Stimulus Anatomy Definition
Aversive stimulus one which when applied following the occurrence of a response decreases the strength of that response on later occurrences. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity.
 Sensory Coding Principles Of Neural Science Fifth Edition
Sensory Coding Principles Of Neural Science Fifth Edition
A stimulus can be internal or external.

Stimulus anatomy definition. Content related to threshold stimulus medical terms you didnt know existed these 10 weird medical terms need to be added to your vernacular faster than you can say diagnosis. A supra maximal stimulus intensity mean supra maximal intensity53 or 11 ma range35 to 66 ma n8 was used which was 20 higher than the intensity used to produce a twitch of maximum amplitude in a relaxed muscle. Choose from 89 different sets of stimulus anatomy flashcards on quizlet.
A conditioned stimulus is a substitute stimulus that triggers the same response in an organism as an unconditioned stimulus. Adequate stimulus a stimulus of the specific form of energy to which a given receptor is sensitive. Contraction produces tension the force exerted on the load or object to be moved.
Sense organs such as the ear and sensory receptors such as those in the skin are sensitive to external stimuli such as sound and touch. 3 that which can evoke a response or has an influence on a system to act. Learn stimulus anatomy with free interactive flashcards.
Force of duration of contraction vary in response to stimuli of different frequencies and intensities. Simply put a conditioned stimulus makes an organism react to something because it is associated with something else. Same principles apply to contraction of a single fiber and a whole muscle.
Specialized to respond to changes in their environment stimuli activation results in graded potentials that trigger nerve impulses sensationawareness of stimulus and perception interpretation of the meaning of stimulus occur in the brain. In physiology a stimulus plural stimuli or stimuluses is a detectable change in the physical or chemical structure of an organisms internal or external environment. 2 physiology that which influences or causes a temporary increase of physiological activity or response in the whole organism or in any of its parts.
Plural stimuli stĭmyə lī physiology something that can elicit or evoke a physiological response in a cell a tissue or an organism. Anatomy and physiology chapter 13. Contraction doesnt always shorten a muscle.
A stimulus that is just strong enough to evoke a response. 1 physiology a detectable change in the internal or external environment.
 Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology I
Homeostasis Anatomy And Physiology I
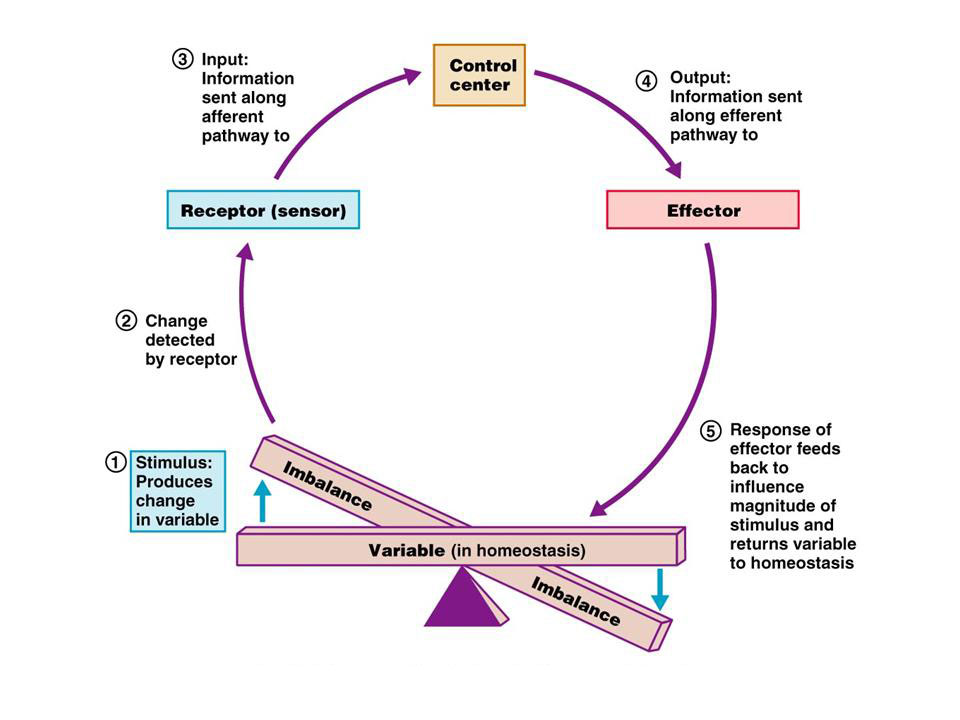 Homeostasis Positive Negative Feedback Mechanisms
Homeostasis Positive Negative Feedback Mechanisms
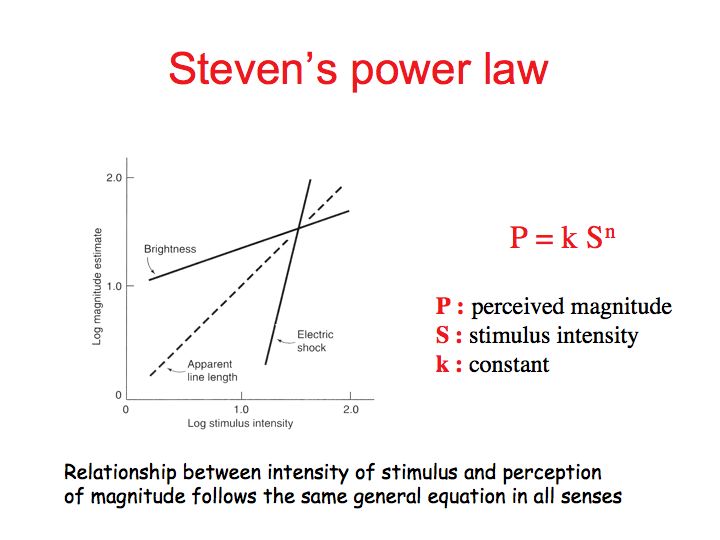 Perception Lecture Notes Psychophysics
Perception Lecture Notes Psychophysics
 Chapter 9 Muscular System Ppt Download
Chapter 9 Muscular System Ppt Download
 Reactions And Reflexes Carolina Com
Reactions And Reflexes Carolina Com
 The Evolution Of The Auditory System A Tutorial
The Evolution Of The Auditory System A Tutorial
 Pdf Anatomy Of Word And Sentence Meaning
Pdf Anatomy Of Word And Sentence Meaning
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-172594438-56a796f13df78cf7729768ee.jpg) All Or None Law For Nerves And Muscles
All Or None Law For Nerves And Muscles
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/auxin_phototropism-5a96b7553418c600366c97ea.jpg) Plant Tropisms Phototropism Thigmotropism And More
Plant Tropisms Phototropism Thigmotropism And More
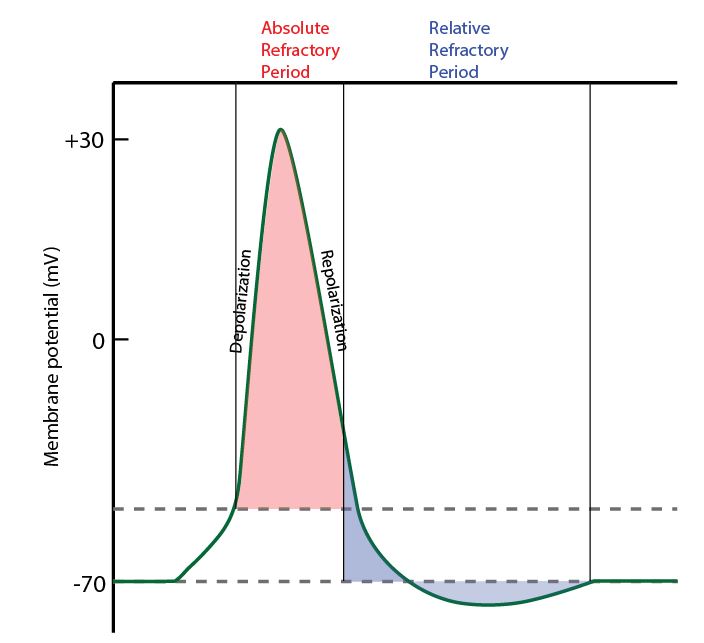
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11522/Action_potential_curve.png) Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub
Action Potential Definition Steps Phases Kenhub
Magnetism Questions And Answers In Mri
Human Physiology Neurons The Nervous System
Human Physiology Neurons The Nervous System
 Stimulus Specific Adaptation Can It Be A Neural Correlate
Stimulus Specific Adaptation Can It Be A Neural Correlate
 Anatomy Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Video Khan Academy
Anatomy Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Video Khan Academy
 An Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Ppt Download
An Introduction To Anatomy And Physiology Ppt Download
 Effects Of Increased Stimulus Frequency And Muscle Fiber
Effects Of Increased Stimulus Frequency And Muscle Fiber
 Decoding Working Memory Of Stimulus Contrast In Early Visual
Decoding Working Memory Of Stimulus Contrast In Early Visual
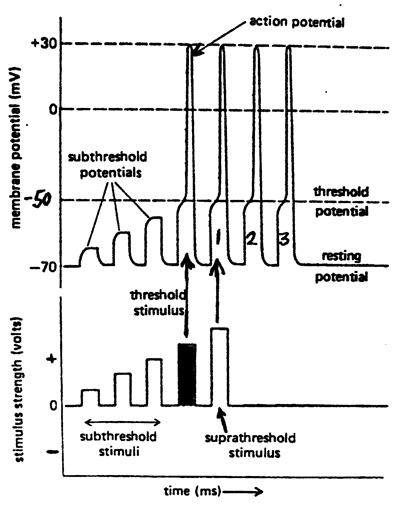 Subthreshold Threshold And Suprathreshold Stimuli
Subthreshold Threshold And Suprathreshold Stimuli
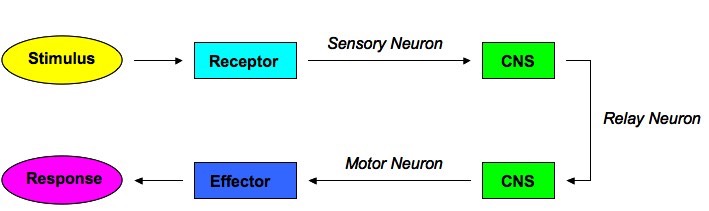
 Reflex Arc Definition Of Reflex Arc By Medical Dictionary
Reflex Arc Definition Of Reflex Arc By Medical Dictionary
 Hthsci 1h06 Lecture 2 Anatomy And Physiology Homeostasis
Hthsci 1h06 Lecture 2 Anatomy And Physiology Homeostasis
 Combinatorial Neural Inhibition For Stimulus Selection
Combinatorial Neural Inhibition For Stimulus Selection
Characteristics Of The Compound Action Potential
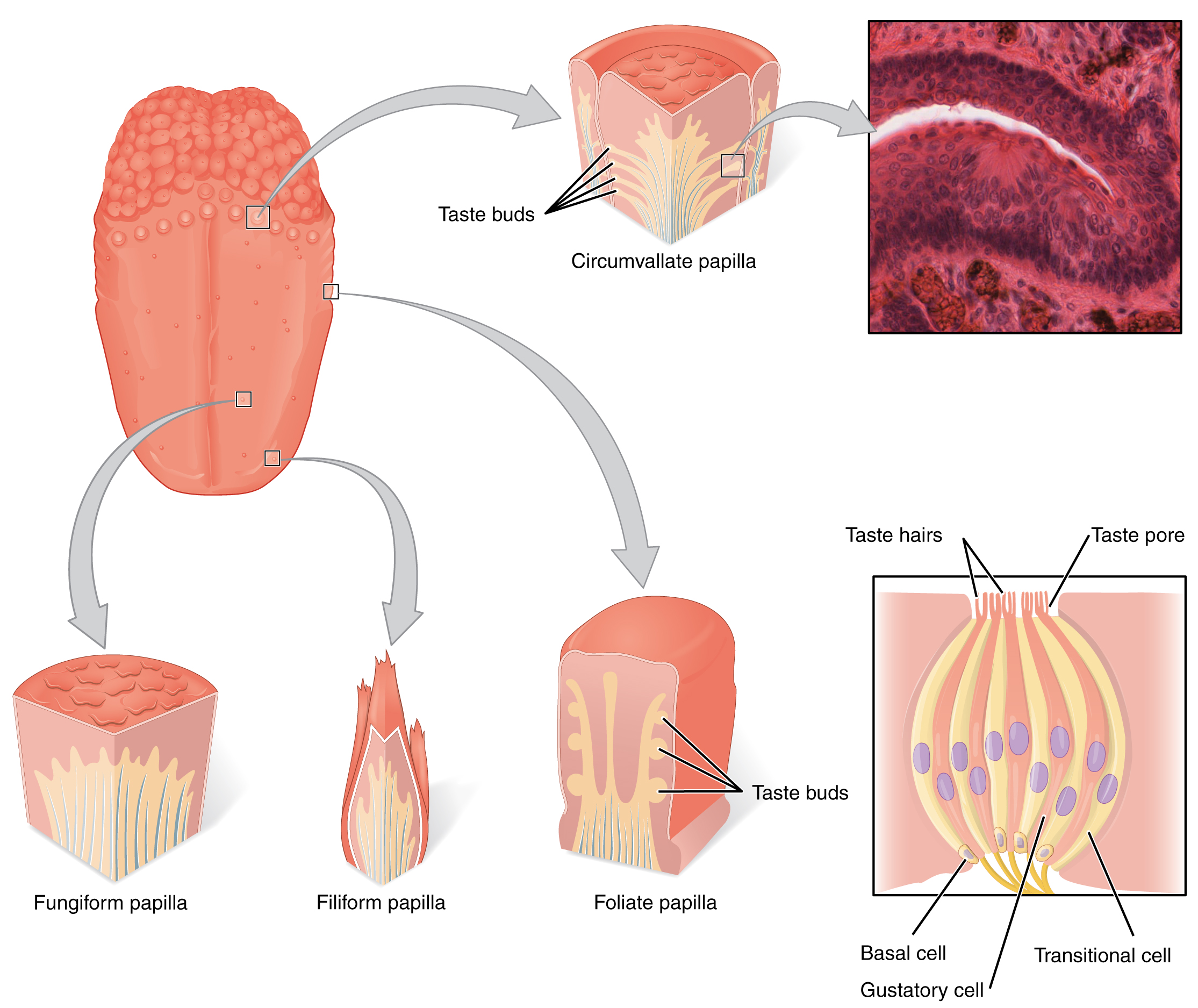 14 1 Sensory Perception Anatomy And Physiology
14 1 Sensory Perception Anatomy And Physiology
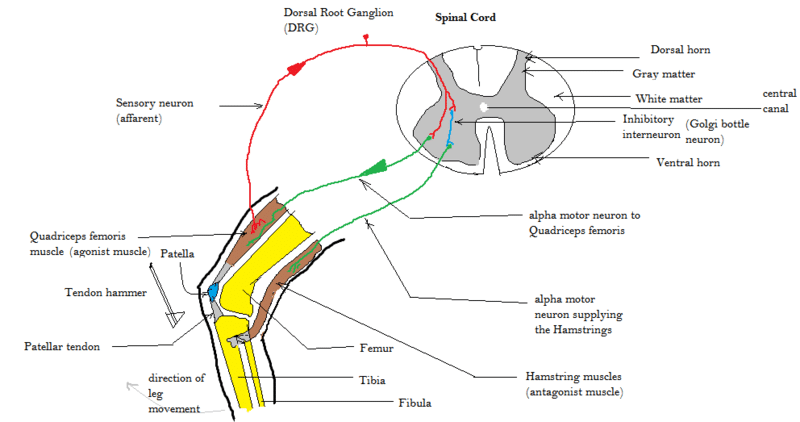 Muscle Stretch Reflex Reflex Arc Components Monosynpatic
Muscle Stretch Reflex Reflex Arc Components Monosynpatic
 Feedback Loops Anatomy And Physiology I
Feedback Loops Anatomy And Physiology I
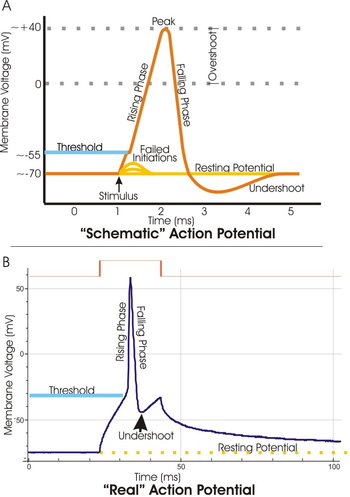




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Stimulus Anatomy Definition"
Posting Komentar