Anatomy Of Orbit
The lacrimal system produces distributes and drains tears. It also protects this vital structure.
 Anatomy The Orbit Flashcards Quizlet
Anatomy The Orbit Flashcards Quizlet
When orbital cellulitis occurs its most likely source is direct extension from the ethmoid sinuses because the thin bone of the medial wall is easily penetrated by expanding masses from the sinus.

Anatomy of orbit. The floor of the orbit is thicker and offers more resistance to maxillary sinus abnormality. Orbit supports the eye and ensures that this organ functions in an optimal manner. The orbit which protects supports and maximizes the function of the eye.
It emphasizes the aspects of eye and orbit anatomy that are most relevant to clinicians in training providing the practical real world foundation necessary for practice. Anatomy of the eye and orbit. The shape of the orbit resembles a four sided pyramid to begin with but as one goes posterior it becomes three sided towards the apex.
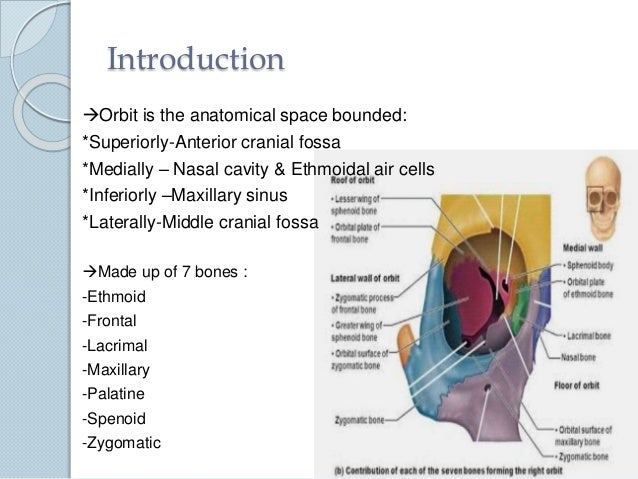
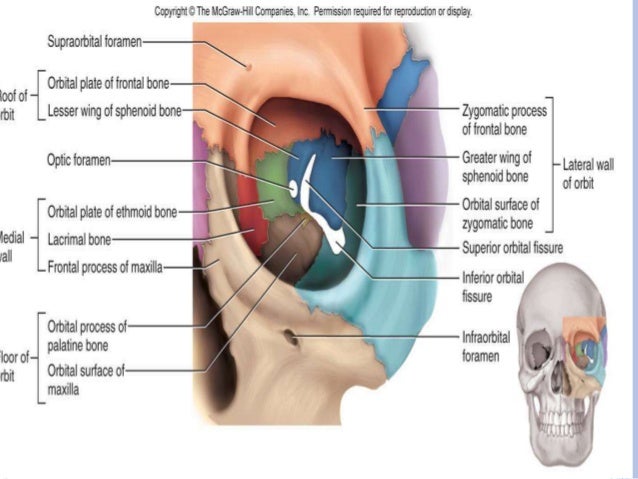
Borders of orbit roof floor base apex medial and lateral walls of orbit superior orbital fissure inferior orbital fissure superior orbital foramen inferior orbital foramen optic. 101 us fl oz. Orbit anatomy in anatomy the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated.
The cranium is the major portion and it consists of three unpaired bones the sphenoid occipital and ethmoid bones and three paired bones the frontal parietal and temporal bones. The contents of the orbit are separated and supported by multiple. Anatomy of the orbit the skull is composed of two segments the cranium and the face.
The volume of the orbital cavity in an adult is roughly about 30cc. Orbit can refer to the bony socket or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human the volume of the orbit is 30 millilitres 106 imp fl oz.
Development orbit develops around the eyeball orbital walls derived from cranial neural crest cells which expand to form frontonasal process maxillary process lateral nasal process maxillary process medial inferior and lateral orbital walls capsule of forebrain forms orbital roof. The clinical essentials achieves the impressive task of presenting ophthalmology residents optometry residents and optometry students with the clinical essentials of ocular anatomy as a foundation for patient care.
 Zygomatic Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Zygomatic Nerve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Superior Orbital Fissure Wikipedia
Superior Orbital Fissure Wikipedia
 Local And Regional Anesthesia For Ophthalmic Surgery Nysora
Local And Regional Anesthesia For Ophthalmic Surgery Nysora
Anatomy Of Orbit And Clinical Aspect Of Orbital Disease
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/orbital-surface-of-zygomatic-bone-1/g05NQEWelrmYIlQUC5ow_orbital_surface_of_zygomatic_bone.png) Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
 Anatomy Of Orbit And Eyelid With Associated Pathologic
Anatomy Of Orbit And Eyelid With Associated Pathologic
 Orbital Tumor Eye Socket Cancer Anatomy
Orbital Tumor Eye Socket Cancer Anatomy
 Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
 Orbital Bones Ophthalmology Review
Orbital Bones Ophthalmology Review
 Anatomy Of The Eye And Orbit The Clinical Essentials
Anatomy Of The Eye And Orbit The Clinical Essentials
 Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Orbits And Eyes Anatomical Illustrations
Anatomy W5 Orbit Flashcards Memorang
 Regional Anatomy The Orbit At Texas Woman S University
Regional Anatomy The Orbit At Texas Woman S University
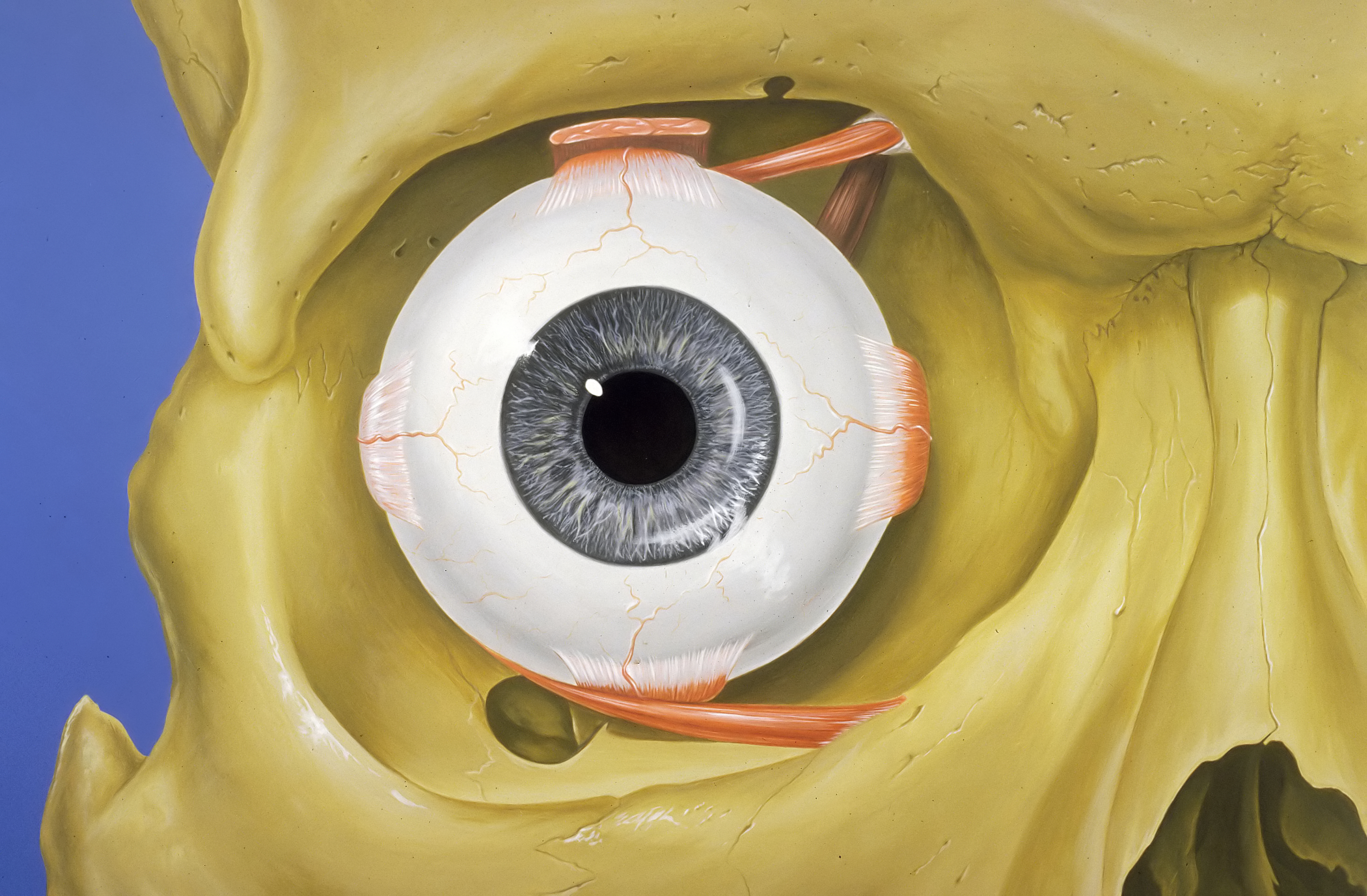
 Orbital Septum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Orbital Septum An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 File 1411 Eye In The Orbit Jpg Wikimedia Commons
File 1411 Eye In The Orbit Jpg Wikimedia Commons

Orbital Compartment Syndrome Curriculum
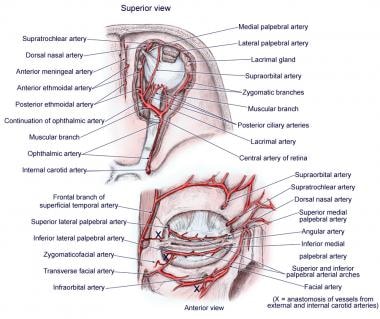 Orbit Arterial Supply Overview The Arterial System The
Orbit Arterial Supply Overview The Arterial System The
 Orbital Bone Anatomy Eye Anatomy Facial Anatomy
Orbital Bone Anatomy Eye Anatomy Facial Anatomy
Anatomy Of Orbit And Clinical Aspect Of Orbital Disease
:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/777/IOA26SbYNKr5nhVqAvklQ_bones-of-the-orbit_english.jpg) Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
Bones Of The Orbit Anatomy Foramina Walls And Diagram
Partial Closure Of Right Superior Orbital Fissure With




Belum ada Komentar untuk "Anatomy Of Orbit"
Posting Komentar