Anatomy For Tracheostomy
Tracheotomy epithelial lined tracheostomy with laryngeal suspension for. Goiter high innominate or pulsating vessels previous neck surgery limited neck extension severe coagulopathy uncorrected.
Anatomy And Physiology Of Tracheostomy
Pathway of the trachea from anterior at the cricoid cartilage c6 to more posterior as it enters the chest behind the sternal notch.
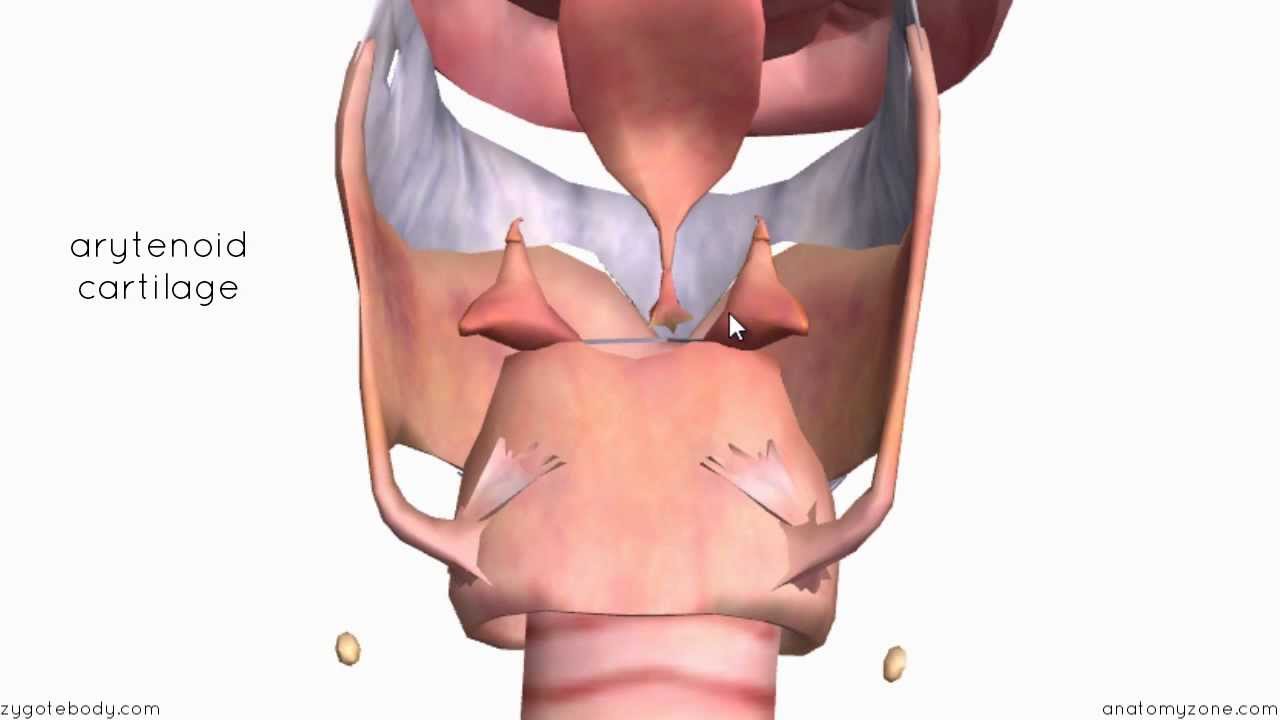
Anatomy for tracheostomy. C shaped cartilages first cartilage is bigger than the others in the cervical trachea. Cancer must know facts. Hood stoma stent tracheostomy stent.
Once an opening is made it needs to be maintained which is by tracheostomy tube of which there are several types. Montgomery cannula canula tracheotomy. A tracheostomy or tracheotomy is a surgical procedure where an opening is created through the neck into the trachea or windpipe to provide direct access to a breathing tube.
And fenestrated tracheostomy tube tracheotomy employing fenestrated trach. The trachea is composed of about 20 rings of tough cartilage. The optimal placement is through the third tracheal ring although this may be difficult in some patients based upon the length of their neck and their anatomy.
Precautions with a tracheostomy. Cuffed and cuffless tracheostomy tubes. Reasons for a tracheostomy.
Tracheostomy basics definitions tracheostomy. The outermost layer of the trachea called the adventitia is fibrous connective tissue that blends into the adventitia of other organs of the mediastinum especially the esophagus. Trachea is 10 cm long stretches to 15cm on inspiration fibroelastic structure tracheal rings.
The midline trachea is identified. Complications of a tracheostomy. Poor neck landmarks neck mass eg.
Tracheostomy is an operative procedure that creates a surgical airway in the cervical trachea. Tracheostomy tubes parts of a tracheostomy tube. The back part of each ring is made of muscle and connective tissue.
A tracheostomy provides direct access to the trachea by surgically making an opening in the neck. Moist smooth tissue called mucosa lines the inside of the trachea. Emergent tracheostomy ie securing emergent airway in any patient population infants and children 15 years relative surgical contraindications.
Trach lore panel hoffman slides april 19 2018. The connective tissue beneath the tracheal epithelium contains lymphatic nodules mucous and serous glands and the tracheal cartilages. What is tracheostomy the word tracheostomy is derived from the latin trachea and tomein to make an opening.
How a tracheostomy works. Construction and design of tracheostomy tubes. Dual and single cannula.
Typically the isthmus of the thyroid is overlying the second and third tracheal ring.
 Anatomy Lab Infant Tracheostomy Care Manikin
Anatomy Lab Infant Tracheostomy Care Manikin
 Figure 2 From Resuscitating The Tracheostomy Patient In The
Figure 2 From Resuscitating The Tracheostomy Patient In The
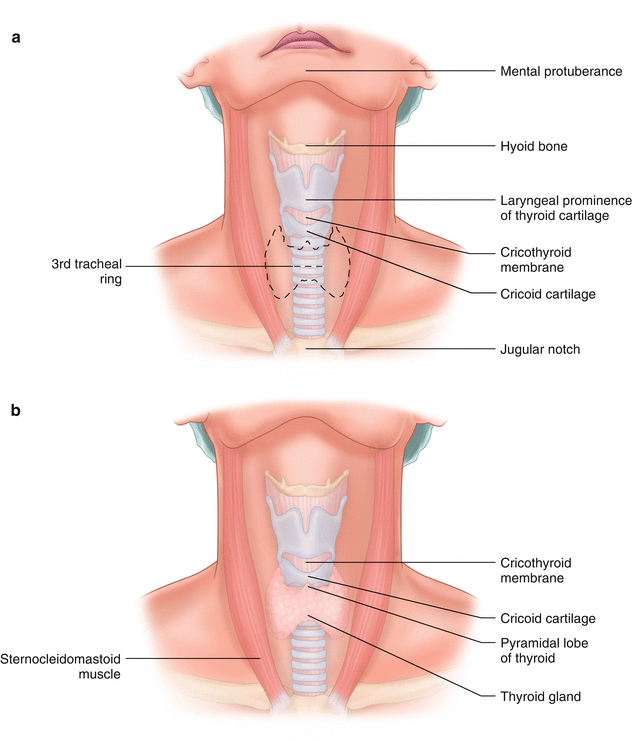 Tracheostomy And Cricothyroidotomy Anesthesia Key
Tracheostomy And Cricothyroidotomy Anesthesia Key
 Sagittal Section Showing A Tracheostomy Tube In Position And
Sagittal Section Showing A Tracheostomy Tube In Position And
 Percutaneous Tracheostomy And Cricothyrotomy Techniques
Percutaneous Tracheostomy And Cricothyrotomy Techniques
Tracheostomy Epidemiology Indications Timing Technique
 Tracheostomy Care In Community Settings
Tracheostomy Care In Community Settings
Tracheostomy Adult Western New York Urology Associates Llc
 Anatomy For Tracheostomy Litfl Medical Blog Ccc Airway
Anatomy For Tracheostomy Litfl Medical Blog Ccc Airway
Tracheostomy Epidemiology Indications Timing Technique
 15061 01x Normal Tracheostomy Tube Placement Anatomy Exhibits
15061 01x Normal Tracheostomy Tube Placement Anatomy Exhibits
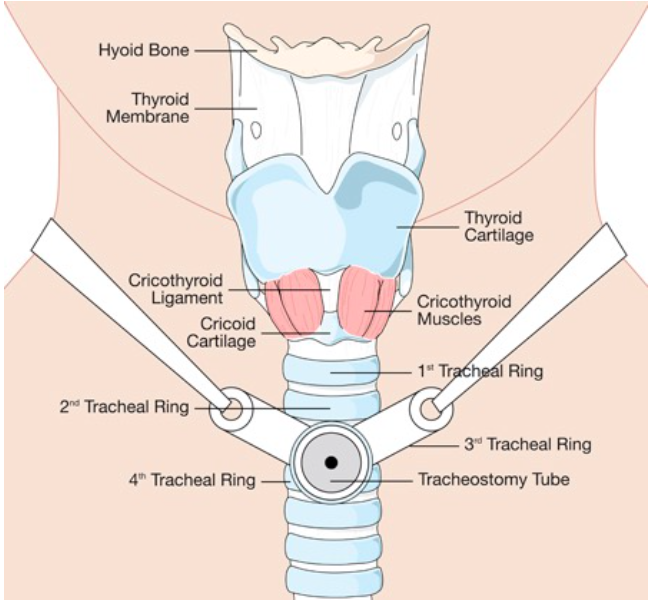 Common Tracheostomy Issues Core Em
Common Tracheostomy Issues Core Em
 Anatomy And Placement Of Tracheostomy Tube Nurse Teaching
Anatomy And Placement Of Tracheostomy Tube Nurse Teaching
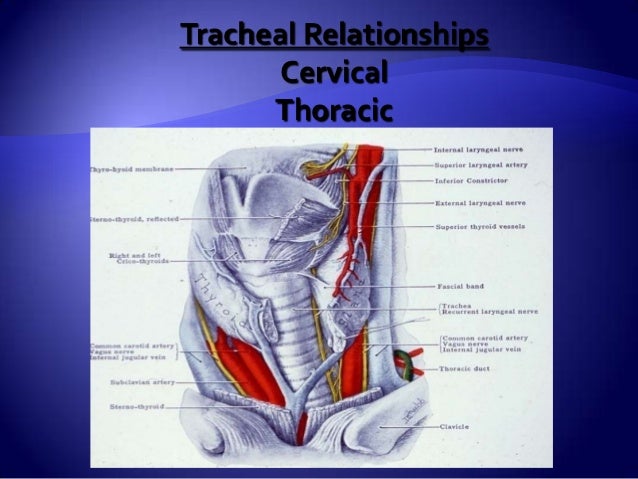 Anatomy Of Trachea Tracheostomy
Anatomy Of Trachea Tracheostomy
Crash Course In Tracheostomies
 Management Of And Indications For Tracheostomy In Care Of
Management Of And Indications For Tracheostomy In Care Of
 Omfs Secrets Ch15 Tracheostomy And Cricothyrotomy
Omfs Secrets Ch15 Tracheostomy And Cricothyrotomy
 Figure 1 From Resuscitating The Tracheostomy Patient In The
Figure 1 From Resuscitating The Tracheostomy Patient In The
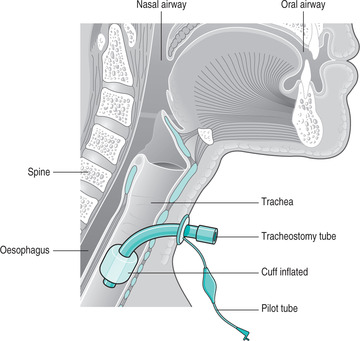 42 Tracheostomy Care Nurse Key
42 Tracheostomy Care Nurse Key
 Tracheostomy Tubes Using A Speaking Valve Fact Sheet
Tracheostomy Tubes Using A Speaking Valve Fact Sheet

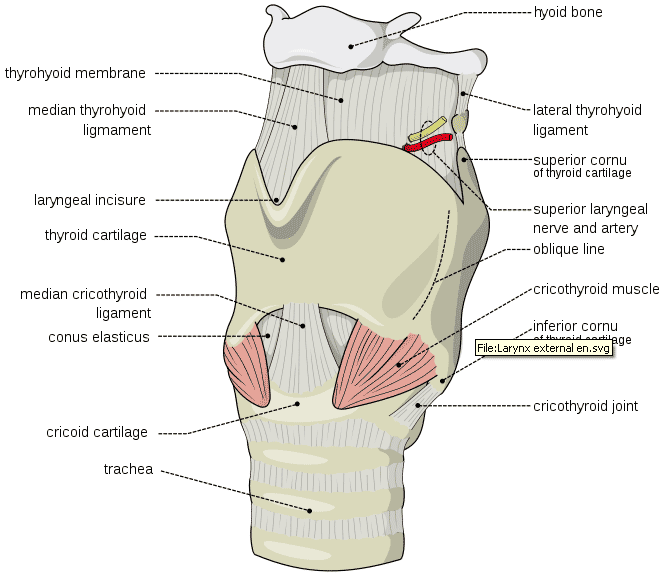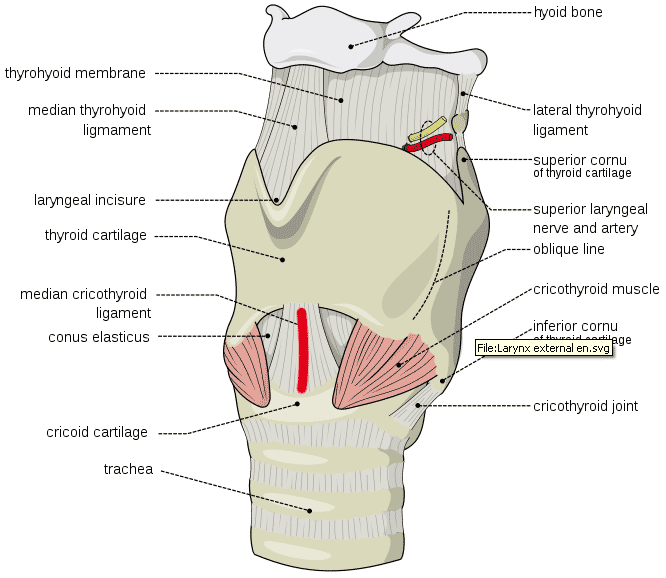

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy For Tracheostomy"
Posting Komentar