Anatomy Of The Ovary
When released this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus where it may become fertilized by a sperm. Anatomy of human ovaries the ovaries develop along with other organs in the womb before birth.
It lies in a shallow depression named the ovarian fossa on the lateral wall of the pelvis.

Anatomy of the ovary. This fossa is bounded above by the external iliac vessels. In this article we will initially look at the basic function location components and clinical significance of the ovaries. The female gonads are called the ovaries.
Each ovary presents a lateral and a medial surface an upper or tubal and a lower or uterine extremity and an anterior or mesovarion and a posterior free border. The ovaries are the female pelvic reproductive organs that house the ova and are also responsible for the production of sex hormones. When a female infant is born her ovaries will contain approximately 400000 egg producing follicles and for the most part her body will not produce anymore follicles for the rest of her life.
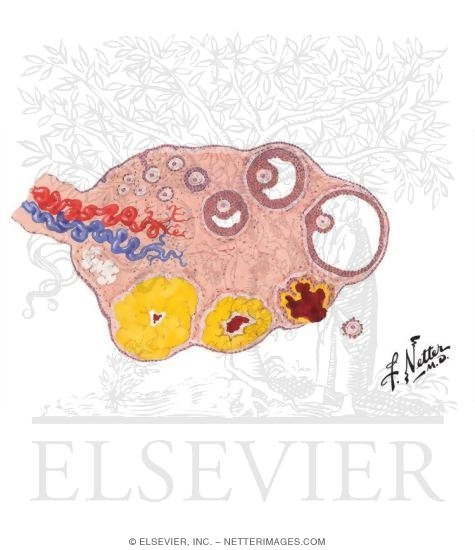
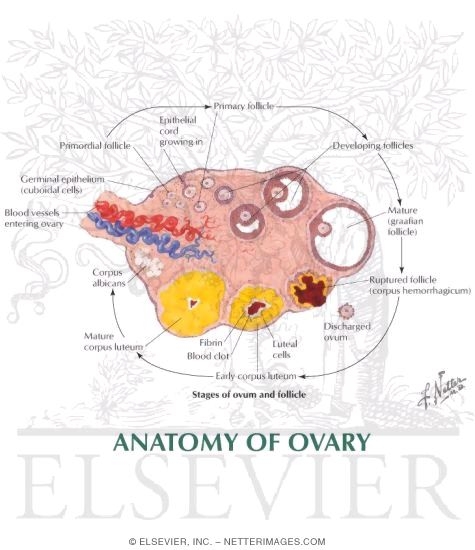
The structures found within the ovary are undergoing constant changes throughout the oestrus cycle from the follicles containing oocytes to the formation of corpus haemorrhagicum corpus luteum and finally corpus albicans. Each ovary is attached to the posterior aspect of this ligament via the ovarian ligament germinal epithelium a simple cuboidal epithelial layer that surrounds the ovary. The ovary is the female gonad homologous to the male testes.
There is an ovary from latin ovarium meaning egg nut found on each side of the body. This chapter deals with the normal macroscopic microscopic and ultrastructural morphology of the human ovary and its hormonal function. Find out the structure development various functions location and anatomy of the ovaries.
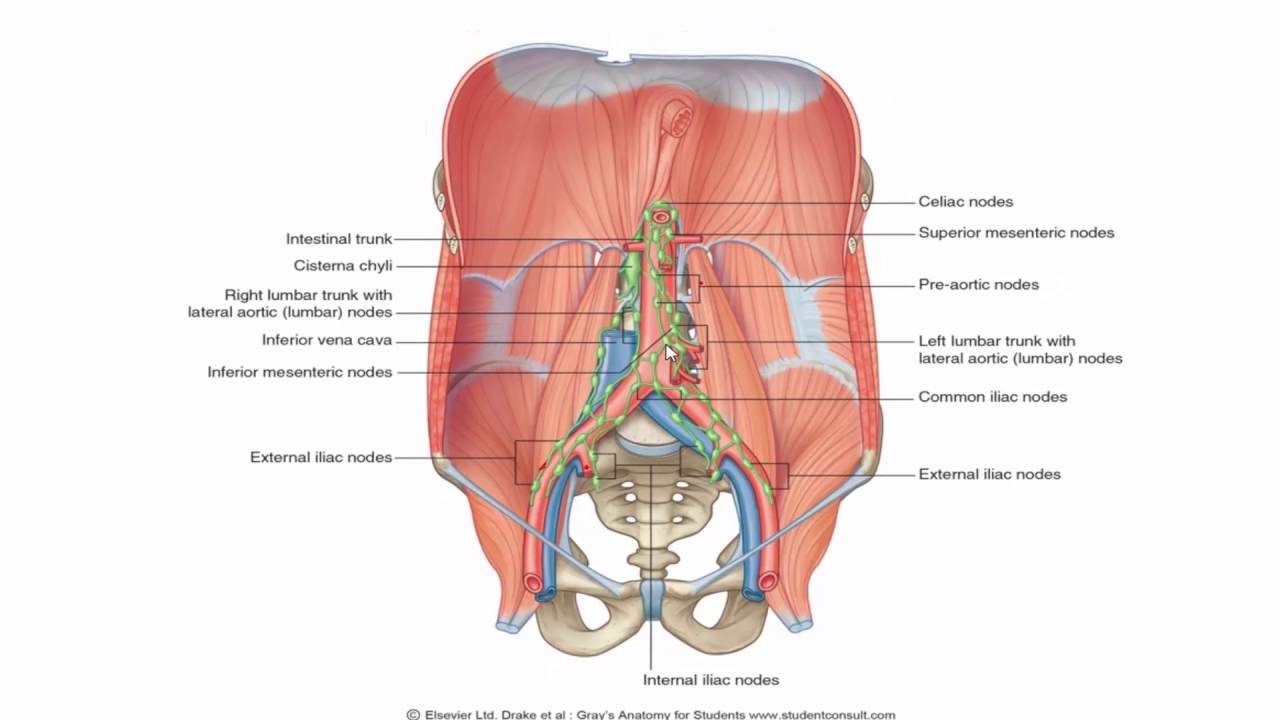
They are paired organs located on either side of the uterus within the broad ligament below the uterine fallopian tubes. It is usually a paired organ in domestic species but in the bird only the left ovary is present. The latter part of the article will cover the ligaments associated with the ovaries and their vasculature lymphatic drainage and innervation.
They produce the ova eggs that when fertilized will develop into a fetus. They also generate the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone. Ovary anatomy the ovaries are female reproductive organs that are akin to the testes in men.
The ovary is an organ found in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. Since the anatomy and function of the ovary vary considerably at different stages in a womans life these aspects will be considered during adulthood childhood and after the menopause. The ovary is the gonadal organ primary sexual organ in females.
Anatomy Of The Uterus Uterine Tubes And Ovary Anat10110
 Ovary Animal And Human Britannica
Ovary Animal And Human Britannica
 28 1 Female Reproductive Anatomy Ovaries Diagram Quizlet
28 1 Female Reproductive Anatomy Ovaries Diagram Quizlet
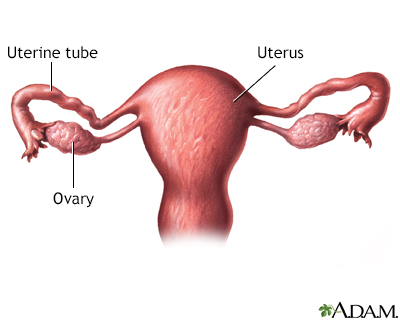 Ovarian Cysts Information Mount Sinai New York
Ovarian Cysts Information Mount Sinai New York
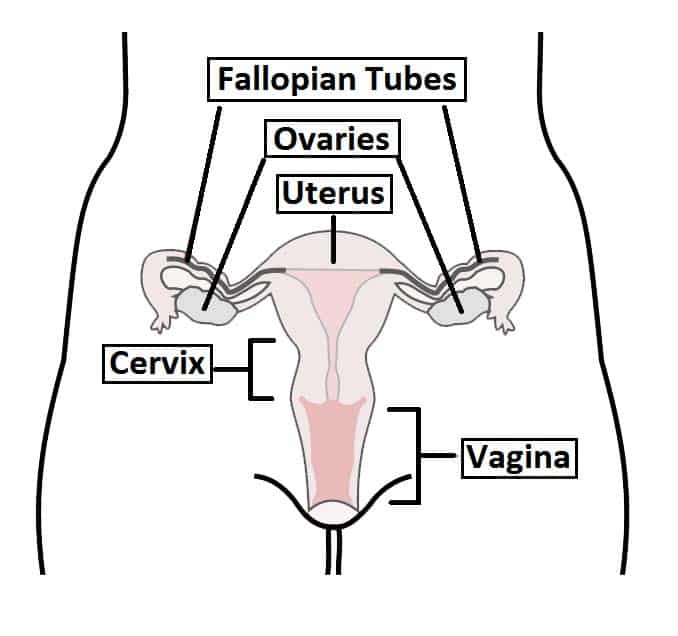 The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
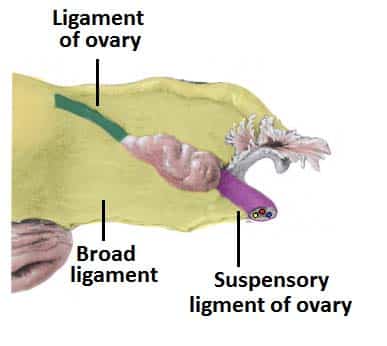 The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
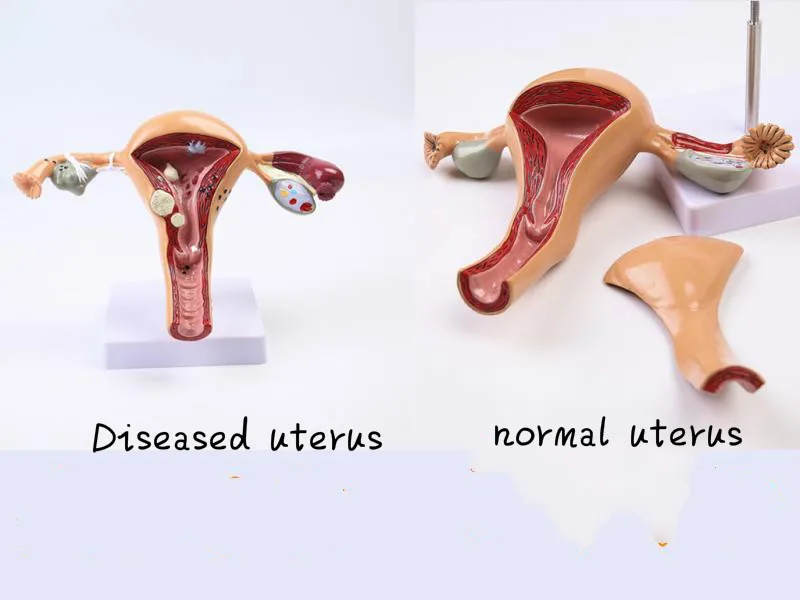 Us 28 93 45 Off Female Anatomy Reproductive Uterus Model Vaginal Ovary Model Teaching Mold Disease Change Science Teaching Aids Biology In
Us 28 93 45 Off Female Anatomy Reproductive Uterus Model Vaginal Ovary Model Teaching Mold Disease Change Science Teaching Aids Biology In
 Uterus Ovary Anatomical Model With Pathologies
Uterus Ovary Anatomical Model With Pathologies
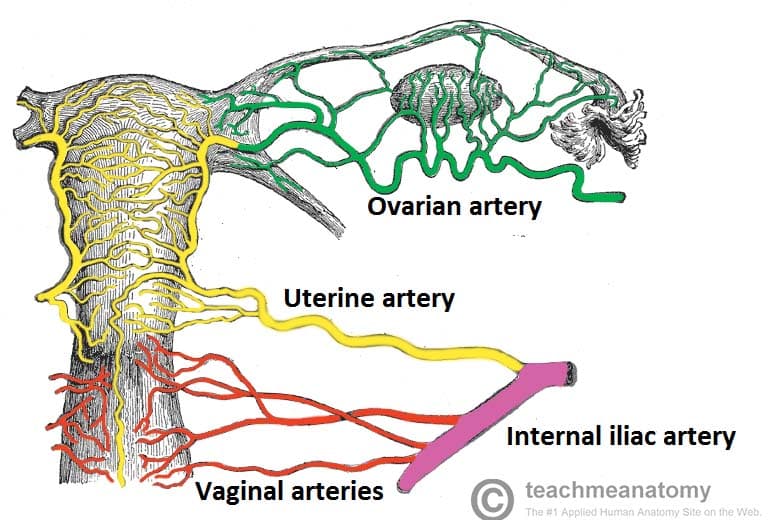 The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
The Ovaries Structure Ligaments Vascular Supply Function
 The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
The Female Reproductive System Boundless Anatomy And
 Vector Isolated Illustration Of Female Reproductive System Anatomy
Vector Isolated Illustration Of Female Reproductive System Anatomy
 General Anatomy Of The Female Reproductive System Ppt
General Anatomy Of The Female Reproductive System Ppt
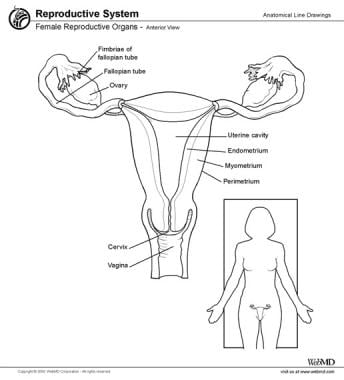 Ovary Anatomy Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy Natural
Ovary Anatomy Gross Anatomy Microscopic Anatomy Natural
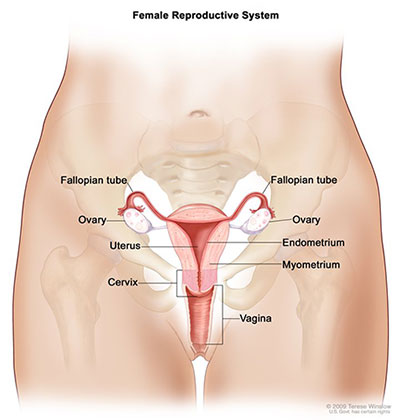 Seer Training Salpingo Ovarian Peritoneal Functional Anatomy
Seer Training Salpingo Ovarian Peritoneal Functional Anatomy
Ovarian Cancer Stage I Image Details Nci Visuals Online
 Ovarian Cancer Anatomy Nexj Health
Ovarian Cancer Anatomy Nexj Health
 Anatomy 1 C3 L3 Ovary And Vagina
Anatomy 1 C3 L3 Ovary And Vagina
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/4248/8s6dP8zToYvAEVcgJ2JQ_A._ovarii_02.png) Ovaries Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
Ovaries Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
 Ovary Model Female Reproductive System Anatomy
Ovary Model Female Reproductive System Anatomy
 Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Treatment Mhealth Org
Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors Treatment Mhealth Org
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/ovarium-3/w35nsclHhoeB6TtFsoWZqQ_Ovaries_01.png) Ovaries Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
Ovaries Anatomy And Embryology Kenhub
 Ovaries Anatomy And Physiology
Ovaries Anatomy And Physiology


Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of The Ovary"
Posting Komentar