Antagonist Anatomy
And 2 they control rapid movement as in shadow boxing without landing a punch or the ability to check the motion of a limb. Six hundred muscles make up the human bodys musculoskeletal system.
Anatomy Of An Injury Piriformis Syndrome Article Ptonthenet
The antagonist in a movement refers to the muscles that oppose the agonist.

Antagonist anatomy. I guess the opposing muscles would be the triceps the muscles at the back of the upper arm. Using the example above of the triceps brachii during a push up the elbow flexor muscles are the antagonists at the elbow during both the up phase and down phase of the movement. Antagonists play two important roles in muscle function.
Antagonist and agonist muscles work in pairs to accomplish a full range of movements and actions. The biceps are the muscles in the front of the upper arm. Physiology a muscle that counteracts the action of another muscle the agonist.
During elbow flexion where the bicep is the agonist the tricep muscle is the antagonist. The muscles of the eyelid the antagonist of the orbicularis oculi is the levator palpebrae. 1 they maintain body or limb position such as holding the arm out or standing erect.
An antagonist is a muscle that is capable of opposing the movement of a joint by producing torque that is opposite to a certain joint action. During slower joint actions that involve gravity just as with the agonist muscle mentioned above the antagonist muscle can shorten and lengthen. A drug or chemical substance that interferes with the physiological action of another especially by combining with and blocking its receptor.
Antagonist muscles act against the agonist muscle and help to move the body part back in place after the action is completed. A muscle with the opposite action of the prime mover is called an antagonist. According to grays anatomy1918 by henry gray 18211865 in anatomy of the human body chapter 4b.
During elbow flexion where the bicep is the agonist the tricep muscle is the antagonist. A muscle that relaxes while another contracts. Tendons attach muscles to bones allow muscles to move bones and give joints their flexibility.
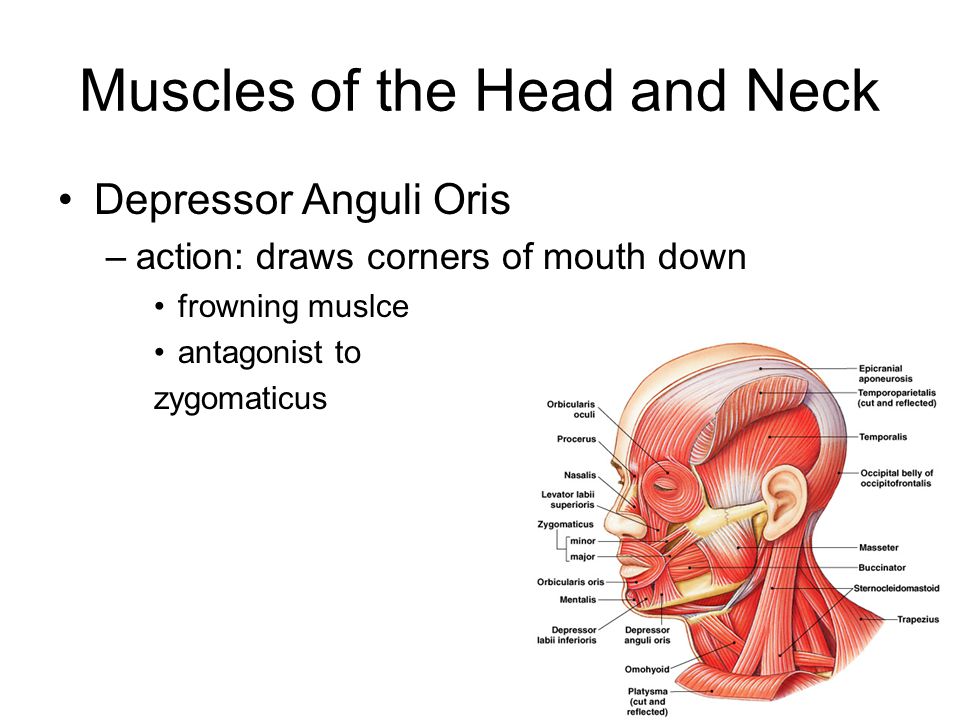
Anatomy muscular system muscles of face and head origininsertion few innervation and action synergistantagonist all frontal belly of occipitofrontalis fro occipital belly of occipitofrontalis o. Antagonist general anatomy definition. This is usually a muscle that is located on the opposite side of the joint from the agonist.
An antagonist is one who opposes.
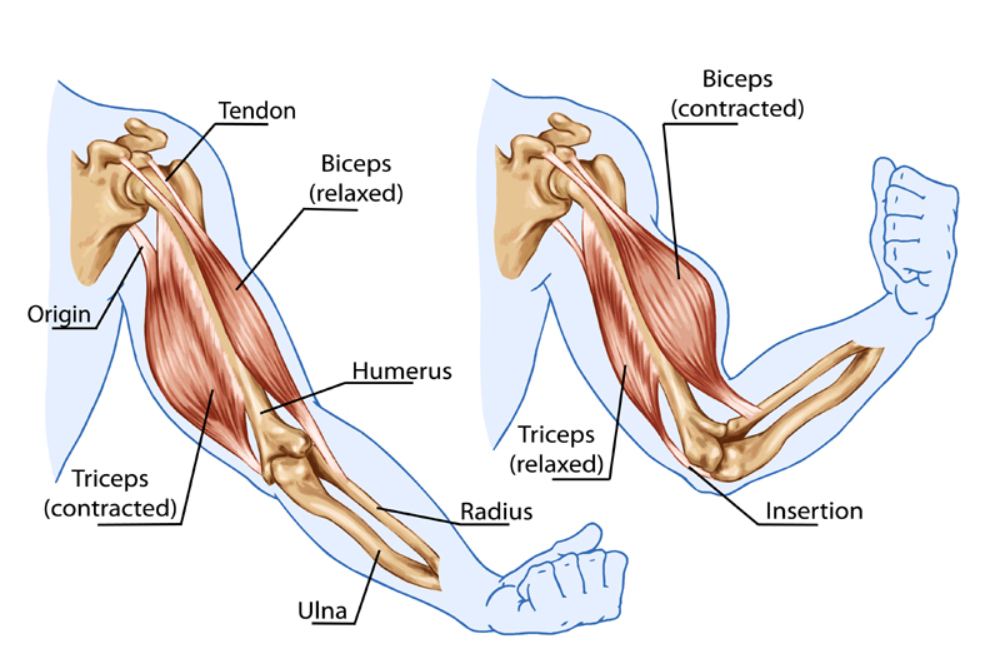 Yoga Teacher Central Anatomy For Yoga Teachers
Yoga Teacher Central Anatomy For Yoga Teachers
 Muscles Of The Upper Arm Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab
Muscles Of The Upper Arm Human Anatomy And Physiology Lab
 Terminology Definitions Basic Definitions
Terminology Definitions Basic Definitions
 What Are Muscle Agonists Antagonists And Synergists 3d
What Are Muscle Agonists Antagonists And Synergists 3d
 Iliopsoas Anatomy Origins Insertions Actions
Iliopsoas Anatomy Origins Insertions Actions
 Yoga Anatomy Using Muscle Awareness To Lower Your Heels In
Yoga Anatomy Using Muscle Awareness To Lower Your Heels In
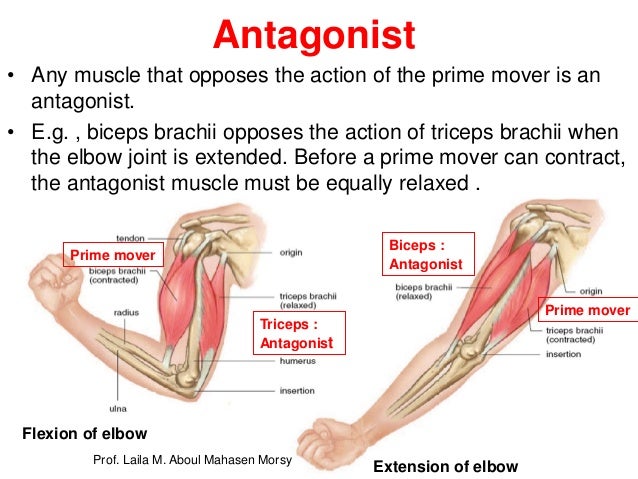 Prof Laila Muscular System 2018
Prof Laila Muscular System 2018
 Getting Started With The Muscle Spikerbox Pro Agonist
Getting Started With The Muscle Spikerbox Pro Agonist

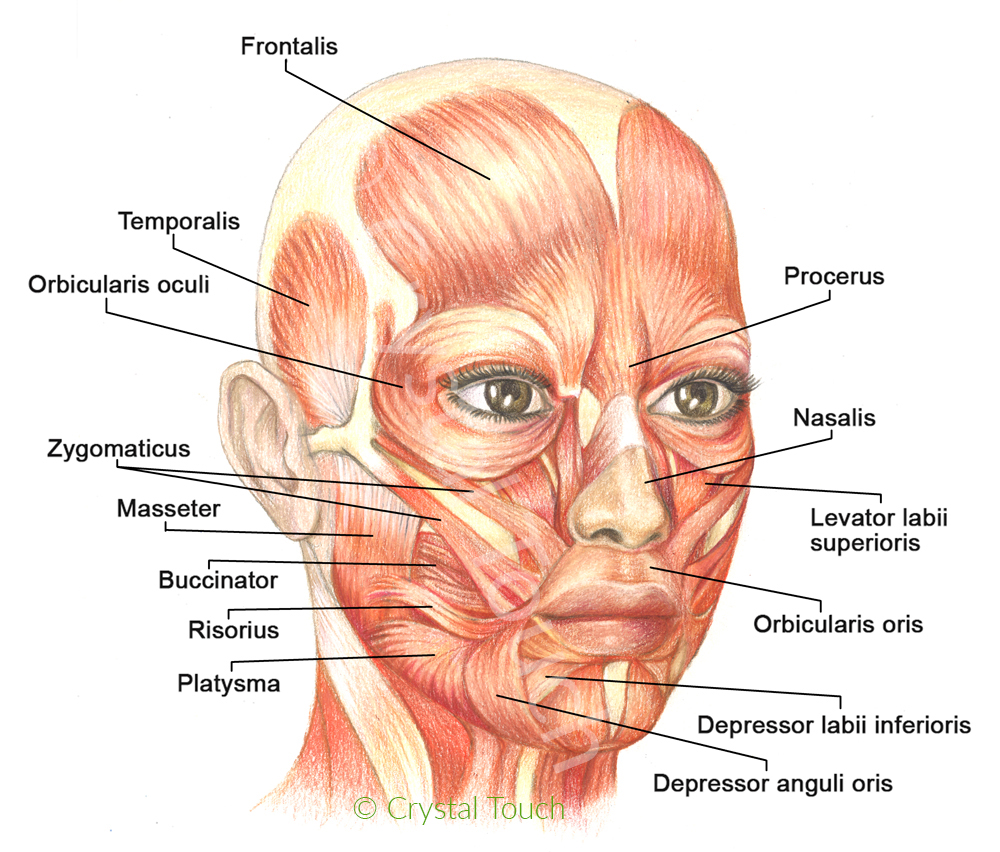 Muscles Of Facial Expressions And How They Work Crystal
Muscles Of Facial Expressions And How They Work Crystal
The Daily Bandha How To Use The Abdominals To Release The
 Muscle Origin And Insertion Definition And Actions Video
Muscle Origin And Insertion Definition And Actions Video
 Anatomical Terms Of Muscle Wikipedia
Anatomical Terms Of Muscle Wikipedia
Antagonist Muscle Definition Examples Video Lesson
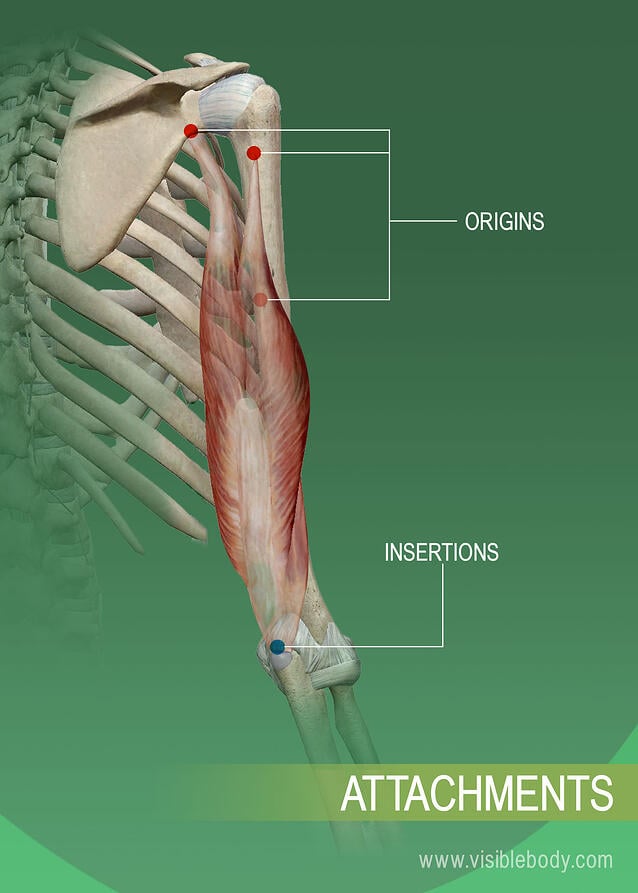 Muscle Attachments And Actions Learn Muscle Anatomy
Muscle Attachments And Actions Learn Muscle Anatomy
 Figure 2 The Tibialis Anterior As Agonist And Gastroc
Figure 2 The Tibialis Anterior As Agonist And Gastroc
 Lower Leg Anatomy Archives The Wellness Digest
Lower Leg Anatomy Archives The Wellness Digest
Agonist Vs Antagonist Plank Pilates
 Antagonist Activity Of Extensor Digitorum Brevis And
Antagonist Activity Of Extensor Digitorum Brevis And
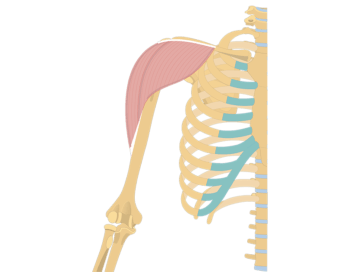 Arm Muscles Muscles That Act On The Arm Anatomy Function
Arm Muscles Muscles That Act On The Arm Anatomy Function
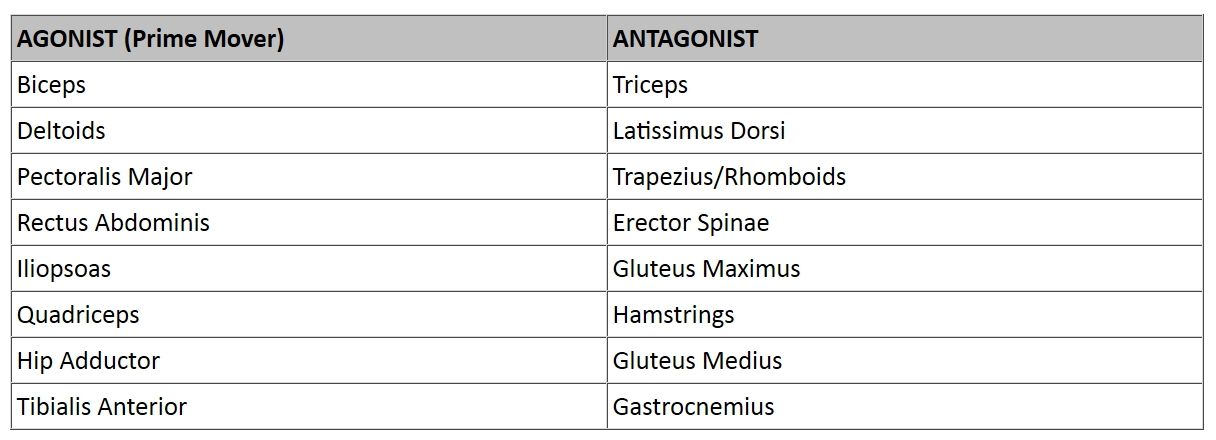
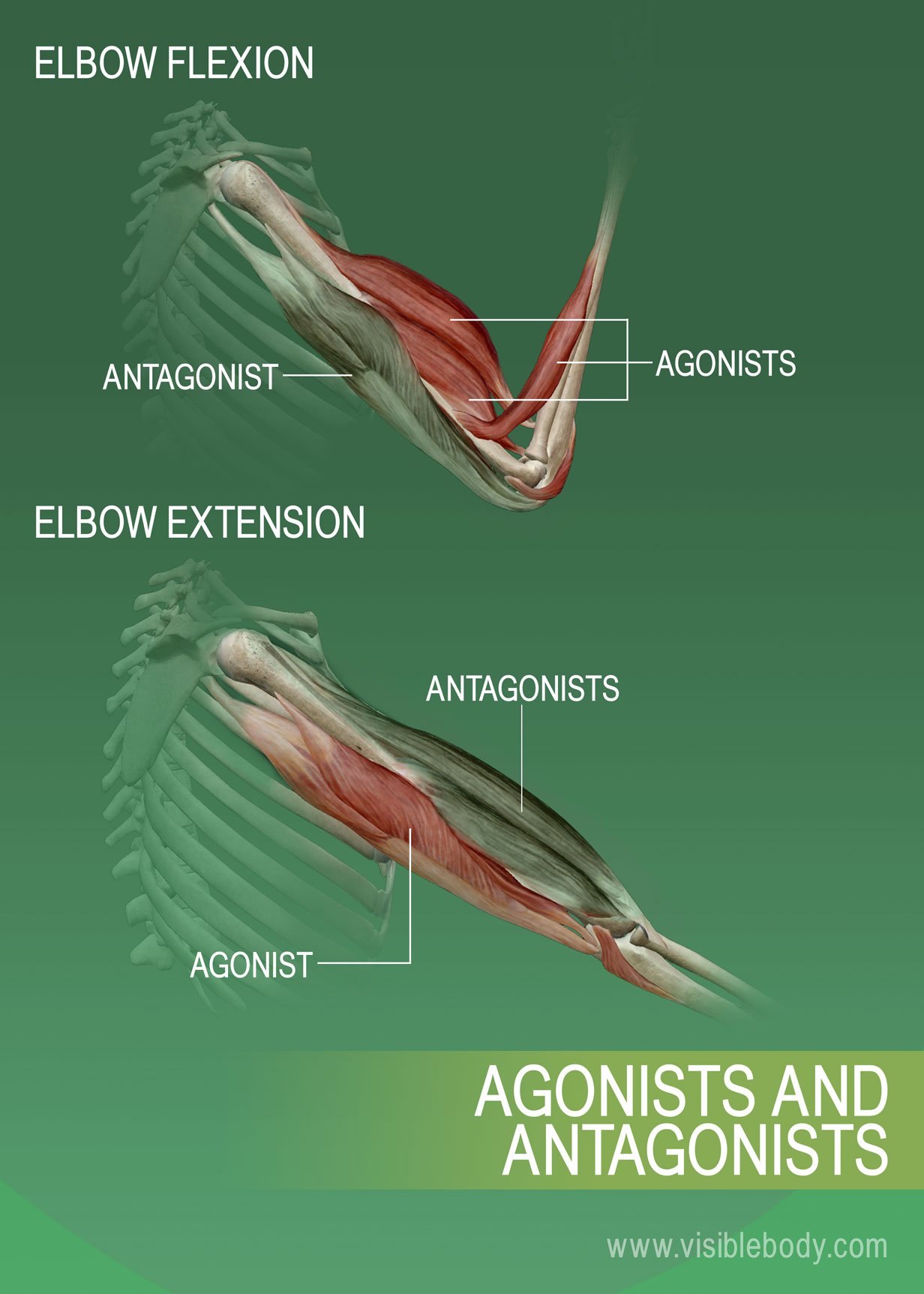 Muscle Attachments And Actions Learn Muscle Anatomy
Muscle Attachments And Actions Learn Muscle Anatomy
Belum ada Komentar untuk "Antagonist Anatomy"
Posting Komentar