Thoracic Anatomy
Some of the thoracic spines most important roles include the following. The lumbar vertebrae are larger than the cervical or thoracic as this spinal region carries most of the bodys weight.
 What You Need To Know About Your Thoracic Spine Yoga Journal
What You Need To Know About Your Thoracic Spine Yoga Journal
Protect the spinal cord.

Thoracic anatomy. Anchor the rib cage. It contains organs including the heart lungs and thymus gland as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Anatomy causes and treatment with clinical somatics.
As youve seen above the. The thoracic spine sits between the cervical spine in the neck and the lumbar spine in the lower back. Collectively these three sections make a tower of 24 bones that gives the body structure and.
It is enclosed by the ribs the vertebral column and the sternum or breastbone and is separated from the abdominal cavity the bodys largest hollow space by a muscular and membranous partition the diaphragm. Thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae. The first step in understanding thorax anatomy is to find out its boundaries.
The thoracic cavity is home to many vital organs notably the lungspleurae and the heart but also includes the thymus gland and the breasts. In order to give intelligent care to the patient before and after surgery one must have adequate knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the chest and thoracic cavity. The sacrum and coccyx are uniquely shaped.
If you take a close look at the previous table and diagram. For example the seven cervical vertebrae are c1 c2 c3 c4 c5 c6 and c7. Now that weve covered the boundaries lets add another layer.
Medical professionals often abbreviate the levels vertebrae of the spinal column. The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans and various other animals located between the neck and the abdomen. As the heart is found here the great vessels associated with it are also found including the pulmonary arteriesveins the superior vena cava and the aorta as well as some of its proximal branches.
The thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. Thoracic cavity the second largest hollow space of the body. Thoracic outlet syndrome might sound a little scary but most cases are functionalmeaning they can be prevented and often eliminated completely.
The spinal cord is a critical bundle of nerves. The rib cage supported by the thoracic spine in the back. Thoracic surgery includes procedures involving the lungs heart and great vessels as well as tracheal resection esophagogastrectomy and repair of hiatal hernia.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11141/the-blood-vessels-of-female-breast_english.jpg) Thorax Anatomy Wall Cavity Organs Neurovasculature
Thorax Anatomy Wall Cavity Organs Neurovasculature
 Thoracic Anatomy A B Drawing Of Dniii 4 In The Thoracic
Thoracic Anatomy A B Drawing Of Dniii 4 In The Thoracic
 Human Skeleton System Thoracic Skeleton Anatomy Anterior View
Human Skeleton System Thoracic Skeleton Anatomy Anterior View
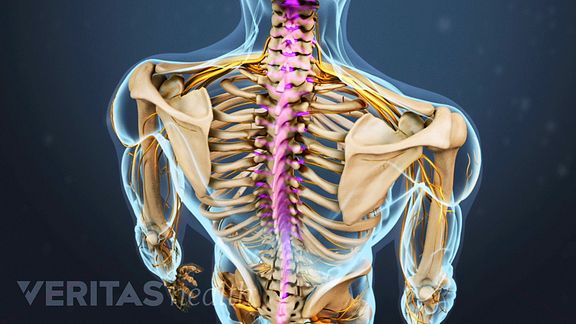 Thoracic Spine Definition Back Pain And Neck Pain Medical
Thoracic Spine Definition Back Pain And Neck Pain Medical
 Medivisuals Thoracic Anatomy Medical Illustration
Medivisuals Thoracic Anatomy Medical Illustration
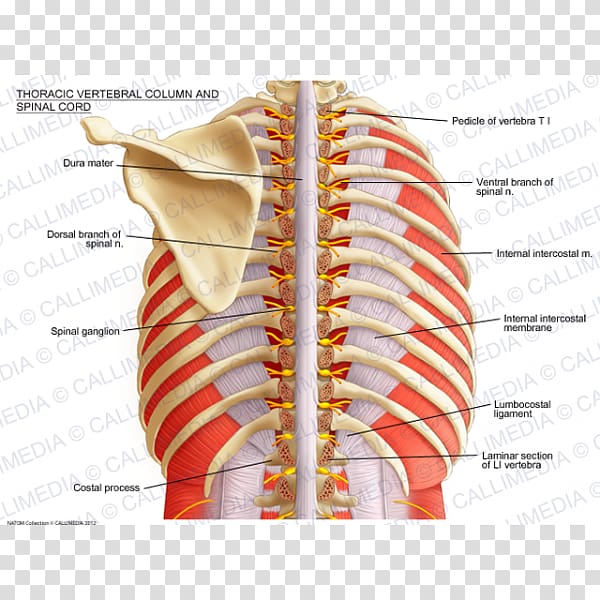 Vertebral Column Spinal Cord Thoracic Vertebrae Anatomy
Vertebral Column Spinal Cord Thoracic Vertebrae Anatomy
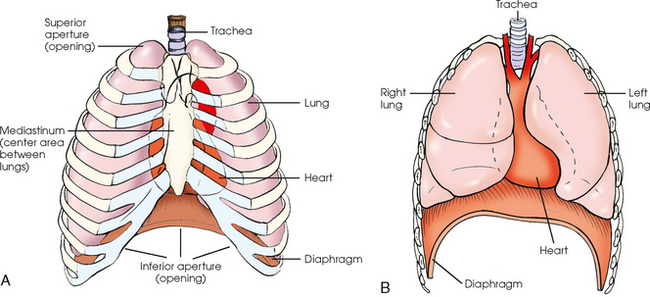 Thoracic Viscera Radiology Key
Thoracic Viscera Radiology Key
 Thoracic Cavity Human Body Thoracic Cavity Human Skeleton
Thoracic Cavity Human Body Thoracic Cavity Human Skeleton
 Anterior Thoracic Wall Muscles 3d Anatomy Tutorial
Anterior Thoracic Wall Muscles 3d Anatomy Tutorial
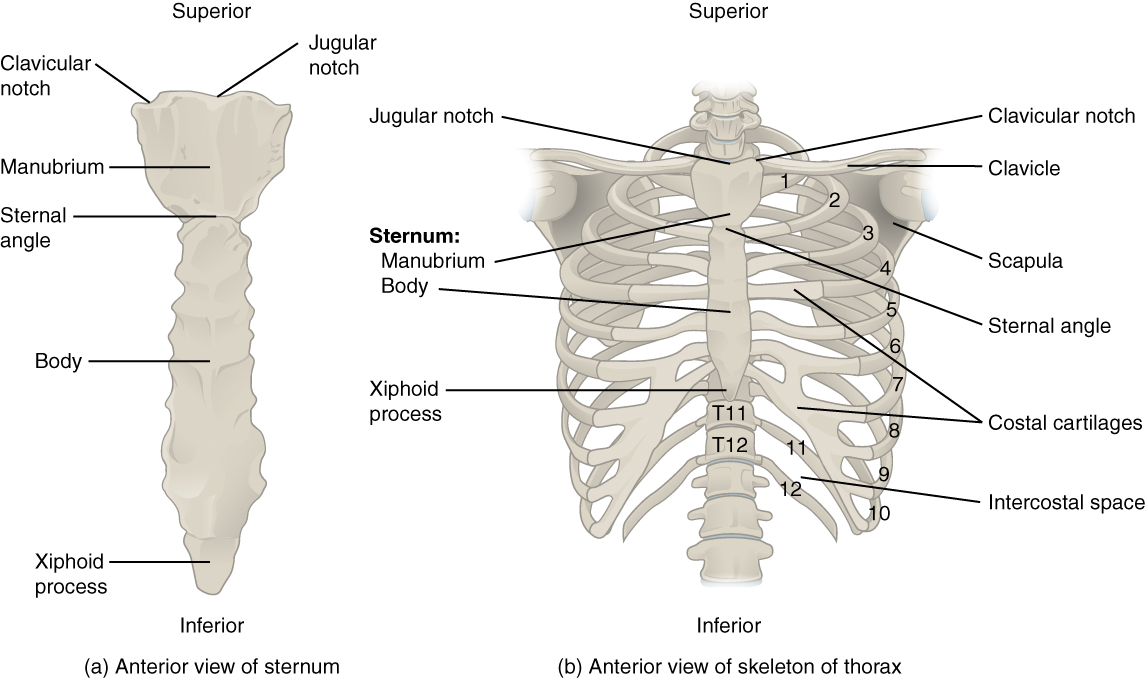 7 4 The Thoracic Cage Anatomy And Physiology
7 4 The Thoracic Cage Anatomy And Physiology

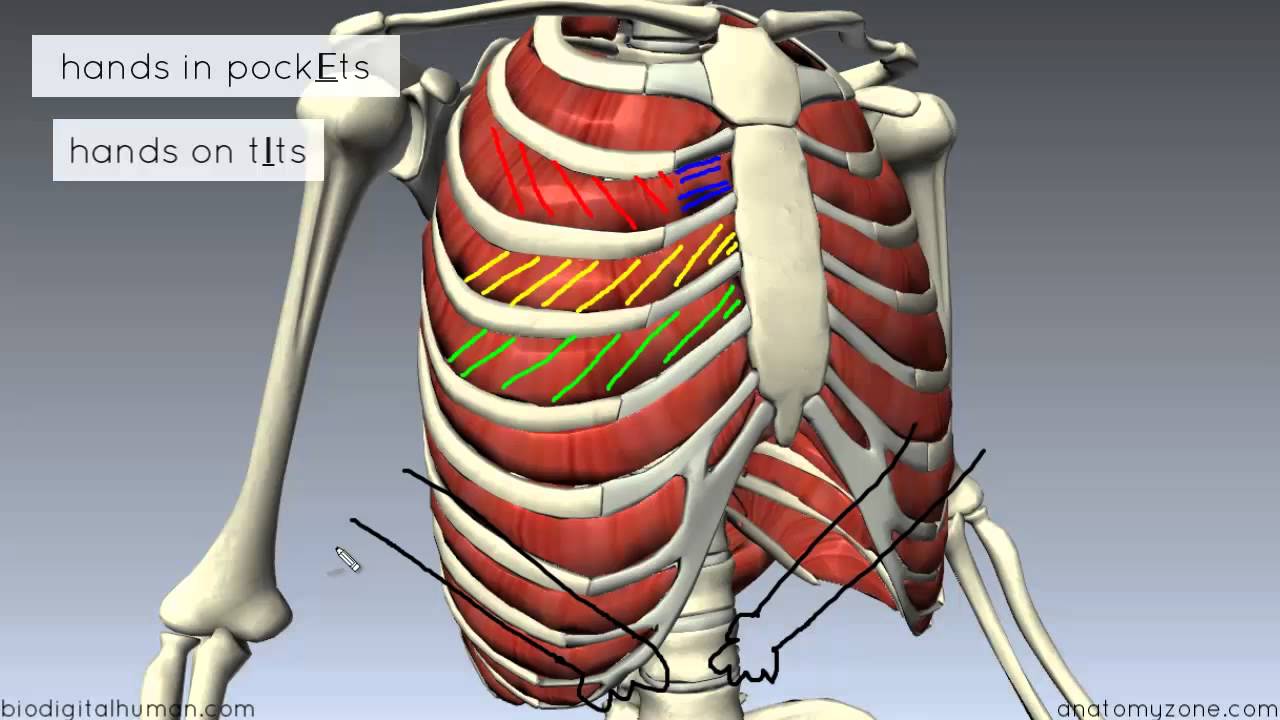 Muscles Of The Thoracic Wall 3d Anatomy Tutorial
Muscles Of The Thoracic Wall 3d Anatomy Tutorial
 Long Thoracic Nerve Anatomy And Significance Bone And Spine
Long Thoracic Nerve Anatomy And Significance Bone And Spine
 Thoracic Wall Atlas Of Anatomy
Thoracic Wall Atlas Of Anatomy
B2w2 Thoracic Anatomy Id B2w2 Thoracic Anatomy Id
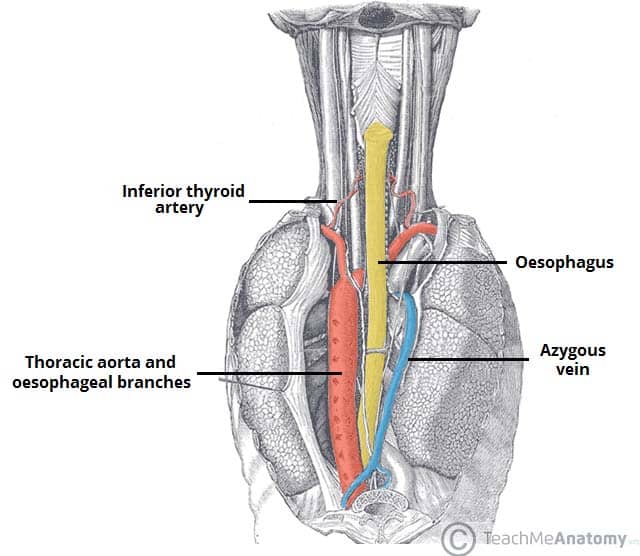 The Posterior Mediastinum Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy
The Posterior Mediastinum Borders Contents Teachmeanatomy
 Anatomy Of The Thoracic Aorta And Of Its Branches
Anatomy Of The Thoracic Aorta And Of Its Branches
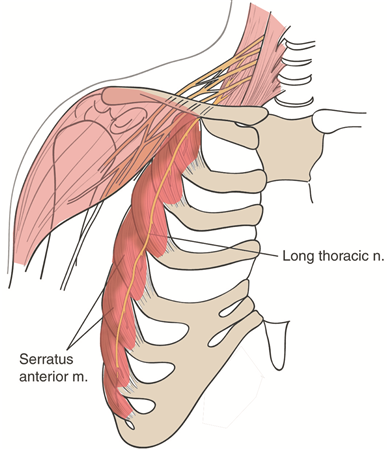 Long Thoracic Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
Long Thoracic Nerve Anatomy Orthobullets
 Thoracic Cavity Anatomy Britannica
Thoracic Cavity Anatomy Britannica
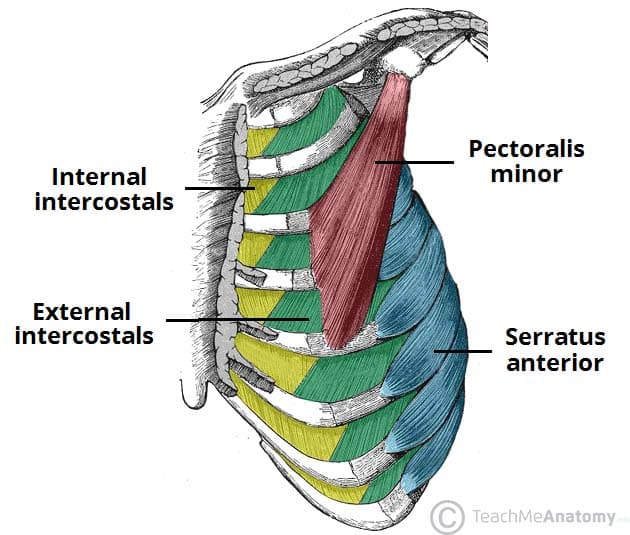 Thoracic Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy
Thoracic Muscles Attachments Actions Teachmeanatomy
 Anterior Thoracic Cage Anatomy
Anterior Thoracic Cage Anatomy
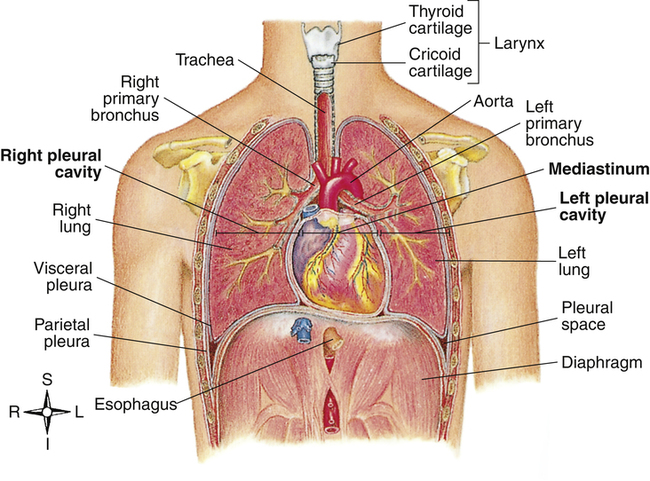 The Lungs And Chest Wall Clinical Gate
The Lungs And Chest Wall Clinical Gate
 Breast Thoracic Wall Concepts Anatomy With Mc Krackin
Breast Thoracic Wall Concepts Anatomy With Mc Krackin
 Human Skeleton System Thoracic Skeleton Anatomy Posterior View
Human Skeleton System Thoracic Skeleton Anatomy Posterior View
 Thoracic Anatomy Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile
Thoracic Anatomy Stock Photos Page 1 Masterfile
 Thoracic Rib Cage Anatomy In Detail Anterior View Rib Cage
Thoracic Rib Cage Anatomy In Detail Anterior View Rib Cage
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/ductus-thoracicus-2/ypokyGBKCr1ggLyTmb8yuQ_Ductus_thoracicus_1.png) Thoracic Duct Anatomy Course And Clinical Significance
Thoracic Duct Anatomy Course And Clinical Significance

Belum ada Komentar untuk "Thoracic Anatomy"
Posting Komentar