Matrix Anatomy Definition
For blood chemistries the matrix includes serum specific proteins and synthetic material. ˈmæ n pl matrices ˈmeɪtrɪˌsiːz.
 What Does Matrix Mean In Biology I Came Across The Term
What Does Matrix Mean In Biology I Came Across The Term
The greco roman world was the matrix for western civilization.
Matrix anatomy definition. Extracellular matrix the extracellular matrix is a mixture of protein and carbohydrate components providing structural and biochemical support to cells. Lab medicine the principal constituents of a material of interest. Dense regular connective tissue that contains abundant collagen fibers giving it a white appearance.
Osteoblasts start in center where medullary cavity is created as well as bone in the primary ossification center. In biology matrix plural. A substance situation or environment in which something has its origin takes form or is enclosed.
Then osteoblasts slowly move out to the epiphysis creating secondary ossification centers. Anatomy anatomy the thick tissue at the base of a nail from which a fingernail or toenail develops. Molecular biology a medium on which in which things are formed developed or embedded.
Anatomy and physiology chapter 4. Matrix anatomy the intercellular substance of a tissue. It is found in various connective tissue.
Matrix definition something that constitutes the place or point from which something else originates takes form or develops. Finger nails and toenails grow from matrices. Matrices is the material or tissue in animal or plant l structure of connective tissues is an extracellular matrix.
Matrix noun mathematics c specialized mathematics a group of numbers or other symbols arranged in a rectangle that can be used together as a single unit to solve particular mathematical problems. Forms structures such as tendons and ligaments. A unique type of stratified epithelium lines the bladder and ureter is positioned to accommodate cell expansion.
It is generally used as a jelly like structure instead of cytoplasm in connective tissue. 2ndary ossification centerspongy bone. The most abundant component of the extracellular matrix is collagen giving the matrix strength and flexibility.
Fibers give the tissue considerable strength and resistance to stretching.
Connective Tissue L2 Microscopic Anatomy Flashcards Memorang
 Spongy Bone Cancellous Bone Definition Function Biology
Spongy Bone Cancellous Bone Definition Function Biology
 The Histology Guide Connective Tissue
The Histology Guide Connective Tissue
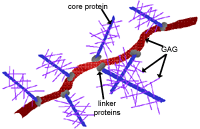
 The Role Of Extracellular Matrix In Tissue Regeneration
The Role Of Extracellular Matrix In Tissue Regeneration
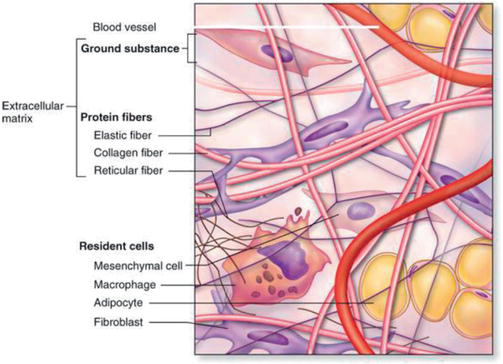
 What Is The Extracellular Matrix
What Is The Extracellular Matrix
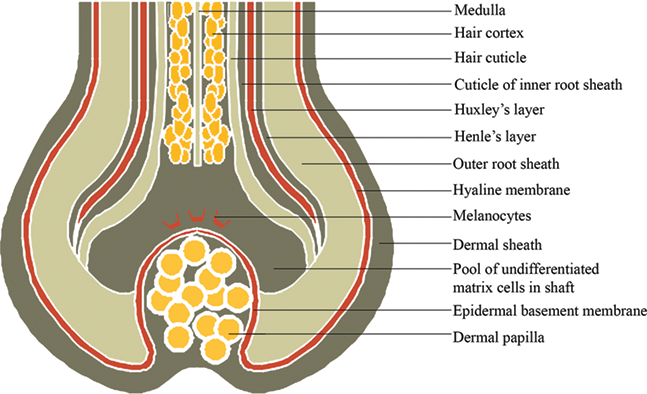 Anatomy And Physiology Of Hair Intechopen
Anatomy And Physiology Of Hair Intechopen
 The Nail Bed Part I The Normal Nail Bed Matrix Stem Cells
The Nail Bed Part I The Normal Nail Bed Matrix Stem Cells
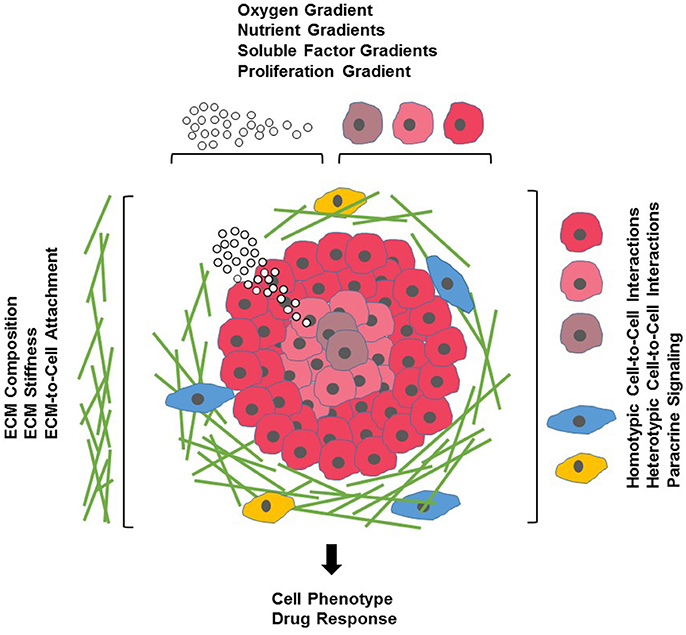 Frontiers Three Dimensional In Vitro Cell Culture Models
Frontiers Three Dimensional In Vitro Cell Culture Models
 Extracellular Matrix Wikipedia
Extracellular Matrix Wikipedia
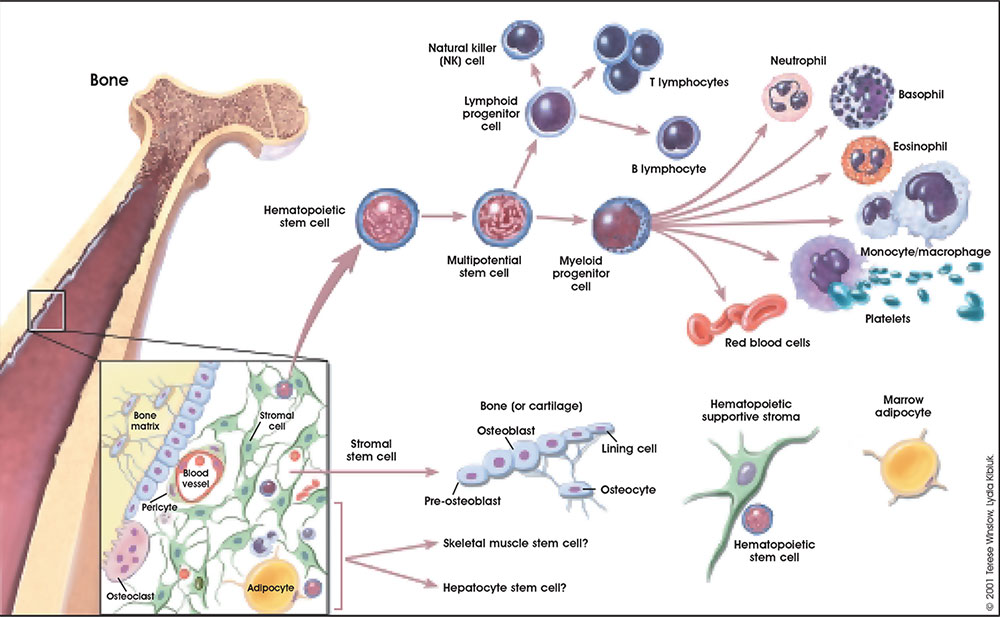 Anat2241 Lymphatic Tissue And Immune System Embryology
Anat2241 Lymphatic Tissue And Immune System Embryology
Connective Tissue Types Structure Cells Functions
 Extracellular Matrix Glycosaminoglycans And Proteoglycans
Extracellular Matrix Glycosaminoglycans And Proteoglycans
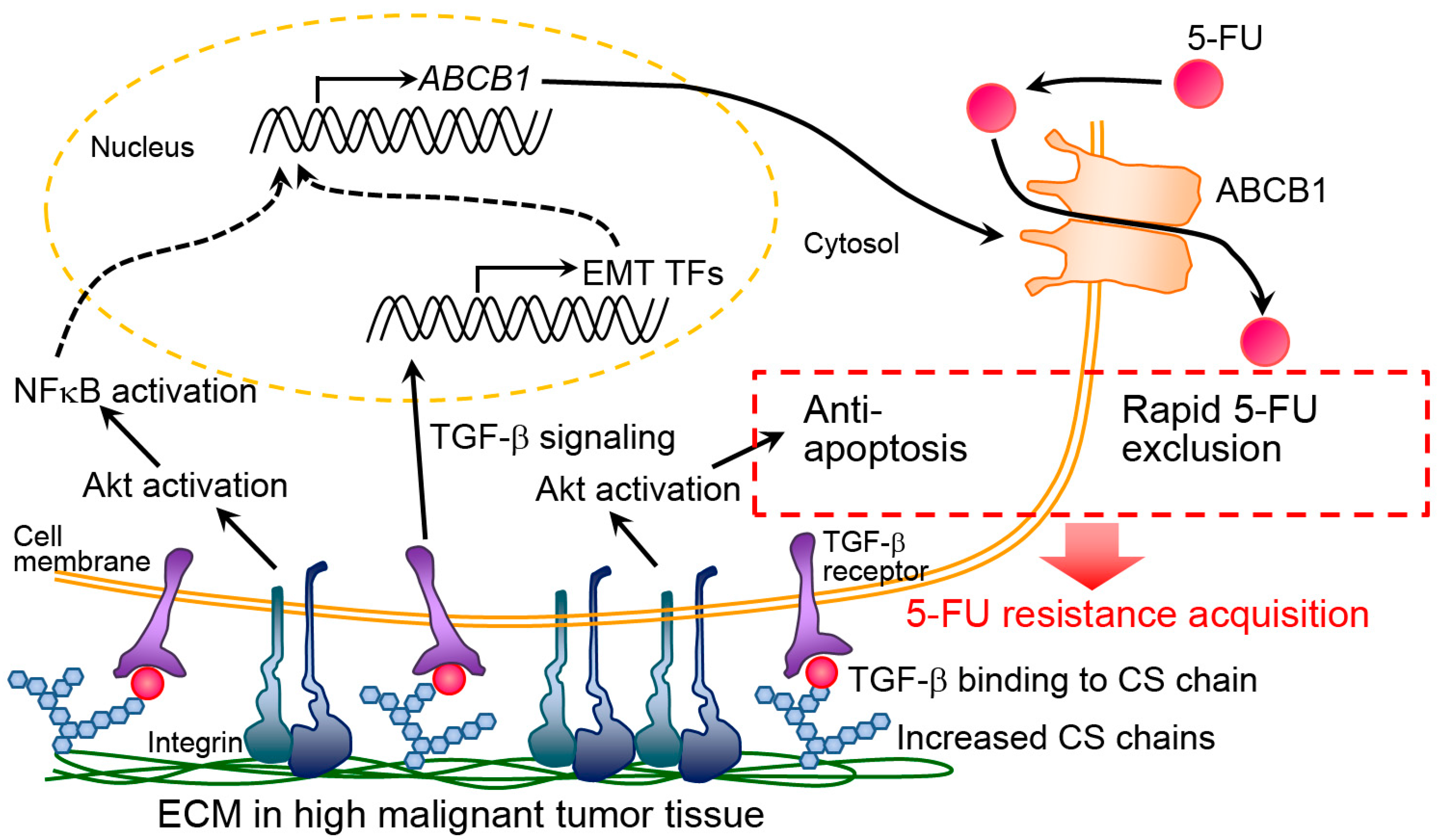 Materials Free Full Text Decellularized Extracellular
Materials Free Full Text Decellularized Extracellular
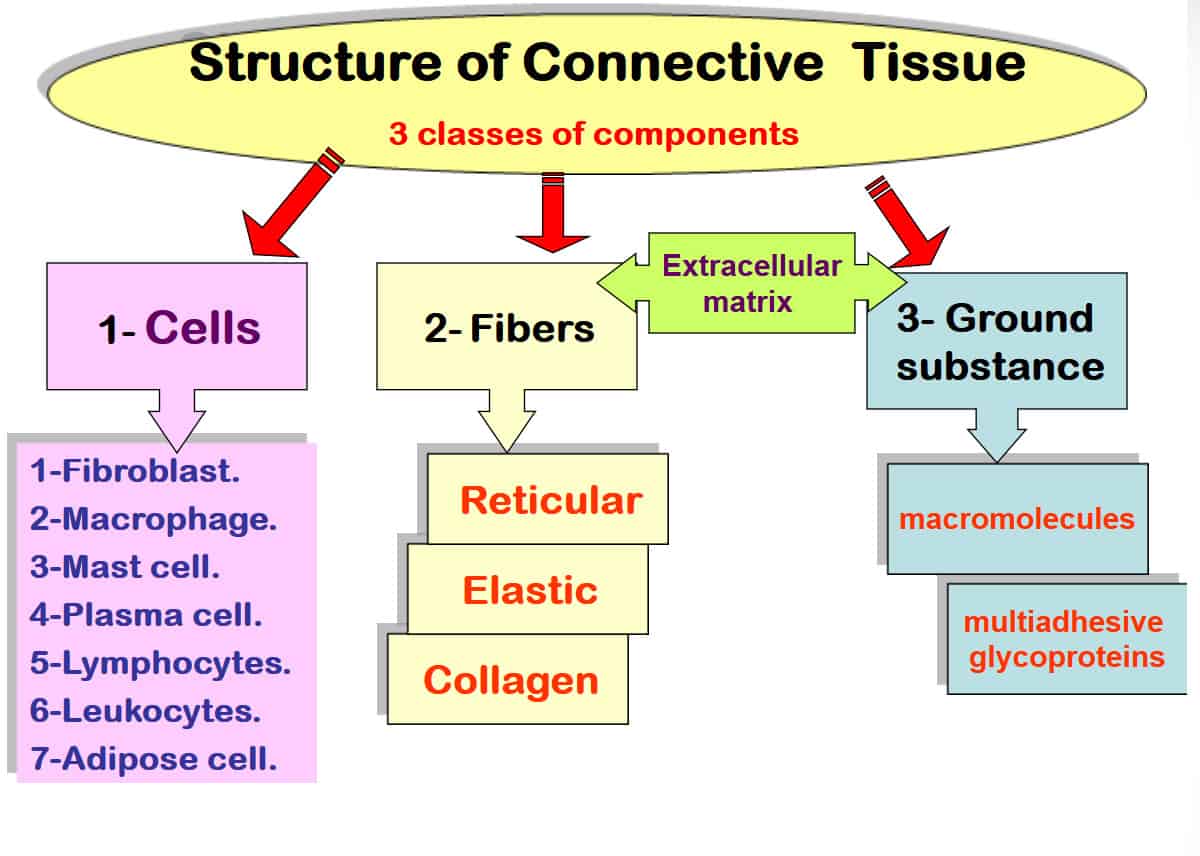 Connective Tissue Types Examples And Functions
Connective Tissue Types Examples And Functions
 Proteoglycans Definition Function Structure
Proteoglycans Definition Function Structure
 Hair Matrix The Griffin Center Of Hair Restoration Research
Hair Matrix The Griffin Center Of Hair Restoration Research
 Fascia And Extra Cellular Matrix Ecm Defining Fascia
Fascia And Extra Cellular Matrix Ecm Defining Fascia
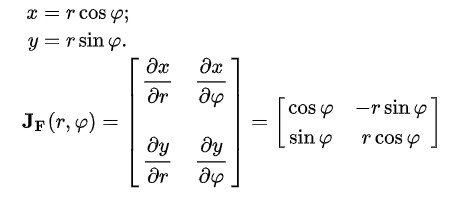 What Is A Jacobian Matrix Science Abc
What Is A Jacobian Matrix Science Abc
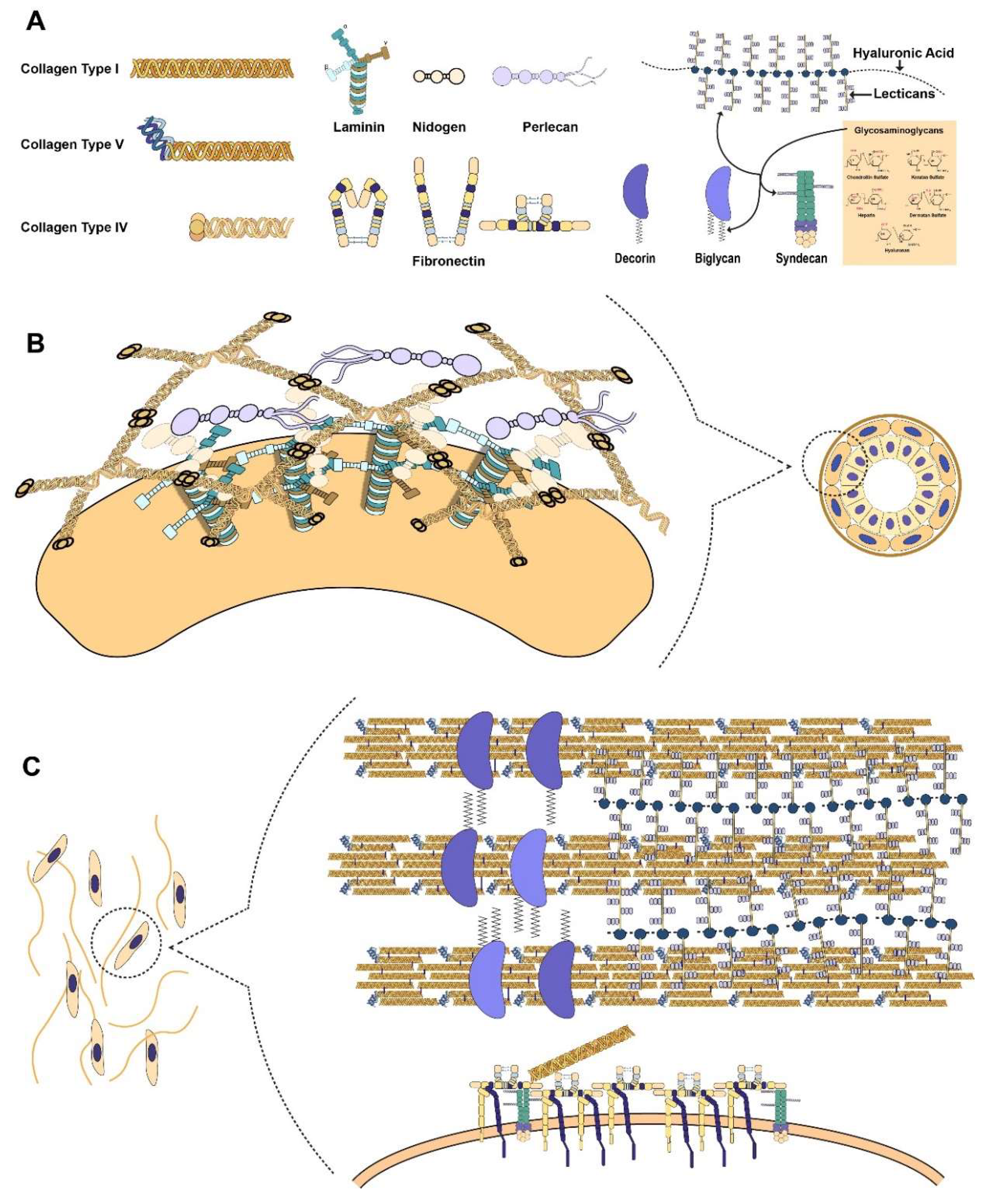 Ijms Free Full Text Role Of Extracellular Matrix In
Ijms Free Full Text Role Of Extracellular Matrix In
 The Role Of Extracellular Matrix In Tissue Regeneration
The Role Of Extracellular Matrix In Tissue Regeneration
 Bone Dr Iram Tassaduq Definition Bone Is A Specialized
Bone Dr Iram Tassaduq Definition Bone Is A Specialized
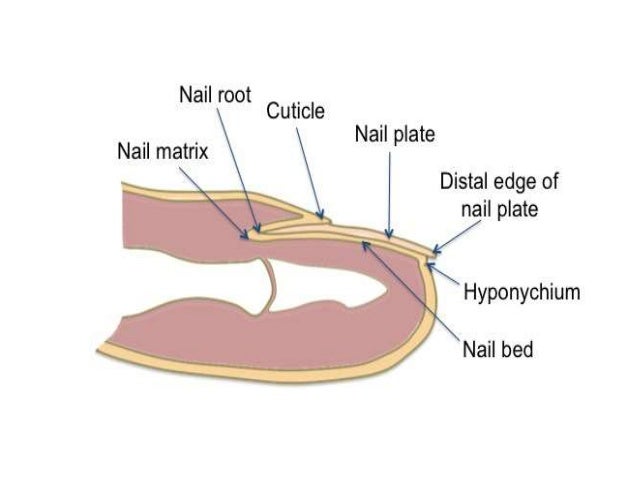 Anatomy Of Nail And Applied Aspects
Anatomy Of Nail And Applied Aspects
Ch04 Mineralized Connective Tissues
Bone Formation And Development Anatomy And Physiology
What Does Matrix Mean In Biology I Came Across The Term
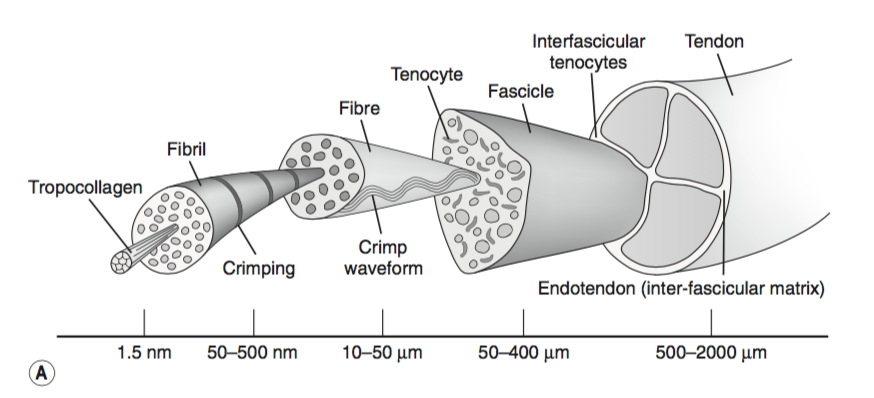


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Matrix Anatomy Definition"
Posting Komentar