Anatomy Spinal Cord
It passes through the spinal canal or spinal cavity of the vertebral column ie the backbone or spine. Cervical enlargement corresponds roughly to the brachial plexus nerves.
Anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord.

Anatomy spinal cord. Lumbar enlargement corresponds to the lumbosacral plexus nerves which innervate the lower limb. Spinal nerves are grouped as cervical c1 c8 thoracic t1 t12 lumbar l1 l5. Together the vertebrae and the membrane make up the spinal column or backbone.
The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system cns which extends caudally and is protected by the bony structures of the vertebral column. Together the spinal cord and the brain form the central nervous system. Spinal cord neural pathways are found within the spinal cord white matter.
When viewed as a cross section from above. It is covered by the three membranes of the cns ie the dura mater arachnoid and the innermost pia mater. The spinal cord is surrounded by rings of bone called vertebrae.
Although continuous with the brain the spinal cord begins where nervous tissue leaves the cranial cavity at the level of the foramen magnum. Basically spinal cord is a long and narrow bundle of nervous tissues and support cells which extends from the base of our brain to the upper lumbar region. The spinal meninges help prevent the spinal cord.
There are two regions where the spinal cord enlarges. The spinal cord is not uniform in diameter along its length. The spinal cord is part of the central nervous system cns.
Cervical spinal cord injury. Both are covered by a protective membrane. Spinal cord major nerve tract of vertebrates extending from the base of the brain through the canal of the spinal column.
It is composed of nerve fibres that mediate reflex actions and that transmit impulses to and from the brain. The spinal cord is a tubular bundle of nervous tissue and supporting cells that extends from the brainstem to the lumbar vertebrae. The brain is surrounded by the skull.
The spinal cord runs down the center of the protective spinal column extending from the neck to the lower back. Here are some basic anatomy facts. The brain and spinal cord are the major components of the central nervous system cns.
The spinal cord is a slender column of nervous tissue that passes downward from the brain into the vertebral canal. In this article we shall examine the macroscopic anatomy of the spinal cord its structure membranous coverings and blood supply. The spinal cord is a cylindrical shaped bundle of nerve fibers that is connected to the brain at the brain stem.
Signs and symptoms of spinal cord compression. Spinal cord anatomy in the neck internal anatomy of the spinal cord. Protective layers of the spinal cord.
 Spinal Cord In Situ Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
Spinal Cord In Situ Preview Human Anatomy Kenhub
 Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Vertebral Column Nerve Root Anatomy
Spinal Nerve Spinal Cord Vertebral Column Nerve Root Anatomy
 Spinal Cord Lesions Neurology Medbullets Step 2 3
Spinal Cord Lesions Neurology Medbullets Step 2 3
 Ch 12 Gross Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord
Ch 12 Gross Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord Picture Anatomy Spinal Cord Picture Anatomy
Spinal Cord Picture Anatomy Spinal Cord Picture Anatomy
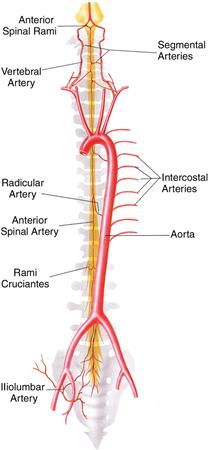 Spinal Cord Anatomy Spine Orthobullets
Spinal Cord Anatomy Spine Orthobullets
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Metro Health Hospital Metro Health
Spinal Cord Anatomy Metro Health Hospital Metro Health
Lab 2 Spinal Cord Gross Anatomy
Ch 12 Gross Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord
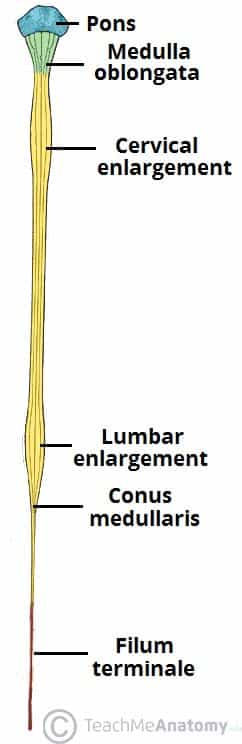 The Spinal Cord Meninges Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Spinal Cord Meninges Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
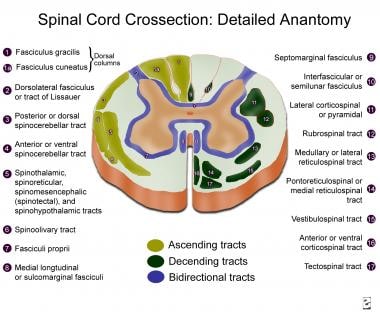 Topographic And Functional Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Gross
Topographic And Functional Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Gross
 Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Function Explanation Video
Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Function Explanation Video
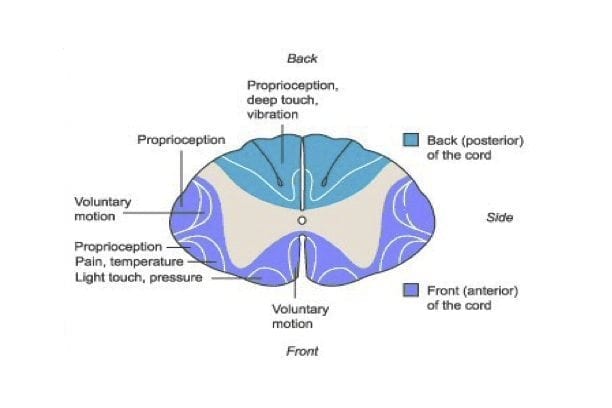 Spinal Cord Anatomy And Syndromes Litfl Ccc Trauma
Spinal Cord Anatomy And Syndromes Litfl Ccc Trauma
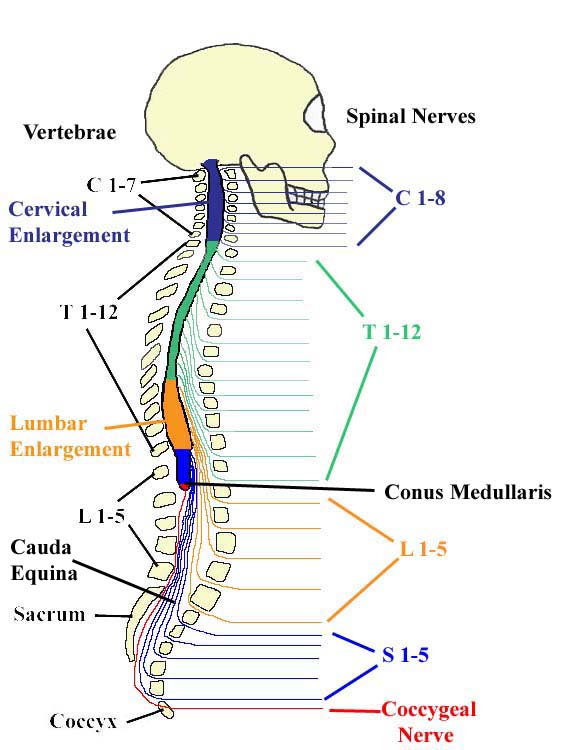 Module Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerve 4 Of 14
Module Spinal Cord And Spinal Nerve 4 Of 14
Anatomy Of Spinal Blood Supply
 Anatomy Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Seattle Cancer Care
Anatomy Of The Brain And Spinal Cord Seattle Cancer Care
 Gross Anatomy Of The Adult Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
Gross Anatomy Of The Adult Spinal Cord Flashcards Quizlet
 Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Download Scientific Diagram
Anatomy Of The Spinal Cord Download Scientific Diagram
 Spinal Cord Anatomy Nerves Impulses Fluid Vertebrae
Spinal Cord Anatomy Nerves Impulses Fluid Vertebrae
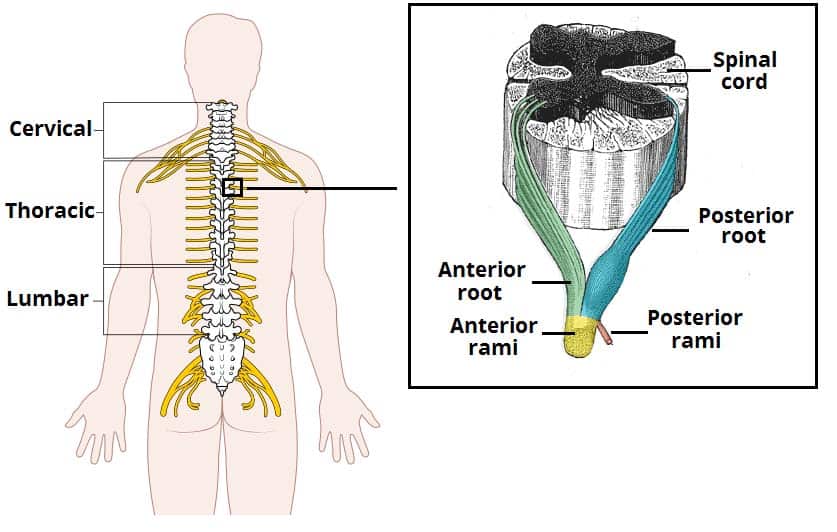 The Spinal Cord Meninges Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
The Spinal Cord Meninges Vasculature Teachmeanatomy
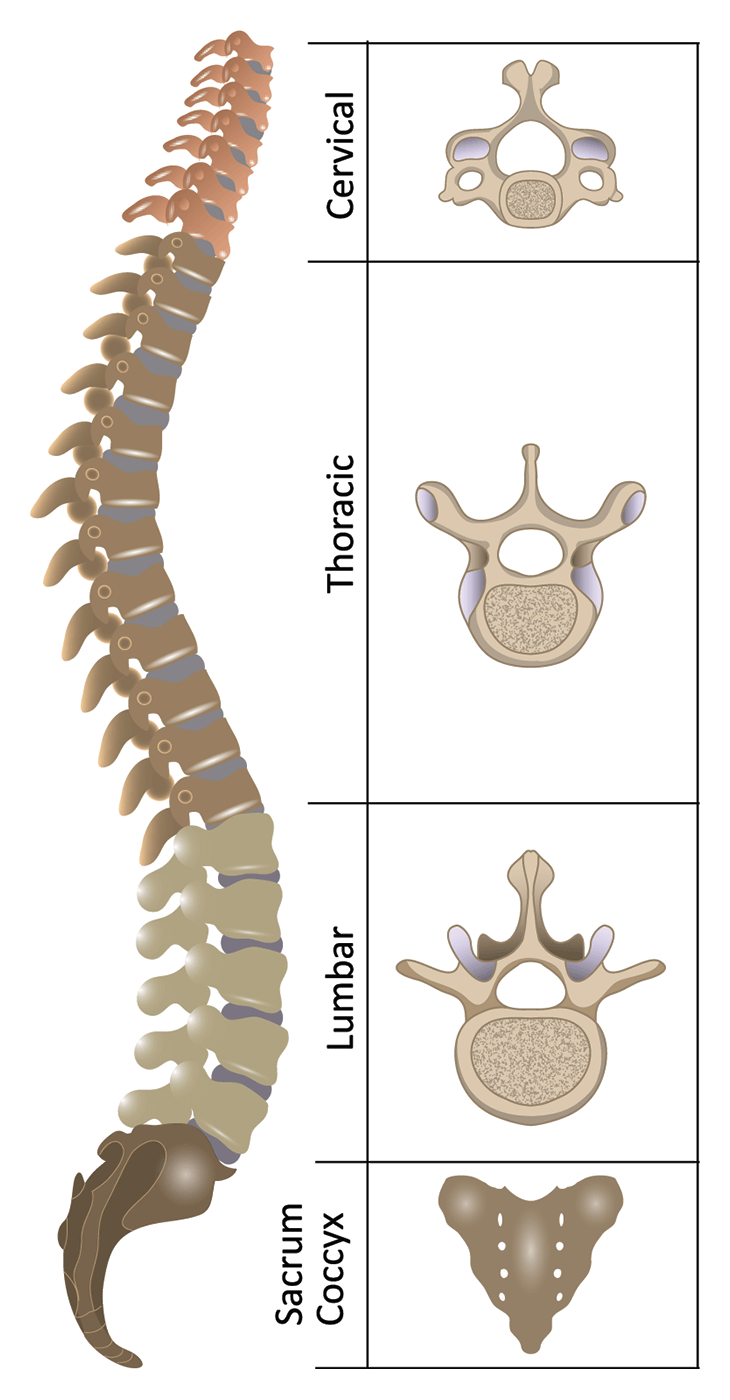 Anatomy Of The Spine Spinal Cord Injury Information Pages
Anatomy Of The Spine Spinal Cord Injury Information Pages
 13 2 Gross Anatomy Of The Adult Spinal Cord Diagram Quizlet
13 2 Gross Anatomy Of The Adult Spinal Cord Diagram Quizlet
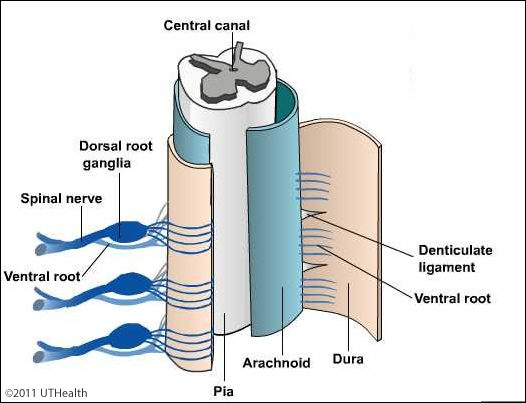 Neuroanatomy Online Lab 4 External And Internal Anatomy
Neuroanatomy Online Lab 4 External And Internal Anatomy
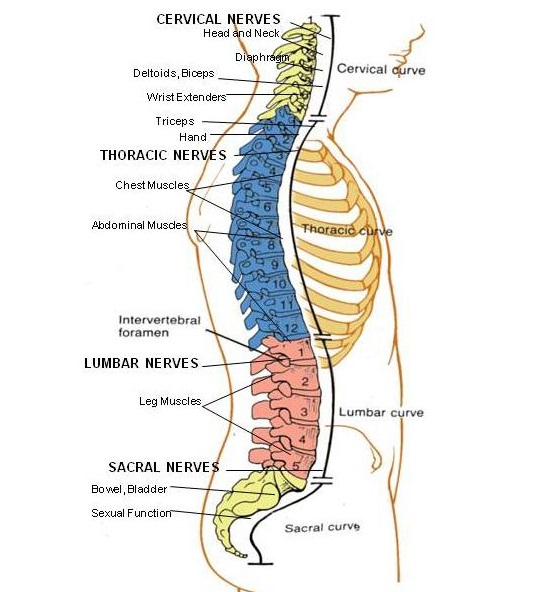 Spinal Cord Injury What Is It And What Does It Affect
Spinal Cord Injury What Is It And What Does It Affect
 Spinal Cord Injury Caused By Car Accidents Healthy Day Life
Spinal Cord Injury Caused By Car Accidents Healthy Day Life







Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Spinal Cord"
Posting Komentar