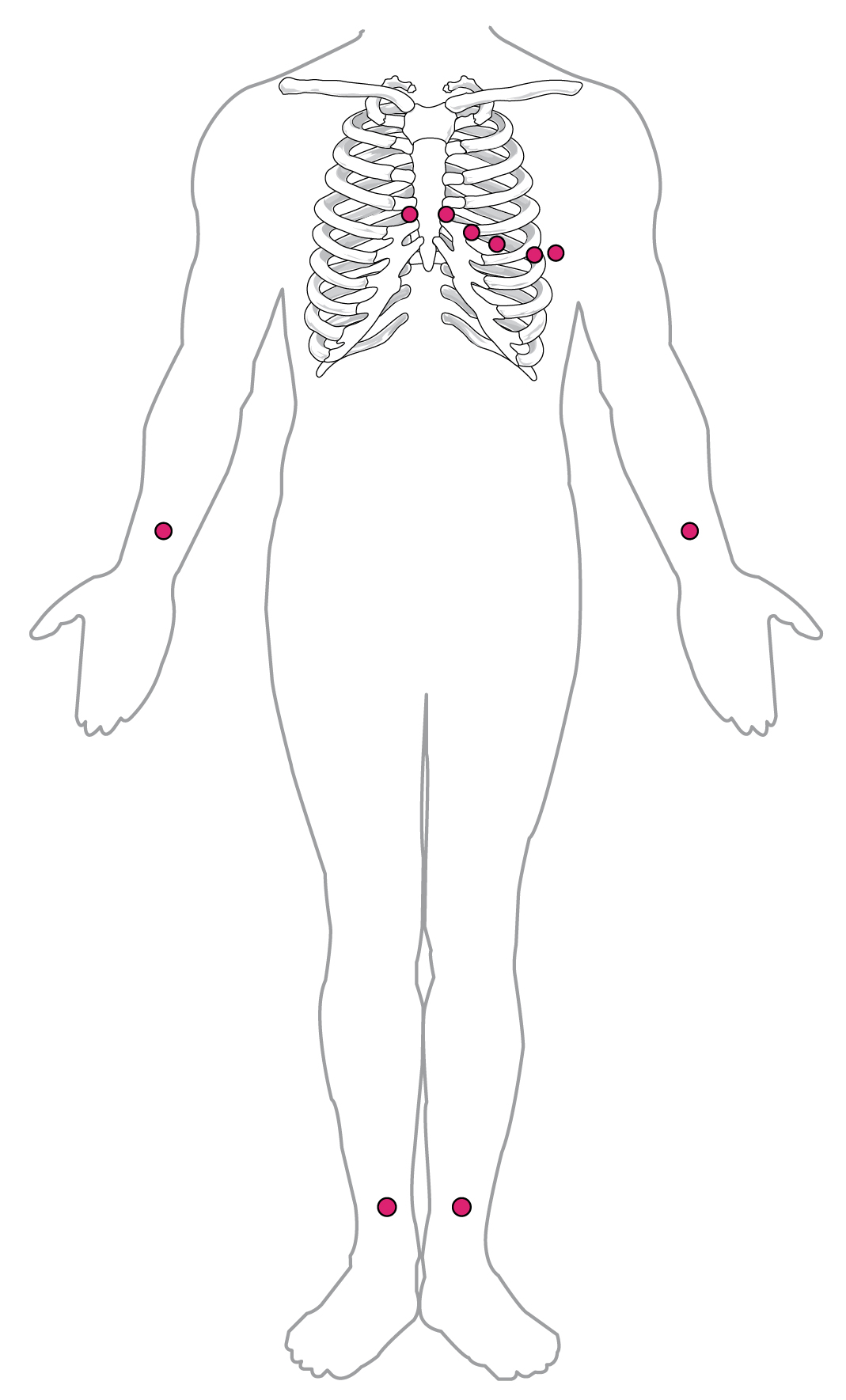 19 2 Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And
19 2 Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And
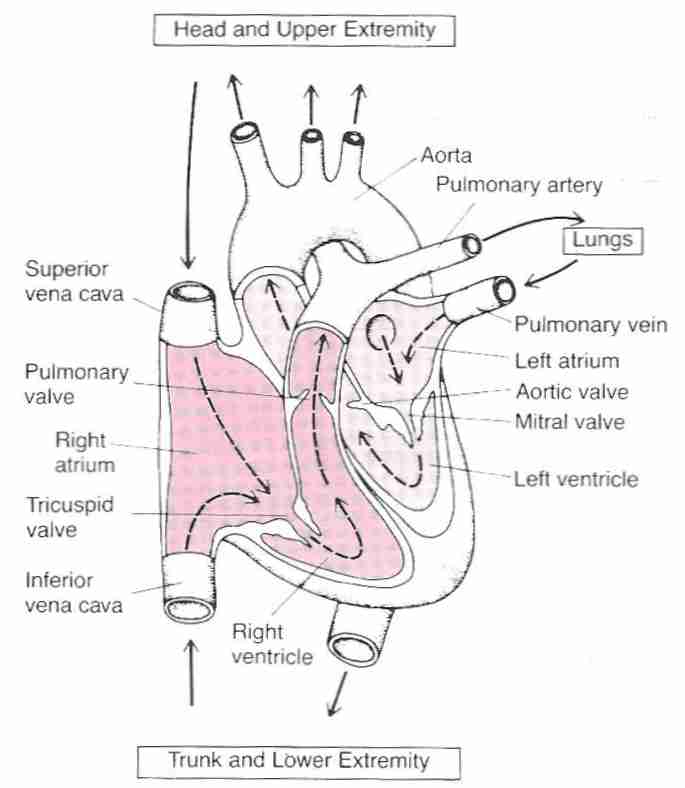 Electrocardiograph Ecg Ekg Interpretaion
Electrocardiograph Ecg Ekg Interpretaion
 Ekg Anatomy Pathology This Is So Helpful To Understand
Ekg Anatomy Pathology This Is So Helpful To Understand
 Cv Physiology Electrocardiogram Ekg Ecg
Cv Physiology Electrocardiogram Ekg Ecg
 Dog Ekg Ecg Heartbeat Anatomy Wolf Hound Wolves Dogs T Shirt Photographic Print
Dog Ekg Ecg Heartbeat Anatomy Wolf Hound Wolves Dogs T Shirt Photographic Print
 Ekg Leads And Where They Represent You Can Understand A Lot
Ekg Leads And Where They Represent You Can Understand A Lot
 6 Fetal Heart Anatomy And Electrical Activation Sequence
6 Fetal Heart Anatomy And Electrical Activation Sequence
 Ecg Copy Ecg Anatomy Of The Heart The Walls Of The Heart
Ecg Copy Ecg Anatomy Of The Heart The Walls Of The Heart
Heart Anatomy Biology Ecg Electrocardiogram Heart Rate Heart
 Heart Anatomy And Ecg Background
Heart Anatomy And Ecg Background
 Electrocardiogram Ecg Ekg Definition Readings Procedure
Electrocardiogram Ecg Ekg Definition Readings Procedure
 Electrocardiogram Ecg Ekg Definition Readings Procedure
Electrocardiogram Ecg Ekg Definition Readings Procedure
 Electrocardiogram Ecg Ekg Definition Readings Procedure
Electrocardiogram Ecg Ekg Definition Readings Procedure



Belum ada Komentar untuk "Ecg Anatomy"
Posting Komentar